* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Surface Anatomy Of Urinary System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
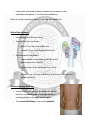
Surface Anatomy Of Urinary System Learning objectives: At the end of the lecture the student should be able to: • Identify the surface anatomy of – Kidney, – Ureter and – Urinary bladder. Surface anatomy of kidney: • Right kidney usually lies about 1 cm. lower than the left, but for practical purposes similar surface markings are taken for each • The kidneys lie in the paravertebral gutters, at the level of T12 to L3 vertebrae. • Their long axis are almost parallel with the axis of the body • It is a firm, smooth, somewhat rounded mass that descends during inspiration. Front of the abdomen: • Upper pole lies midway between the plane of the lower end of the body of the sternum and the transpyloric plane, 5 cm. from the middle line. • Lower pole is situated midway between the transpyloric and intertubercular planes, 7 cm. from the middle line. Hilum is on the transpyloric plane, 5 cm. from the middle line. Back of the abdomen: • Parallellogram of Morris is used; • Two vertical lines are drawn – First 2.5 cm. from the middle line – Second 9.5 cm. from the middle line the • Two horizontal lines drawn – Upper border at the levels of the tips of the spinous process of the T11 – lower border of the spinous process of the L3 – Hilum is 5 cm. from the middle line at the level of the spinous process of the L1. Surface anatomy of kidney: • In thin adults with poorly developed abdominal muscles, the inferior pole of the right kidney is usually palpable in the right lateral region. • The normal left kidney is not usually palpable. Surface Anatomy Of Ureter: • On the front of the abdomen • line of the ureter runs from the hilum of the kidney to the pubic tubercle; • On the back • From the hilum vertically downward, passing practically through the posterior superior iliac spine. Surface anatomy of urinary bladder: • When empty the bladder sinks into the pelvis. • When distended it rises toward the umbilicus, carrying the peritoneal fold with it so as to leave a space of 2.5 to 5 cm. (1 to 2 in.) between it and the top of the pubis. Thank you.