* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Human Body: Anatomical Regions, Directions
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
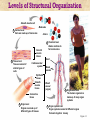
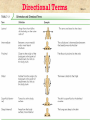
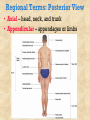
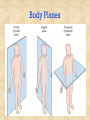
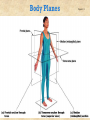
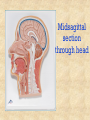
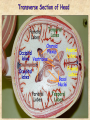
The Human Body: Anatomical Regions, Directions, and Body Cavities Chapter 1 Things to know for the Quiz: • • • • • Directional Terms Body Cavities Body Systems Levels of organization Prefixes Overview of Anatomy and Physiology • Anatomy – the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another 1. Gross anatomy and 2. Microscopic anatomy) • Physiology – the study of the function of the body’s structural machinery 1. Gross Anatomy • Regional – all structures in one part of the body – Example: studying all structures in the abdomen • Systemic – gross anatomy of the body studied by system – Example: studying the digestive system • Surface – study of external features as they relate to the underlying features – Example: The jugular notch/ sternal angle can help locate the second rib. 2. Microscopic Anatomy • Cytology – study of the cell – “cyto” means cell • Histology – study of tissues – “histo” means tissue Physiology • Considers the operation of specific organ systems – Renal – kidney function – Neurophysiology – workings of the nervous system – Cardiovascular – operation of the heart and blood vessels • Focuses on the functions of the body, often at the cellular or molecular level Physiology • Understanding physiology also requires a knowledge of physics, which explains electrical currents, blood pressure, and the way muscle uses bone for movement Levels of Structural Organization Smooth muscle cell Molecules 2 Cellular level Cells are made up of molecules Atoms Smooth muscle tissue 3 Tissue level Tissues consist of similar types of cells 1 Chemical level Atoms combine to form molecules Heart Cardiovascular system Epithelial tissue Smooth muscle tissue Connective tissue 4 Organ level Organs are made up of different types of tissues Blood vessels Blood vessel (organ) 6 Organismal level The human organism is made up of many organ systems 5 Organ system level Organ systems consist of different organs that work together closely Figure 1.1 Levels of Structural Organization • Chemical – atoms combined to form molecules • Cellular – cells are made of molecules • Tissue – consists of similar types of cells • Organ – made up of different types of tissues • Organ system – consists of different organs that work closely together • Organism – made up of the organ systems Homeostasis • Homeostasis is the ability to maintain a relatively stable internal environment in an ever-changing outside world • The internal environment of the body is in a dynamic state of equilibrium • Chemical, thermal, and neural factors interact to maintain homeostasis Negative Feedback • When a deviation from homeostasis occurs, the system makes the deviation smaller. • Think of negative as opposite. Positive Feedback • When a deviation from homeostasis occurs, the system responds by making the deviation EVEN greater. • Rare in healthy individuals. • Not enough blood to the heart? Your heart will contract and move blood – but if you’ve LOST blood, the heart rate increases and pumps more. And you lose MORE blood, so the heart pumps more…etc. etc. Anatomical Position • • • • Body erect Feet slightly apart Palms facing forward Thumbs point away from body • Right and Left are absolute. RIGHT LEG LEFT LEG Figure 1.7a Anatomical Position • • • • Body erect Feet slightly apart Palms facing forward Thumbs point away from body • PRONE is face down. • SUPINE is face up. RIGHT LEG LEFT LEG Figure 1.7a Directional Terms • Superior and inferior – toward and away from the head, respectively • Anterior and posterior – toward the front and back of the body • Medial, lateral, and intermediate – toward the midline, away from the midline, and between a more medial and lateral structure Directional Terms • Proximal and distal – closer to and farther from the origin of the body • Superficial and deep – toward and away from the body surface Directional Terms Table 1.1 Directional Terms Table 1.1 Regional Terms: Anterior View In your book: Page 11 Figure 1.8 Regional Terms: Posterior View • Axial – head, neck, and trunk • Appendicular – appendages or limbs Body Planes • Sagittal – divides the body into right and left parts • Midsagittal or medial – sagittal plane that lies on the midline • Frontal or coronal – divides the body into anterior and posterior parts • Transverse or horizontal (cross section) – divides the body into superior and inferior parts Body Planes Body Planes Figure 1.8 Midsagittal section through head