* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Positional Terminology and Body Movements Lecture Guide
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
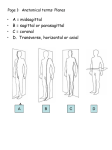
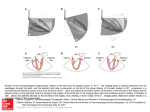
Positional Terminology and Body Movements Lecture Guide Anatomical Position • It is important to have a • The anatomical position is the reference point. It is the position from which anatomical structures are described. • In the anatomical position, the body is the palms face forward. for descriptive purposes. the upper limbs are at the sides, and Body Planes • Sagittal Plane • Imaginary vertical plane that separates the body into • • Median Sagittal Plane = Vertical plane that divides the body into equal right and left. Parasagittal Plane= Vertical plane that is parallel to the median plane and divides the body into unequal right and left parts. Coronal/Frontal Plane • Vertical planes at right angles to the sagittal plane. They divide the body into (front and back) parts. Transverse /Horizontal Plane • Directional Terms Superior (Cephalad) • A term meaning • . Ex: The head is superior to the neck. Inferior (caudad) • A term meaning • Ex: The abdomen is inferior to the chest. Dorsal • Pertains to the • Ventral parts. surface of the body. Ex: The bones of your vertebral column on the dorsal surface of the trunk. • Pertains to the • Ex: The umbilicus or belly button is located on the ventral surface of the body. surface of the body. Anterior • Referencing the • side of the body. Ex: The knee caps form the anterior surface of the knee. Posterior • Referencing the side of the body. • Ex: The vertebral column lies posterior the heart. • Ex: The nose is medial to the ears. Medial • Lateral • Towards the • of the structure or the body. Away from the midline. Ex: The eyes are lateral to the body’s midline or the eyes are lateral to the nose. Proximal • • References landmarks on structures that are branches or appendages of other structures (limbs, nerves, bronchial), meaning nearer the base or point of origin of the structure. • Ex: The shoulder joint is proximal to the elbow. Distal • • References landmarks on structures that are branches or appendages of other structures (limbs, bronchial tree), meaning farther from the base or point of origin of the structure. • Ex: The wrist is distal to the elbow. Superficial • Latin for meaning • or something on the surface. Ex: The skin is the superficial most organ of the human body. DEEP/Profundus • other layers of anatomy. Flexion • Bending movement that the angle between two parts. Extension • The opposite of flexion; • A straightening movement that the angle between body parts. Hypertension • Adduction • A motion that pulls a structure or part • It “adds” to the body. Abduction • A motion that pulls a structure or part Pronation • A rotation of the forearm that moves the palm from an anterior-facing position to a -facing position. Supination • A rotation of the forearm so that the palm faces Retraction • Movement of a body part in the direction, i.e. being drawn backwards. Protraction • Movement of a body part in the direction, i.e. being drawn forwards. Elevation • Movement in a direction. Depression • Movement in an Rotation • A motion that occurs when a part Circumduction direction. • Movement of a limb or extremity so that the distal end describes a proximal end remains fixed. while the External rotation (Lateral rotation) • Rotation from the center of the body. Internal rotation (Medial rotation) • Rotation the center of the body. Lateral Flexion • Bending to the • Has an Anterior/Posterior Axis (AP axis). (left side, or right side). Inversion • Movement of the sole Eversion • The movement of the sole of the foot Dorsiflexion • Backward flexion (bending), as of the hand or foot. Plantar Flexion • Movement of the foot in which the foot or toes flex the sole. Radial Deviation • Movement of the wrist toward the of the forearm. Ulnar Deviation (ulnar drift) • Movement of the wrist toward the • Can occur in a hand deformity in which the swelling of the metacarpophalangeal joints (the big knuckles at the base of the fingers) causes the fingers to move towards the little finger. of the forearm. Opposition • The relation between the thumb and the other digits of the hand for the purpose of grasping objects between the .