Introduction to A and P Outline
... • Two methods to map abdominal and pelvic regions • Four abdominopelvic quadrants • Nine abdominopelvic regions A few anatomical directions: • Anterior (= ventral) • Lateral • Posterior (= dorsal) • Medial • Superior • Proximal • Inferior • Distal Sectional Anatomy: Planes and Sections • Frontal sec ...
... • Two methods to map abdominal and pelvic regions • Four abdominopelvic quadrants • Nine abdominopelvic regions A few anatomical directions: • Anterior (= ventral) • Lateral • Posterior (= dorsal) • Medial • Superior • Proximal • Inferior • Distal Sectional Anatomy: Planes and Sections • Frontal sec ...
MASA_PowerPoint_Basic_Anatomy_of_Musculoskeletal_System
... on the medial or proximal aspect. INSERTION: the attachment of the muscle at the most movable bone site, often on the distal or lateral aspect. ACTION: what movement(s) the muscle performs, eg flexion, extension, rotation. INNERVATION: the nerve supply for that muscle ...
... on the medial or proximal aspect. INSERTION: the attachment of the muscle at the most movable bone site, often on the distal or lateral aspect. ACTION: what movement(s) the muscle performs, eg flexion, extension, rotation. INNERVATION: the nerve supply for that muscle ...
Major Concepts of Anatomy and Physiology
... Median Plane: Passes exactly through midline (middle) of the body; divides the body into equal halves. Parasagittal Plane: Any sagittal plane that passes through the body to the left or right of the midline; divides the body into unequal left & right portions. ...
... Median Plane: Passes exactly through midline (middle) of the body; divides the body into equal halves. Parasagittal Plane: Any sagittal plane that passes through the body to the left or right of the midline; divides the body into unequal left & right portions. ...
Kaan Yücel MD, Ph.D. 24. September 2013 Tuesday
... Diaphragm divides body cavity into thoracic & abdominopelvic cavities. Mediastinum contains all structures of the thoracic cavity except the lungs. ...
... Diaphragm divides body cavity into thoracic & abdominopelvic cavities. Mediastinum contains all structures of the thoracic cavity except the lungs. ...
upper limb - yeditepe anatomy fhs 121
... Diaphragm divides body cavity into thoracic & abdominopelvic cavities. Mediastinum contains all structures of the thoracic cavity except the lungs. ...
... Diaphragm divides body cavity into thoracic & abdominopelvic cavities. Mediastinum contains all structures of the thoracic cavity except the lungs. ...
upper limb - yeditepe anatomy fhs 121
... Diaphragm divides body cavity into thoracic & abdominopelvic cavities. Mediastinum contains all structures of the thoracic cavity except the lungs. ...
... Diaphragm divides body cavity into thoracic & abdominopelvic cavities. Mediastinum contains all structures of the thoracic cavity except the lungs. ...
Anatomical Language - Mrs. Reid's Webpage
... body or organ into right and left sides. Midsagittal plane – equal right and left halves Parasagittal plane – unequal right and left halves ...
... body or organ into right and left sides. Midsagittal plane – equal right and left halves Parasagittal plane – unequal right and left halves ...
anatomical terminology, directional terms, planes - TCHS
... Right hypochondriac region: positioned immediately to the right lateral area of the epigastric region Left hypochondriac region: positioned immediately to the left lateral area of the epigastric region Hypogastric region: positioned immediately below the umbilical region Right iliac region: position ...
... Right hypochondriac region: positioned immediately to the right lateral area of the epigastric region Left hypochondriac region: positioned immediately to the left lateral area of the epigastric region Hypogastric region: positioned immediately below the umbilical region Right iliac region: position ...
File
... Posterior- back, means that which follows, dorsal means back, posterior is the dorsal surface or back which follows as we are walking Proximal- nearest Distal- distant These terms are used to describe linear structures such as limbs in which one end is nearer another structure and the other end is f ...
... Posterior- back, means that which follows, dorsal means back, posterior is the dorsal surface or back which follows as we are walking Proximal- nearest Distal- distant These terms are used to describe linear structures such as limbs in which one end is nearer another structure and the other end is f ...
Medial and Lateral Rotation
... humerus. When the knee flexes, the ankle moves closer to the buttock, and the angle between the femur and tibia gets smaller. Extension refers to a movement that increases the angle between two body parts. Extension at the elbow is increasing the angle between the ulna and the humerus. Extension of ...
... humerus. When the knee flexes, the ankle moves closer to the buttock, and the angle between the femur and tibia gets smaller. Extension refers to a movement that increases the angle between two body parts. Extension at the elbow is increasing the angle between the ulna and the humerus. Extension of ...
Antomical Selfie/Directional Project
... 3) Be able to label, define, or determine through a scenario (ex: The sternum is ___________to the heart) Assignment 1) Take photos in the anterior/posterior anatomical position and a side view. 2) Create a page in Collaboration space. Call it: HR_yourlastnames 3) Use your resources to label the ter ...
... 3) Be able to label, define, or determine through a scenario (ex: The sternum is ___________to the heart) Assignment 1) Take photos in the anterior/posterior anatomical position and a side view. 2) Create a page in Collaboration space. Call it: HR_yourlastnames 3) Use your resources to label the ter ...
Learning Modules - Medical Gross Anatomy Anatomical
... Learning Modules - Medical Gross Anatomy Anatomical Orientation - Page 7 of 9 Proximal - Distal In referring to structures within the limbs specifically, the term proximal means toward the limb's attachment to the trunk, while distal means away from its attachment. Example: The knee is proximal to ...
... Learning Modules - Medical Gross Anatomy Anatomical Orientation - Page 7 of 9 Proximal - Distal In referring to structures within the limbs specifically, the term proximal means toward the limb's attachment to the trunk, while distal means away from its attachment. Example: The knee is proximal to ...
Personal Fitness Quiz 5 Study Guide
... * IF YOU FILL OUT THE STUDY GUIDE YOU CAN USE IT ON THE TEST!!!* Anatomy of the Thoracic Region - Where is this on the body? - What does the thoracic cage protect? Bones of the Thoracic Region - Also called the ___________________ - Ribs: - What are the three types of ribs and what number are they? ...
... * IF YOU FILL OUT THE STUDY GUIDE YOU CAN USE IT ON THE TEST!!!* Anatomy of the Thoracic Region - Where is this on the body? - What does the thoracic cage protect? Bones of the Thoracic Region - Also called the ___________________ - Ribs: - What are the three types of ribs and what number are they? ...
Anatomical Planes
... Understanding these will help learning terms related to position of structures relative to each other and movement of various parts of the body. ...
... Understanding these will help learning terms related to position of structures relative to each other and movement of various parts of the body. ...
Anatomy Notes section 1.7 - Johnson 1st Anatomy and Physiology
... planes. 1. Sagittal: lengthwise plane, divides body into right and left portions. (midsagittal-If a sagittal plane passes along the midline and divides the body into equal parts.) (Parasagittal a sagittal section lateral to the midline.) 2. Transverse: horizontal- divides body into superior and infe ...
... planes. 1. Sagittal: lengthwise plane, divides body into right and left portions. (midsagittal-If a sagittal plane passes along the midline and divides the body into equal parts.) (Parasagittal a sagittal section lateral to the midline.) 2. Transverse: horizontal- divides body into superior and infe ...
Gross Anatomy: Muscles of the Trunk
... muscles; most superficial of abs; flexes vertebral column, compressed abdomen during defecation & childbirth • External Obliques – paired muscles on lateral wall of abdomen; flex & rotate vertebral column • Internal Obliques – deep to external; flex & rotate vertebral column • Transversus Abdominis ...
... muscles; most superficial of abs; flexes vertebral column, compressed abdomen during defecation & childbirth • External Obliques – paired muscles on lateral wall of abdomen; flex & rotate vertebral column • Internal Obliques – deep to external; flex & rotate vertebral column • Transversus Abdominis ...
Anatomical Position and Directional Terms
... arms are at the sides of the body with palms turned forward. ...
... arms are at the sides of the body with palms turned forward. ...
Terminology
... The next pair is similar to anterior and posterior. Ventral and dorsal can be used interchangeably with anterior and posterior when talking about structures that are not part of the head. Ventral means “front” and can be used interchangeably with the term anterior when referring to structures of the ...
... The next pair is similar to anterior and posterior. Ventral and dorsal can be used interchangeably with anterior and posterior when talking about structures that are not part of the head. Ventral means “front” and can be used interchangeably with the term anterior when referring to structures of the ...
Atlas A General Orientation to Human Anatomy
... anterior in a four-legged animal is the head end posterior surface of human is back side posterior in a four-legged animal is the tail end ...
... anterior in a four-legged animal is the head end posterior surface of human is back side posterior in a four-legged animal is the tail end ...
Anatomical Directions and Major Body Regions
... Bilateral Symmetry • In the anatomical position, the body is in an erect, or standing, posture with the arms at the sides and palms forward. The head and feet are also pointing forward. • Bilateral Symmetry – the left and right sides are mirror images of each other, and only one plane can divide the ...
... Bilateral Symmetry • In the anatomical position, the body is in an erect, or standing, posture with the arms at the sides and palms forward. The head and feet are also pointing forward. • Bilateral Symmetry – the left and right sides are mirror images of each other, and only one plane can divide the ...
Basic anatomy
... Direction is used, when the body is in the anatomical position to explain the location of a structure relative to the structures surrounding it. Anterior (or ventral): Towards the front of the body (in front of) e.g. The sternum lies anterior to the heart. Posterior (or dorsal): Towards the back ...
... Direction is used, when the body is in the anatomical position to explain the location of a structure relative to the structures surrounding it. Anterior (or ventral): Towards the front of the body (in front of) e.g. The sternum lies anterior to the heart. Posterior (or dorsal): Towards the back ...
Anatomical Terms Worksheet
... Fill in the blank with the appropriate anatomical direction. a. The liver is ___________ to the diaphragm. b. Fingers are located_____________ to the wrist bones. c. The skin on the dorsal surface of your body is located on your____ surface. d. The great (big) toe is _____ to the little toe. e. The ...
... Fill in the blank with the appropriate anatomical direction. a. The liver is ___________ to the diaphragm. b. Fingers are located_____________ to the wrist bones. c. The skin on the dorsal surface of your body is located on your____ surface. d. The great (big) toe is _____ to the little toe. e. The ...
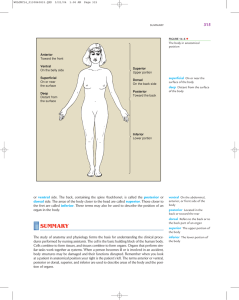
Anterior Toward the front Ventral On the belly side Superficial On or
... The study of anatomy and physiology forms the basis for understanding the clinical procedures performed by nursing assistants. The cell is the basic building block of the human body. Cells combine to form tissues, and tissues combine to form organs. Organs that perform similar tasks work together as ...
... The study of anatomy and physiology forms the basis for understanding the clinical procedures performed by nursing assistants. The cell is the basic building block of the human body. Cells combine to form tissues, and tissues combine to form organs. Organs that perform similar tasks work together as ...
Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology
... What factors probably stimulated an early interest in anatomy and physiology? What kinds of activities helped promote the development of modern medicine? Why is it difficult to separate the topics of anatomy and physiology? List several examples that illustrate how the structure of a body part makes ...
... What factors probably stimulated an early interest in anatomy and physiology? What kinds of activities helped promote the development of modern medicine? Why is it difficult to separate the topics of anatomy and physiology? List several examples that illustrate how the structure of a body part makes ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.