Chapter 8
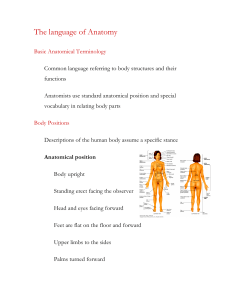
... Directions of the Body • Anatomical Position – The erect position of the body with the face directed forward the arms at the side and the palms of the hands directed forward. ...
... Directions of the Body • Anatomical Position – The erect position of the body with the face directed forward the arms at the side and the palms of the hands directed forward. ...
Exercise Science
... ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ Sagittal (median) plane: _____ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ Transverse (horizontal) plane: ___________________________ ___________________________ __________ ...
... ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ Sagittal (median) plane: _____ ___________________________ ___________________________ ___________________________ Transverse (horizontal) plane: ___________________________ ___________________________ __________ ...
TheLanguageofAnatomy..
... Anterior – In front of; toward the front of the body; ventral Posterior – In back of; toward the back of the body; dorsal Superior – Above; refers to the structures closer to the head or tow ...
... Anterior – In front of; toward the front of the body; ventral Posterior – In back of; toward the back of the body; dorsal Superior – Above; refers to the structures closer to the head or tow ...
Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
... 2. Which of the life processes from the list above were mentioned in the video? Review the list of life processes and consider Kati Mori’s symptoms. processes that you think might be related. ...
... 2. Which of the life processes from the list above were mentioned in the video? Review the list of life processes and consider Kati Mori’s symptoms. processes that you think might be related. ...
Skeletal/Muscular System Study Guide Pair of long bones that
... 3. What is the medical name of the jawbone? _____________ 4. The only bone in the upper arm._______________ 5. The more lateral and slightly shorter of the two forearm bones and is found on the thumb side of the forearm._______________ 6. The longest, heaviest, and strongest bone in the entire human ...
... 3. What is the medical name of the jawbone? _____________ 4. The only bone in the upper arm._______________ 5. The more lateral and slightly shorter of the two forearm bones and is found on the thumb side of the forearm._______________ 6. The longest, heaviest, and strongest bone in the entire human ...
Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Essential
... 2. Which of the life processes from the list above were mentioned in the video? Review the list of life processes and consider Kati Mori’s symptoms. Choose three of the processes ...
... 2. Which of the life processes from the list above were mentioned in the video? Review the list of life processes and consider Kati Mori’s symptoms. Choose three of the processes ...
skeletal muscles part 1
... Origin – Galea aponuerotica (a flat tendon attached to both the frontalis and occipitalis muscles) Insertion – Integument (skin) above the orbits of the eyes. Action – Draws the scalp forward, raises eyebrows, and wrinkles the skin of the forehead horizontally ...
... Origin – Galea aponuerotica (a flat tendon attached to both the frontalis and occipitalis muscles) Insertion – Integument (skin) above the orbits of the eyes. Action – Draws the scalp forward, raises eyebrows, and wrinkles the skin of the forehead horizontally ...
ch1-notes - WordPress.com
... Directional Terms Anatomic position refers to a person standing erect with face forward, upper limbs hanging to the sides, and palms of the hands facing forward Superior = above Inferior = below Anterior = front Posterior = back Ventral = front Dorsal = back ...
... Directional Terms Anatomic position refers to a person standing erect with face forward, upper limbs hanging to the sides, and palms of the hands facing forward Superior = above Inferior = below Anterior = front Posterior = back Ventral = front Dorsal = back ...
Skeletal Worksheet Answers
... 1. Divided into sections using ___imaginary planes___ 2. The _____Tranverse___ runs from R/L and divides the body into _Superior__ and ___Inferior__ a. The head is ___Superior___ to the neck b. The ______________ is superior to the waist (you fill in ) 3. The ___Frontal__ plane runs from head to foo ...
... 1. Divided into sections using ___imaginary planes___ 2. The _____Tranverse___ runs from R/L and divides the body into _Superior__ and ___Inferior__ a. The head is ___Superior___ to the neck b. The ______________ is superior to the waist (you fill in ) 3. The ___Frontal__ plane runs from head to foo ...
Test Review
... 4. The ____________________ is the attachment to the immovable or less movable bone 5. The ____________________ is the attachment to the movable bone 6. Muscles can only ____________ they never ___________ 7. During contraction, the muscle ___________________ moves toward the ____________ __________ ...
... 4. The ____________________ is the attachment to the immovable or less movable bone 5. The ____________________ is the attachment to the movable bone 6. Muscles can only ____________ they never ___________ 7. During contraction, the muscle ___________________ moves toward the ____________ __________ ...
Words and the anatomical position
... Two meanings: Loose connective and fatty tissue, of variable thickness: superficial fascia, prevertebral fascia Fairly tough sheath or membrane: deep fascia, clavipectoral fascia ...
... Two meanings: Loose connective and fatty tissue, of variable thickness: superficial fascia, prevertebral fascia Fairly tough sheath or membrane: deep fascia, clavipectoral fascia ...
The Human Body: Anatomical Regions, Directions
... • Sagittal – divides the body into right and left parts • Midsagittal or medial – sagittal plane that lies on the midline • Frontal or coronal – divides the body into anterior and posterior parts • Transverse or horizontal (cross section) – divides the body into superior and inferior parts ...
... • Sagittal – divides the body into right and left parts • Midsagittal or medial – sagittal plane that lies on the midline • Frontal or coronal – divides the body into anterior and posterior parts • Transverse or horizontal (cross section) – divides the body into superior and inferior parts ...
Document
... Further away from the midline, towards the outside of the body E.g. The thumb is the lateral part of the hand *Distal Further away from the trunk (limbs) e.g. The wrist is distal to the elbow *Proximal Closer to the body (limbs) E.g. The shoulder is proximal to the elbow ...
... Further away from the midline, towards the outside of the body E.g. The thumb is the lateral part of the hand *Distal Further away from the trunk (limbs) e.g. The wrist is distal to the elbow *Proximal Closer to the body (limbs) E.g. The shoulder is proximal to the elbow ...
Directional Terms
... Discuss regions of the body by their medical names Describe where regions of the body are located in relation to one another using directional terms ...
... Discuss regions of the body by their medical names Describe where regions of the body are located in relation to one another using directional terms ...
Language of Anatomy
... Closest part of the arm or leg to the attachment point on the body The elbow is proximal to the wrist (it is closer to the attachment point of the arm to the body) ...
... Closest part of the arm or leg to the attachment point on the body The elbow is proximal to the wrist (it is closer to the attachment point of the arm to the body) ...
Anatomy Basic Concepts - Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation
... • Defense barrier – Skin & microbes – Bone, muscle and soft organs ...
... • Defense barrier – Skin & microbes – Bone, muscle and soft organs ...
Spring 2014 - Unit 1 Study Guide
... A. Serous membranes line cavities that open to the outside of the body. B. Visceral serous membranes are in contact with internal organs. C. Retroperitoneal organs are surrounded by both parietal and ...
... A. Serous membranes line cavities that open to the outside of the body. B. Visceral serous membranes are in contact with internal organs. C. Retroperitoneal organs are surrounded by both parietal and ...
Chapter 11 Muscles of the body
... Chapter 11 Axial Muscles of the body Course objectives: Name and be able to identify specific axial muscles in the body. ...
... Chapter 11 Axial Muscles of the body Course objectives: Name and be able to identify specific axial muscles in the body. ...
A&P_Lab 1 Rat Dissection
... • Lateral: away from the middle • Proximal: closer to the point of attachment or origin • Distal: farther from the point of attachment or origin • Supine: facing up • Prone: facing down ...
... • Lateral: away from the middle • Proximal: closer to the point of attachment or origin • Distal: farther from the point of attachment or origin • Supine: facing up • Prone: facing down ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.