Webquest- Skeletal and Muscular System
... 14 Where are involuntary muscles found and how do they move? ...
... 14 Where are involuntary muscles found and how do they move? ...
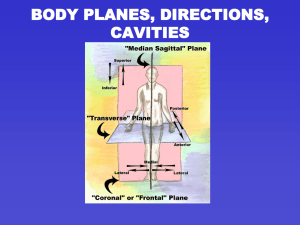
BODY PLANES, DIRECTIONS, CAVITIES
... • BODY PARTS ABOVE OTHER PARTS – Superior Example: nose is superior to the mouth • BODY PARTS BELOW OTHER PARTS – Inferior Example: the abdomen is inferior to the head. ...
... • BODY PARTS ABOVE OTHER PARTS – Superior Example: nose is superior to the mouth • BODY PARTS BELOW OTHER PARTS – Inferior Example: the abdomen is inferior to the head. ...
anatomy chapter 1 anatomical regions (2)
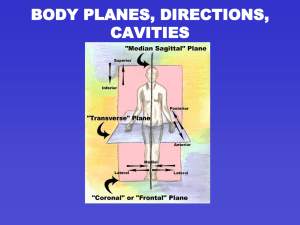
... • Midsagittal or medial – sagittal plane that lies on the midline • Frontal or coronal – divides the body into anterior and posterior parts • Transverse or horizontal (cross section) – divides the body into superior and inferior parts • Oblique section – cuts made diagonally ...
... • Midsagittal or medial – sagittal plane that lies on the midline • Frontal or coronal – divides the body into anterior and posterior parts • Transverse or horizontal (cross section) – divides the body into superior and inferior parts • Oblique section – cuts made diagonally ...
NAME____________________________________ MUSCULAR
... 6. What are the conditions like for this muscle problem? ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Is there a cure for fibromyalgia? Where is a common tender spot? _____ ...
... 6. What are the conditions like for this muscle problem? ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Is there a cure for fibromyalgia? Where is a common tender spot? _____ ...
Anatomy
... left sides Sagittal: divides the body into right and left parts – parallel to the median plan (the “doing plane”) Coronal (frontal): divides the body into front and back Transverse: divides the body in half at the waist ...
... left sides Sagittal: divides the body into right and left parts – parallel to the median plan (the “doing plane”) Coronal (frontal): divides the body into front and back Transverse: divides the body in half at the waist ...
anatomical terminology
... Directions or Positions: 1. anterior (cranial) = toward the head, in front of 2. posterior (caudal) = toward the tail or rear, behind 3. dorsal (superior) = toward the backbone 4. ventral (inferior) = toward the stomach, opposite of dorsal 5. lateral = toward the side, away from the midline of the b ...
... Directions or Positions: 1. anterior (cranial) = toward the head, in front of 2. posterior (caudal) = toward the tail or rear, behind 3. dorsal (superior) = toward the backbone 4. ventral (inferior) = toward the stomach, opposite of dorsal 5. lateral = toward the side, away from the midline of the b ...
PEP 3250 Anatomical Kinesiology
... reference or to the trunk. *use these terms in reference to the extremities* Dorsal—top side (back of your hand); Palmar & Plantar also known as volar—bottom aspect of structure (palm side, bottom of foot=plantar side) ...
... reference or to the trunk. *use these terms in reference to the extremities* Dorsal—top side (back of your hand); Palmar & Plantar also known as volar—bottom aspect of structure (palm side, bottom of foot=plantar side) ...
Homeostasis and feedback loops
... forward and flat on flood, head facing forward with eyes facing forward also. What is a prone position? The person is lying face down in the anatomical position. What is a supine position? The person is lying face upwards in the anatomical position. What are the major regions of the body? The major ...
... forward and flat on flood, head facing forward with eyes facing forward also. What is a prone position? The person is lying face down in the anatomical position. What is a supine position? The person is lying face upwards in the anatomical position. What are the major regions of the body? The major ...
Unit 1 Anatomy Study Guide KD16
... Term a. cephalic b. sternal c. acromial d. popliteal e. cubital f. buccal g. mental h. occipital i. ...
... Term a. cephalic b. sternal c. acromial d. popliteal e. cubital f. buccal g. mental h. occipital i. ...
BODY PLANES, DIRECTIONS, CAVITIES
... • BODY PARTS ABOVE OTHER PARTS – Superior Example: nose is superior to the mouth • BODY PARTS BELOW OTHER PARTS – Inferior Example: the abdomen is inferior to the head. ...
... • BODY PARTS ABOVE OTHER PARTS – Superior Example: nose is superior to the mouth • BODY PARTS BELOW OTHER PARTS – Inferior Example: the abdomen is inferior to the head. ...
Skeletal System
... Kyphosis – increased roundness of the thoracic curvature Scoliosis – abnormal lateral curvature that occurs most often in the thoracic region ...
... Kyphosis – increased roundness of the thoracic curvature Scoliosis – abnormal lateral curvature that occurs most often in the thoracic region ...
1st Semester Review
... At what age does bone loss begin to exceed bone gain? What is the epiphysis? Its function? Know the functions of the different microscopic structures within bone. Identify the different types of fractures. What is the most common type of skeletal tissue tumor? What is the most common malignant tumor ...
... At what age does bone loss begin to exceed bone gain? What is the epiphysis? Its function? Know the functions of the different microscopic structures within bone. Identify the different types of fractures. What is the most common type of skeletal tissue tumor? What is the most common malignant tumor ...
Body Cavities The internal body is divided into a number of spaces
... colon, and the internal reproductive organs (primarily female). The abdominal cavity is lined by a membrane, the Parietal Perotineum, which is continuous with the organs of the abdominal cavity. This membrane is called the Visceral Perotineum. The space between these two is the Peritoneal cavity. ...
... colon, and the internal reproductive organs (primarily female). The abdominal cavity is lined by a membrane, the Parietal Perotineum, which is continuous with the organs of the abdominal cavity. This membrane is called the Visceral Perotineum. The space between these two is the Peritoneal cavity. ...
Movement - Cloudfront.net
... 1. Several body cavities 2. Layers of membranes within cavities 3. Variety of organs and organ systems within cavities (VISCERA = internal organs. "Visceral organs") ...
... 1. Several body cavities 2. Layers of membranes within cavities 3. Variety of organs and organ systems within cavities (VISCERA = internal organs. "Visceral organs") ...
Terms Related to Position Median Sagittal Plane
... nearer to the median plane of the body than another is said to be medial to the other. ...
... nearer to the median plane of the body than another is said to be medial to the other. ...
1 - andrus medical anatomy and physiology
... of bones serving to bind them together and to facilitate or limit motion Controlled by the will Tough cord or band of dense, white, connective tissue that attaches a muscle to another part and that transmits the force which the muscle exerts Muscles that are responsible for prime action Sac or cavit ...
... of bones serving to bind them together and to facilitate or limit motion Controlled by the will Tough cord or band of dense, white, connective tissue that attaches a muscle to another part and that transmits the force which the muscle exerts Muscles that are responsible for prime action Sac or cavit ...
1 - Andrus alta anatomy
... of bones serving to bind them together and to facilitate or limit motion Controlled by the will Tough cord or band of dense, white, connective tissue that attaches a muscle to another part and that transmits the force which the muscle exerts Muscles that are responsible for prime action Sac or cavit ...
... of bones serving to bind them together and to facilitate or limit motion Controlled by the will Tough cord or band of dense, white, connective tissue that attaches a muscle to another part and that transmits the force which the muscle exerts Muscles that are responsible for prime action Sac or cavit ...
Anatomical Terminology Power Point
... • Midsagittal or medial – sagittal plane that lies on the midline • Frontal or coronal – divides the body into anterior and posterior parts • Transverse or horizontal (cross section) – divides the body into superior and inferior parts • Oblique section – cuts made diagonally ...
... • Midsagittal or medial – sagittal plane that lies on the midline • Frontal or coronal – divides the body into anterior and posterior parts • Transverse or horizontal (cross section) – divides the body into superior and inferior parts • Oblique section – cuts made diagonally ...
Dr.Kaan Yücel yeditepeanatomy1.org Terminology in anatomy
... It is important for medical personnel to have a sound knowledge and understanding of the basic anatomic terms. With the aid of a medical dictionary, you will find that understanding anatomic terminology greatly assists you in the learning process. The accurate use of anatomic terms by medical person ...
... It is important for medical personnel to have a sound knowledge and understanding of the basic anatomic terms. With the aid of a medical dictionary, you will find that understanding anatomic terminology greatly assists you in the learning process. The accurate use of anatomic terms by medical person ...
human anatomy 101
... abdominal organs as they lie within the abdomen. Clinicians might use several different ways of subdividing the surface of the anterior abdominal wall but I will only present two of them here. By subdividing the surface into regions, one person can tell another person exactly where to look for possi ...
... abdominal organs as they lie within the abdomen. Clinicians might use several different ways of subdividing the surface of the anterior abdominal wall but I will only present two of them here. By subdividing the surface into regions, one person can tell another person exactly where to look for possi ...
Branches of Anatomy - Straight A Nursing
... original stimulus. If the original stimulus is saying that it is too cold, then the effector’s response will negate the cold. It works to returns organism to equilibrium and is the most common type of feedback. In POSITIVE FEEDBACK the effector’s response enhances the original stimulus. In this case ...
... original stimulus. If the original stimulus is saying that it is too cold, then the effector’s response will negate the cold. It works to returns organism to equilibrium and is the most common type of feedback. In POSITIVE FEEDBACK the effector’s response enhances the original stimulus. In this case ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.