* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genitourinary Surgery
Intersex medical interventions wikipedia , lookup
Kidney transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Kidney stone disease wikipedia , lookup
Interstitial cystitis wikipedia , lookup
Urethroplasty wikipedia , lookup
IgA nephropathy wikipedia , lookup
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease wikipedia , lookup
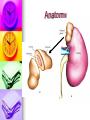
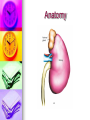
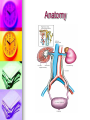
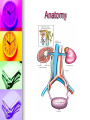
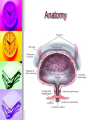
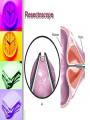
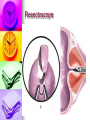
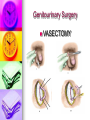
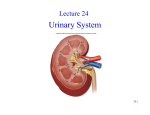
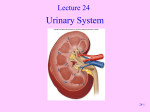
Genitourinary Surgery Chapter 20 Anatomy Suprarenal Glands (Adrenal Glands) Situated on the superior/medial portion of the kidney. Outer Cortex secretes steroidal hormones Inner Medulla secrete epinephrine and norepinephrine. Highly vascular. Anatomy Anatomy Kidneys (2) Two bean shaped organs located in the retroperitoneal space. Medial indention is known as the hilum. Lie in a bed of fatty and fibrous connective tissue. Surrounded by a smooth fibrous capsule. Gerota’s Fascia Right kidney is smaller and lower. Left kidney is larger and higher. Genitourinary Surgery Anatomy Anatomy Kidneys Outer portion – Cortex Inner portion - Medulla Comprised of millions of Nephrons Divided into two units Renal corpuscle Renal tubule Responsible for filtration, reabsorbtion, and secretion. Renal arteries Anatomy Renal corpuscle Consists of a network of capillaries called the glomerulus. Contained within the Bowman’s Capsule. Responsible for filtration. Anatomy Renal tubules Consists of 3 units Proximal convoluted tubule Loop of Henle Distal convoluted tubule Responsible for reabsorbtion and secretion. Most of the reabsorbtion happens in the Proximal tube. Anatomy Kidneys As urine is produced, it flows inward from the: Renal pyramids Renal papillae Minor calyces Major calyces Renal pelvis The renal pelvis forms a funnel like upper end of the ureters. Anatomy Anatomy Ureters Two tubes conducting urine from each kidney to the bladder. Uses wave like muscular contraction to move urine to the bladder. Anatomy Anatomy Urinary bladder Elastic sac-like organ that stores urine, until it is eliminated out of the body through the urethra. Located in the pelvis surrounded: Holds up to 600ml on average Levator ani – Inferior Obturator internus – Superior Rectum – Posterior Abdominal wall – Anterior Blood supply – Vesical arteries Anatomy Urinary bladder Lined with a folded mucous membrane that will stretch when distended. Trigone Triangular smooth area from the ureteral openings to the urethral opening. Anatomy Anatomy Urethra Tube conducting urine from the bladder to the urethral meatus to be expelled from the body. Portion of the male urinary and reproductive system. Divided into 3 portions Prostatic (proximal) Membranous Spongy (distal) Male Reproductive System Testis Tunica abuginea Seminiferious tubules Septum Epididymis Ductus (Vas) Deferens Seminal Vesicles Ejaculatory ducts Prostate Gland Penis Prepuce Pathology Affecting the Adrenal Glands Cushing’s Syndrome Addison’s Disease Over production of cortisol due to tumor of the adrenals or pituitary. Under production of adrenal hormones. Treated medically. Pheochromocytoma Tumor of the medulla, resulting in overproduction of adrenaline. Pathology Affecting the Urinary System Bladder tumors Present with hematuria Single growth or multiple present. Benign (papillomas) occur in young adults. Malignant neoplasms usually occur in men over 50. Early removal transurethrally. Cancer of the bladder may recur. Pathology Affecting the Urinary System Urinary Calculi Small solid particles Form in one or both kidneys Travel through the urinary system Partial or total obstruction The size and location will determine the signs and symptoms. Pathology Affecting the Urinary System Calculi symptoms Dysuria Polyuria Passage of small amounts of urine Flank pain Nausea and vomiting Urinary tract infection Pathology Affecting the Urinary System Kidney disorders Polycystic Kidney Disease Diabetic Nephropathy End-Stage Renal Disease Hemodialysis Peritoneal Dialysis Renal Cell Carcinoma Congenital Nephroblastoma Pathology Affecting the Male Reproductive System Phimosis Hypospadias/Epispadias Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy Cancer of the Prostate Cryptorchidism Testicular Torsion Testicular Cancer Diagnostic Procedures Hemotology Urinalysis PSA Simple Void Clean-catch Catheterized 24 hour urine KUB IVU/IVP Retrograde Urogram Instrumentation General Kidney Major, Long Stone Forceps Thoracic Rib retractors Elevators Rib shears/approximator Instrumentation Urethral sounds/dilators Resectoscope Ellik evacuator Working element Removes tumor segments Flexible endoscopes Rigid endoscopes Resectoscope Resectoscope Resectoscope Incisions Inguinal Scrotal Lower portion of the ureter Flank Vasectomy Abdominal Gibson Radical Orchietomy Lateral Position Lumbar Common Procedures Nephrectomy MMK Circumcision Orchiopexy Vasectomy/Vasovasotomy TURP Suprapubic prostatectomy Genitourinary Surgery Genitourinary Surgery CIRCUMCISION Genitourinary Surgery ORCHIECTOMY Genitourinary Surgery VASECTOMY Genitourinary Surgery QUESTIONS?