* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 8
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
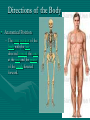
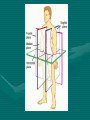
Chapter 8 Introduction to the body! The cell • Cells are microscopic • Every cell is programmed to do a specific job that allows the body to function. – Each cell reproduced, grows and repairs itself, uses oxygen and nutrients, digests food for energy, eliminates waste, produces heat and energy and is able to move around Three Main Parts • Nucleus • Cytoplasm • Cell membrane Tissues • Tissues are specialized groups of cells – Five types • • • • • Nerve Epithelial Connective Blood Muscle – Smooth – Striated – Cardiac Tissues of the Body • Nerve tissue – Through out the body • Sends impulses to/from the CNS and to/from the body • Epithelial Tissue – Forms the outer skin and lines the body cavities and passages to the outside of the body • Protects, secretes, absorbs and receives sensations • Connective tissue – Bones, tendons, fat • Binds, supports and connects body tissues • Blood and Lymph Tissue – Moves through the circulatory system • Delivers nourishment electrolytes, hormones, vitamins, antibodies, heat and oxygen to all body tissues • Muscle tissue 1. Cardiac – Heart muscle only – Contracts the heart 2. Smooth – Internal Organs – Contracts internal organs 3. Striated – Through out the body for movement – Contracts and flexes to allow movement Where are these found? Organs are made up of different types of tissue that work together • Example-Heart is an organ made up of: – Connective – Nerve – Muscle-Cardiac Systems A system is a group of organs working together to perform a certain function. The body is composed of several systems. – Skeletal – Muscular – Circulatory – Lymphatic – Respiratory -Digestive -Urinary -Glandular -Nervous -Reproductive -Integumentary Directions of the Body • Anatomical Position – The erect position of the body with the face directed forward the arms at the side and the palms of the hands directed forward. • Directional terms describe the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body. • Superior or cranial toward the head end of the body; upper (example, the hand is part of the superior extremity). Inferior or caudal away from the head; lower (example, the foot is part of the inferior extremity). • Anterior or ventral front (example, the kneecap is located on the anterior side of the leg). Posterior or dorsal back (example, the shoulder blades are located on the posterior side of the body). • • Medial toward the midline of the body (example, the middle toe is located at the medial side of the foot). • Lateral away from the midline of the body (example, the little toe is located at the lateral side of the foot). • Proximal toward or nearest the trunk or the point of origin of a part (example, the proximal end of the femur joins with the pelvic bone). • Distal away from or farthest from the trunk or the point or origin of a part (example, the hand is located at the distal end of the forearm). Cavities of Body • Cranial Cavity – Houses the brain • Spinal Cavity – Houses the spinal cord • Thoracic Cavity – Houses the heart lungs and large blood vessels • Abdominal Cavity – Stomach, most of intestines, kidney, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen • Pelvic Cavity – Urinary bladder, part of intestine, rectum, parts of repo system.