Terminologies, Planesand Positions By Dr. Nand Lal Dhomeja
... Medial indicates a structure nearer to the median plane of the body. For example, 5th digit of the hand (little finger) is medial to other digits. ...
... Medial indicates a structure nearer to the median plane of the body. For example, 5th digit of the hand (little finger) is medial to other digits. ...
The Muscular System
... Answer: The Sartorius The Sartorius runs from the outside of the hip, down and across to the inside of the knee. It twists and pulls the thigh outwards. ...
... Answer: The Sartorius The Sartorius runs from the outside of the hip, down and across to the inside of the knee. It twists and pulls the thigh outwards. ...
Chapter 1 Chapter Overview Anatomy Physiology
... • Anatomical position • Regions of the body • Anatomical planes, sections and directional terms ...
... • Anatomical position • Regions of the body • Anatomical planes, sections and directional terms ...
Exercise 2 body systems and muscles - PCC
... Acromial: the point of the shoulder Antebrachial: forearm Antecubital: anterior surface of the elbow Axillary: armpit Brachial: upper arm Buccal: cheek of the face Calcaneal: heel of the foot Carpal: wrist Cephalic: head ...
... Acromial: the point of the shoulder Antebrachial: forearm Antecubital: anterior surface of the elbow Axillary: armpit Brachial: upper arm Buccal: cheek of the face Calcaneal: heel of the foot Carpal: wrist Cephalic: head ...
The Muscular System
... Answer: The Sartorius The Sartorius runs from the outside of the hip, down and across to the inside of the knee. It twists and pulls the thigh outwards. ...
... Answer: The Sartorius The Sartorius runs from the outside of the hip, down and across to the inside of the knee. It twists and pulls the thigh outwards. ...
Basic Anatomical Terms
... Median or Mid-Sagittal plane: This is the plane which divides the body into equal right and left halves. Sagittal plane: It is any plane parallel to the median plane. This plane divides the body into unequal right and left halves. ...
... Median or Mid-Sagittal plane: This is the plane which divides the body into equal right and left halves. Sagittal plane: It is any plane parallel to the median plane. This plane divides the body into unequal right and left halves. ...
Q = quadratus lumborum The quadratus lumborum (QL) muscle is a
... restriction of the blood flow which can eventually cause muscle spasm and pain. Continuous poor posture, especially in this seated position, can also cause kyphosis and will also put greater stress on the QL due to the weight being shifted forward and the spine and pelvis coming out of alignment. Pr ...
... restriction of the blood flow which can eventually cause muscle spasm and pain. Continuous poor posture, especially in this seated position, can also cause kyphosis and will also put greater stress on the QL due to the weight being shifted forward and the spine and pelvis coming out of alignment. Pr ...
A horizontal cut that divides the body into upper and lower parts.
... the body. It is enclosed by the ribs, the vertebral column, and the sternum, or breastbone, and is separated from the abdominal cavity (the body’s largest hollow space) by a muscular & membranous partition, the diaphragm. • It contains the lungs, the middle & lower airways—the tracheobronchial tree— ...
... the body. It is enclosed by the ribs, the vertebral column, and the sternum, or breastbone, and is separated from the abdominal cavity (the body’s largest hollow space) by a muscular & membranous partition, the diaphragm. • It contains the lungs, the middle & lower airways—the tracheobronchial tree— ...
Chapter One
... Anatomic Directions Allow us to describe the relative position of one body structure in relation to another • Anterior vs. posterior • Superior vs. inferior ...
... Anatomic Directions Allow us to describe the relative position of one body structure in relation to another • Anterior vs. posterior • Superior vs. inferior ...
INTRODUCTON
... You are familiar with the terminology of your community and family. You may talk about the front room of your home, use directional terms such north and south, turn right or left, or the end of your big toe or the back of your heel. With these terms and others, you are able to communicate easily wit ...
... You are familiar with the terminology of your community and family. You may talk about the front room of your home, use directional terms such north and south, turn right or left, or the end of your big toe or the back of your heel. With these terms and others, you are able to communicate easily wit ...
divides the body or an organ into left and right sides
... • A plane is an imaginary flat surface that passes through the body. • A section is one of the 2 surfaces (pieces) that results when the body is cut by a plane passing through it. ...
... • A plane is an imaginary flat surface that passes through the body. • A section is one of the 2 surfaces (pieces) that results when the body is cut by a plane passing through it. ...
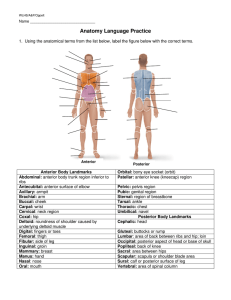
HANDOUT - Anatomy Language Practice
... 4. Using the terms from the following word bank, complete the following statements by choosing an anatomical term from the word bank. Letters may be used more than once. A. Anterior ...
... 4. Using the terms from the following word bank, complete the following statements by choosing an anatomical term from the word bank. Letters may be used more than once. A. Anterior ...
unit 1 human body orientation ppt teacher
... ex. The wrist is distal to the shoulder. Superficial (external) – toward or at the body surface ex. The skin is superficial to the skeleton. Deep – (internal) away from the body surface ex. The lungs are deep to the sternum. ...
... ex. The wrist is distal to the shoulder. Superficial (external) – toward or at the body surface ex. The skin is superficial to the skeleton. Deep – (internal) away from the body surface ex. The lungs are deep to the sternum. ...
Sample
... 2. The location of the nine abdominopelvic regions are: Right and left hypochondriac regions: under the ribs Epigastric region: between hypochondriac regions Right and left lumbar regions: sides of trunk above hips Umbilical region: between lumbar regions, surrounds navel Right and left in ...
... 2. The location of the nine abdominopelvic regions are: Right and left hypochondriac regions: under the ribs Epigastric region: between hypochondriac regions Right and left lumbar regions: sides of trunk above hips Umbilical region: between lumbar regions, surrounds navel Right and left in ...
Sample
... 2. The location of the nine abdominopelvic regions are: Right and left hypochondriac regions: under the ribs Epigastric region: between hypochondriac regions Right and left lumbar regions: sides of trunk above hips Umbilical region: between lumbar regions, surrounds navel Right and left in ...
... 2. The location of the nine abdominopelvic regions are: Right and left hypochondriac regions: under the ribs Epigastric region: between hypochondriac regions Right and left lumbar regions: sides of trunk above hips Umbilical region: between lumbar regions, surrounds navel Right and left in ...
anatomical terminology, directional terms, planes, sections, and
... Body positions are the manner in which the human body is positioned in relation to the surrounding area. Label these positions in Figure C based on the descriptions below. Dorsal recumbent- also known as supine; lying on the back Ventral recumbent- also known as prone; lying face down Right lateral ...
... Body positions are the manner in which the human body is positioned in relation to the surrounding area. Label these positions in Figure C based on the descriptions below. Dorsal recumbent- also known as supine; lying on the back Ventral recumbent- also known as prone; lying face down Right lateral ...
1-Week 1-121
... reinforce and expand your knowledge, and develop personally and professionally. We hope that this experience drives you to learn more and experience more of what Anatomy has to offer. We wish you the most exciting, stimulating, rewarding, and transforming experience over the upcoming period of time. ...
... reinforce and expand your knowledge, and develop personally and professionally. We hope that this experience drives you to learn more and experience more of what Anatomy has to offer. We wish you the most exciting, stimulating, rewarding, and transforming experience over the upcoming period of time. ...
Anatomical Planes
... that a structure situated nearer to the median plane of the body. Lateral; is a term that is used to indicate that a structure situated farther away from the median plane. Superficial; is a term that is used to indicate that a structure situated nearer to the surface of the body. ...
... that a structure situated nearer to the median plane of the body. Lateral; is a term that is used to indicate that a structure situated farther away from the median plane. Superficial; is a term that is used to indicate that a structure situated nearer to the surface of the body. ...
File
... A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the location at which bones connect. They are constructed to allow movement (except for skull, sacral, sternal, and pelvic bones) and provide mechanical support, and are classified structurally and functionally. There are 3 different types of joints. ...
... A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the location at which bones connect. They are constructed to allow movement (except for skull, sacral, sternal, and pelvic bones) and provide mechanical support, and are classified structurally and functionally. There are 3 different types of joints. ...
Anatomy introduction11
... • 4. Simple cuboidal—one layer of cube-shaped cells. Sites: thyroid gland (to secrete thyroid hormones); salivary glands (to secrete saliva); kidney tubules (to reabsorb useful materials back to the blood). • 5. Simple columnar—one layer of column-shaped cells. Sites: stomach lining (to secrete gast ...
... • 4. Simple cuboidal—one layer of cube-shaped cells. Sites: thyroid gland (to secrete thyroid hormones); salivary glands (to secrete saliva); kidney tubules (to reabsorb useful materials back to the blood). • 5. Simple columnar—one layer of column-shaped cells. Sites: stomach lining (to secrete gast ...
Body Cavities
... Homeostasis: all body systems working together to maintain a stable internal environment Systems respond to external and internal changes to function within a normal range (body temperature, fluid balance) Mechanisms of Regulation ...
... Homeostasis: all body systems working together to maintain a stable internal environment Systems respond to external and internal changes to function within a normal range (body temperature, fluid balance) Mechanisms of Regulation ...
Superior
... toward or closest the point of attachment or trunk “close proximity” Distal away from the point of attachment or trunk “distance” ...
... toward or closest the point of attachment or trunk “close proximity” Distal away from the point of attachment or trunk “distance” ...
Anatomical positions, Anatomical Planes, Terms of position
... Medial indicates a structure nearer to the median plane of the body. For example, 5th digit of the hand (little finger) is medial to other digits. Lateral stipulates a structure is away Rostral used instead of anterior when describing parts of the brain, means towards the rostrum. In humans, it deno ...
... Medial indicates a structure nearer to the median plane of the body. For example, 5th digit of the hand (little finger) is medial to other digits. Lateral stipulates a structure is away Rostral used instead of anterior when describing parts of the brain, means towards the rostrum. In humans, it deno ...
Q2 Outline the principal anatomical features of the
... Q2 Outline the principal anatomical features of the diaphragm that are important to its function. (March 2011) ...
... Q2 Outline the principal anatomical features of the diaphragm that are important to its function. (March 2011) ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.