Muscle Anatomy Team Sports 1
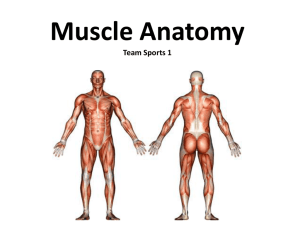
... • Skeletal/Voluntary- Skeletal muscle fibers occur in muscles which are attached to the skeleton. Those muscles that can be moved by our thoughts and actions. • Smooth/Involuntary MuscleMuscles that moves internal organs, such as the bowels, and vessels. Reflex action is made without our thought. • ...
... • Skeletal/Voluntary- Skeletal muscle fibers occur in muscles which are attached to the skeleton. Those muscles that can be moved by our thoughts and actions. • Smooth/Involuntary MuscleMuscles that moves internal organs, such as the bowels, and vessels. Reflex action is made without our thought. • ...
Anatomy and Physiology Intro Study Guide
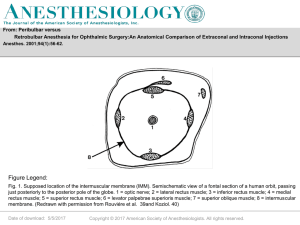
... Source: http://www.ajnr.org/content/vol27/issue10/images/large/zj40100602330001.jpeg July 17, 2008 ...
... Source: http://www.ajnr.org/content/vol27/issue10/images/large/zj40100602330001.jpeg July 17, 2008 ...
Chap 12
... What are “Slow” and “Fast” twitch fibers? What are “red” or “white” fibers? Which are “oxidative”? Which are “glycolytic”? What do these terms mean? Read about the various causes of muscle fatigue. What are “upper” and “lower” motor neurons? Where is each found? What is “muscle atrophy”? Study Fig. ...
... What are “Slow” and “Fast” twitch fibers? What are “red” or “white” fibers? Which are “oxidative”? Which are “glycolytic”? What do these terms mean? Read about the various causes of muscle fatigue. What are “upper” and “lower” motor neurons? Where is each found? What is “muscle atrophy”? Study Fig. ...
It`s Time For Earth Science Chapter 1
... These muscles are located on the posterior surface of the humerus; movements include bending and extending the arms.. ...
... These muscles are located on the posterior surface of the humerus; movements include bending and extending the arms.. ...
Bones and joints of the lower limb: pelvic girdle and femur
... - explain how is anatomy of hip bones/pelvis adjusted to its function - name and describe all joints of pelvis focusing of anatomical and functional properties - remember concepts and common structural properties of flat and long bones SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES: Bones of the pelvic girdle and femur HIP BO ...
... - explain how is anatomy of hip bones/pelvis adjusted to its function - name and describe all joints of pelvis focusing of anatomical and functional properties - remember concepts and common structural properties of flat and long bones SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES: Bones of the pelvic girdle and femur HIP BO ...
Musculoskeletal Biomechanics
... The smallest muscle in the body is Stapedius. It is located deep in the ear. It is only 5mm long and thinner than cotton thread. It is involved in hearing. The biggest muscle in the body is Gluteus Maximus. It is located in the buttock. It pulls the leg backwards powerfully for walking and running. ...
... The smallest muscle in the body is Stapedius. It is located deep in the ear. It is only 5mm long and thinner than cotton thread. It is involved in hearing. The biggest muscle in the body is Gluteus Maximus. It is located in the buttock. It pulls the leg backwards powerfully for walking and running. ...
Chapter 1 Anatomy
... maintain life. This is usually accomplished by one of two mechanisms. A. Negative Feedback Loop – any mechanism that makes the deviation from normal smaller – most systems of the body are regulated by these – consists of 2 parts and ...
... maintain life. This is usually accomplished by one of two mechanisms. A. Negative Feedback Loop – any mechanism that makes the deviation from normal smaller – most systems of the body are regulated by these – consists of 2 parts and ...
File - biologywithsteiner
... Name ___________________________________ Date ______________________ Per ________ Pre AP Biology ...
... Name ___________________________________ Date ______________________ Per ________ Pre AP Biology ...
Medical Terminology
... Superficial - relating to, or located near the surface Deep - relating to, or located away from the surface Median- midline Intermediate -between two other structures External refers to a hollow structure -external being outside Internal refers to a hollow structure -internal being inside Cephalad- ...
... Superficial - relating to, or located near the surface Deep - relating to, or located away from the surface Median- midline Intermediate -between two other structures External refers to a hollow structure -external being outside Internal refers to a hollow structure -internal being inside Cephalad- ...
File
... The human body is the sum of its parts and these parts can be studied at a variety of levels of organization. 1. Atoms are the simplest level. 2. Two or more atoms comprise a molecule 3. Macromolecules are large, biologically important molecules inside cells. 4. Organelles are aggregates of macromol ...
... The human body is the sum of its parts and these parts can be studied at a variety of levels of organization. 1. Atoms are the simplest level. 2. Two or more atoms comprise a molecule 3. Macromolecules are large, biologically important molecules inside cells. 4. Organelles are aggregates of macromol ...
Body Cavities - Grosse Pointe Public School System
... • Midsagittal or medial – sagittal plane that lies on the midline • Frontal or coronal – divides the body into anterior and posterior parts • Transverse or horizontal (cross section) – divides the body into superior and inferior parts • Oblique section – cuts made diagonally ...
... • Midsagittal or medial – sagittal plane that lies on the midline • Frontal or coronal – divides the body into anterior and posterior parts • Transverse or horizontal (cross section) – divides the body into superior and inferior parts • Oblique section – cuts made diagonally ...
homework 1 - cloudfront.net
... ____ 13. Which of the following statements is correct regarding the location of the spleen and stomach: a. both of these organs are located in the left upper quadrant b. both of these organs are located in the right upper quadrant c. the spleen is located in the left upper quadrant and the stomach i ...
... ____ 13. Which of the following statements is correct regarding the location of the spleen and stomach: a. both of these organs are located in the left upper quadrant b. both of these organs are located in the right upper quadrant c. the spleen is located in the left upper quadrant and the stomach i ...
The Human Body: Anatomical Regions, Directions, and Body Cavities
... • Popliteal: behind the knee • Pubic: genital region • Sacral: lower back between the hips • Scapular: shoulder blade • Tarsal: ankle • Thoracic: chest • Vertebral: spine ...
... • Popliteal: behind the knee • Pubic: genital region • Sacral: lower back between the hips • Scapular: shoulder blade • Tarsal: ankle • Thoracic: chest • Vertebral: spine ...
Chapter 1 The Human Body
... • Sagittal – divides the body into right and left parts • Midsagittal or medial – sagittal plane that lies on the midline • Frontal or coronal – divides the body into anterior and posterior parts • Transverse or horizontal (cross section) – divides the body into superior and inferior parts ...
... • Sagittal – divides the body into right and left parts • Midsagittal or medial – sagittal plane that lies on the midline • Frontal or coronal – divides the body into anterior and posterior parts • Transverse or horizontal (cross section) – divides the body into superior and inferior parts ...
Unit 1 Notes Outline
... 2. Homeostatic Control (Mechanism) a. Negative Feedback Mechanism b. Positive Feedback Mechanism ...
... 2. Homeostatic Control (Mechanism) a. Negative Feedback Mechanism b. Positive Feedback Mechanism ...
Language of Anatomy Lab
... A section is a cut; and when the cut is extended through a body or body part, it is carried along an imaginary division called a plane (Fig. 1.3). A cut from anterior to posterior, separating the body into right and left halves, is a midsagittal section, made in the median plane. The term parasagitt ...
... A section is a cut; and when the cut is extended through a body or body part, it is carried along an imaginary division called a plane (Fig. 1.3). A cut from anterior to posterior, separating the body into right and left halves, is a midsagittal section, made in the median plane. The term parasagitt ...
Anatomical Terms - Winston Knoll Collegiate
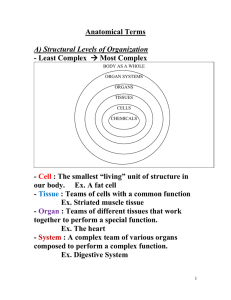
... - Body As A Whole : Unification of all the teams that work together to ensure healthy survival. ...
... - Body As A Whole : Unification of all the teams that work together to ensure healthy survival. ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.