Mahdiyah Johnson, Noor Emrech, Sanaa Bhatti and
... Pelvis: a sturdy ring of bones that protects the organs of the abdominopelvic cavity while fixing the powerful muscles of the hip, thigh, and abdomen. Patella: Knee extension. It increases the leverage that tendon can exert on the femur by increasing at which it acts. Tibia: also known as the shinbo ...
... Pelvis: a sturdy ring of bones that protects the organs of the abdominopelvic cavity while fixing the powerful muscles of the hip, thigh, and abdomen. Patella: Knee extension. It increases the leverage that tendon can exert on the femur by increasing at which it acts. Tibia: also known as the shinbo ...
Organ
... Anatomical Terminology Anatomical Position – body standing erect, facing forward, upper limbs at the sides, palms facing forward Terms of Relative Position • Superior versus Inferior •Anterior versus Posterior •Medial versus Lateral •Ipsilateral versus Contralateral •Proximal versus Distal •Superfi ...
... Anatomical Terminology Anatomical Position – body standing erect, facing forward, upper limbs at the sides, palms facing forward Terms of Relative Position • Superior versus Inferior •Anterior versus Posterior •Medial versus Lateral •Ipsilateral versus Contralateral •Proximal versus Distal •Superfi ...
Bellringer: All directional terms are relative to proper anatomical
... Bellringer: All directional terms are relative to proper anatomical position. Review each sentence below to verify if the correct directional term was used. If the sentence is incorrect, supply a term which would make it correct. The mouth is superior to the nose. The stomach is inferior to the mamm ...
... Bellringer: All directional terms are relative to proper anatomical position. Review each sentence below to verify if the correct directional term was used. If the sentence is incorrect, supply a term which would make it correct. The mouth is superior to the nose. The stomach is inferior to the mamm ...
Directional Terms
... • The chin is superior to the navel. • Inferior • A structure below another • The navel is inferior to the chin. ...
... • The chin is superior to the navel. • Inferior • A structure below another • The navel is inferior to the chin. ...
Name_________________ Anatomy I Mrs. Adams Anatomical
... 1. Mrs. Cicoria is mad at Mr. Cicoria. Her posture is as follows...She is standing with her left foot pointed forward, her right foot is pointed out the the side, her hands are on her hips, she is tapping her right foot up and down off the floor. Which answer best describes the action of her right H ...
... 1. Mrs. Cicoria is mad at Mr. Cicoria. Her posture is as follows...She is standing with her left foot pointed forward, her right foot is pointed out the the side, her hands are on her hips, she is tapping her right foot up and down off the floor. Which answer best describes the action of her right H ...
Surface Anatomy Of Urinary System
... • In thin adults with poorly developed abdominal muscles, the inferior pole of the right kidney is usually palpable in the right lateral region. • The normal left kidney is not usually palpable. ...
... • In thin adults with poorly developed abdominal muscles, the inferior pole of the right kidney is usually palpable in the right lateral region. • The normal left kidney is not usually palpable. ...
Gummy Bear Lab
... The knee is proximal to the ankle. The knee is distal to the hip. A visceral membrane covers the heart. A parietal membrane lines the inside of the body cavity. The thighbone is deep to the surrounding skeletal muscles. The skin is superficial to the skeletal muscles. The medullary region of the kid ...
... The knee is proximal to the ankle. The knee is distal to the hip. A visceral membrane covers the heart. A parietal membrane lines the inside of the body cavity. The thighbone is deep to the surrounding skeletal muscles. The skin is superficial to the skeletal muscles. The medullary region of the kid ...
Muscles
... 28. The fine sheath of connective tissue surrounds each individual muscle fiber is the _______________. 29. The endomysium-wrapped fibers are grouped into ________________ bundles. 30. The surrounding layer of tissue around those is called _________________. 31. The “overcoat” of dense irregular con ...
... 28. The fine sheath of connective tissue surrounds each individual muscle fiber is the _______________. 29. The endomysium-wrapped fibers are grouped into ________________ bundles. 30. The surrounding layer of tissue around those is called _________________. 31. The “overcoat” of dense irregular con ...
Ch1.Human.Body.Lecture
... Body Planes and Sections • Coronal (frontal) plane = Lies vertically & divides body into anterior & posterior parts • Median (midsagittal) plane = Specific sagittal plane that lies vertically in the midline • Transverse plane = Runs horizontally & divides body into superior & inferior parts Frontal ...
... Body Planes and Sections • Coronal (frontal) plane = Lies vertically & divides body into anterior & posterior parts • Median (midsagittal) plane = Specific sagittal plane that lies vertically in the midline • Transverse plane = Runs horizontally & divides body into superior & inferior parts Frontal ...
MAIN ANATOMICAL TERMS TO LEARN: From Nicola ABDUCTION
... The only muscle you will not be able to see is the erector spinae because it lies underneath the latissimus dorsi and trapezius. ...
... The only muscle you will not be able to see is the erector spinae because it lies underneath the latissimus dorsi and trapezius. ...
Chapter 5 Review File - Northwest ISD Moodle
... ______ 3. The anatomical position is best described as a person: A. standing, facing forward, palms facing forward. B. lying on his back, palms facing down. C. standing, facing sideways, palms facing thighs. D. lying on his stomach, palms up. ______ 4. An imaginary line down the center of the body t ...
... ______ 3. The anatomical position is best described as a person: A. standing, facing forward, palms facing forward. B. lying on his back, palms facing down. C. standing, facing sideways, palms facing thighs. D. lying on his stomach, palms up. ______ 4. An imaginary line down the center of the body t ...
LAB: CAT DISSECTION
... How many lobes (sections) does a cat's lung have? __ How many lobes in a human lung? __ What prevents the mammalian "windpipe" from collapsing when there is no air moving through ...
... How many lobes (sections) does a cat's lung have? __ How many lobes in a human lung? __ What prevents the mammalian "windpipe" from collapsing when there is no air moving through ...
Anatomical position
... standardized method of observing or imaging the body that allows precise and consistent anatomical references. When in the anatomical position, the subject stands: ...
... standardized method of observing or imaging the body that allows precise and consistent anatomical references. When in the anatomical position, the subject stands: ...
Copy of Movement Patterns
... Define and demonstrate the different movement patterns allowed at each joint ...
... Define and demonstrate the different movement patterns allowed at each joint ...
EMTB Anatomical Terms and Body Systems Drill PREPARATION
... a. refers to palm of the hand 14. Plantar a. refers to sole of the foot 15. Mid-clavicular line a. runs through the center of clavicle and the nipple below 16. Abdominal quadrants a. created by drawing horizontal and vertical lines through the navel b. left upper quadrant (LUQ) 1) stomach 2) spleen ...
... a. refers to palm of the hand 14. Plantar a. refers to sole of the foot 15. Mid-clavicular line a. runs through the center of clavicle and the nipple below 16. Abdominal quadrants a. created by drawing horizontal and vertical lines through the navel b. left upper quadrant (LUQ) 1) stomach 2) spleen ...
Movement Patterns
... Define and demonstrate the different movement patterns allowed at each joint ...
... Define and demonstrate the different movement patterns allowed at each joint ...
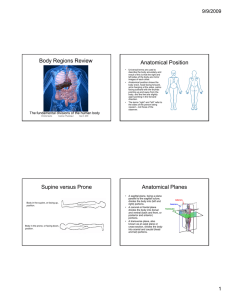
Body Regions Review Anatomical Position Supine versus Prone
... A sagittal plane, being a plane parallel to the sagittal suture, divides the body into (left and right) portions. A coronal or frontal plane divides the body into dorsal and ...
... A sagittal plane, being a plane parallel to the sagittal suture, divides the body into (left and right) portions. A coronal or frontal plane divides the body into dorsal and ...
Chapter 1_5 Anatomical Terminology
... Complete these sentences using the terms superior and inferior. •The hands are ________________to the feet •The knees are ________________ to the waist. •The elbow is ________________ to the wrist. •The calf muscle is ________________to the ankle. ...
... Complete these sentences using the terms superior and inferior. •The hands are ________________to the feet •The knees are ________________ to the waist. •The elbow is ________________ to the wrist. •The calf muscle is ________________to the ankle. ...
PowerPoint to accompany Hole`s Human Anatomy and Physiology
... – For example: Incisors are a ___________ __________than molars. They have a different number of points on them. – Why is that? Because they perform different ...
... – For example: Incisors are a ___________ __________than molars. They have a different number of points on them. – Why is that? Because they perform different ...
CHAPTER 3: Human Anatomy
... These planes can also be used to describe different movements or actions. Sagittal, frontal, or transverse plane movements occur in a plane that is parallel to these specific planes. For example, a forward roll would be considered a sagittal plane movement because the forward and backward motion is ...
... These planes can also be used to describe different movements or actions. Sagittal, frontal, or transverse plane movements occur in a plane that is parallel to these specific planes. For example, a forward roll would be considered a sagittal plane movement because the forward and backward motion is ...
Anatomical position
... the plane which divides the body into equal right and left halves. Sagittal plane: It is any plane parallel to the median plane. This plane divides the body into unequal right and left halves. Frontal plane: It is a vertical plane at right angle to median plane. If you draw a line from one ear to an ...
... the plane which divides the body into equal right and left halves. Sagittal plane: It is any plane parallel to the median plane. This plane divides the body into unequal right and left halves. Frontal plane: It is a vertical plane at right angle to median plane. If you draw a line from one ear to an ...
Positional Terminology and Body Movements Lecture Guide
... bronchial tree), meaning farther from the base or point of origin of the structure. ...
... bronchial tree), meaning farther from the base or point of origin of the structure. ...
Intramuscular Injections
... • Small muscle with little subcu fat • Absorbed quickly • Smaller volume of medication (no more than 1 mL) • Anatomical risk: radial nerve and brachial artery ...
... • Small muscle with little subcu fat • Absorbed quickly • Smaller volume of medication (no more than 1 mL) • Anatomical risk: radial nerve and brachial artery ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.