* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to the Human body/Chapter I
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
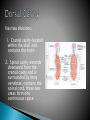
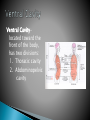
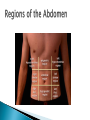
Joe Pistack MS/ED Anatomy-the branch of science that studies the structure of the body. Ex. Describes what the heart looks like. Physiology-the branch of science that describes how the body works or functions. Ex. How the heart pumps. Pathophysiology-the branch of science that describes the consequences of the improper functioning of body parts. Body is organized from simple to complex. Tiny atoms form molecules. Larger molecules organize into cells. Groups of cells form tissues. Tissues are arranged into organs. The human body is made up of eleven major organ systems: (1) Integumentary system-consists of skin and related structures such as hair and nails. (2) Skeletal system-forms the basic framework of the body. (3) Muscular system-responsible for movement of the skeleton and maintenance of body posture. (4) Nervous system-consists of the brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sense organs. (5) Endocrine system-consists of numerous glands that secrete hormones and chemical substances that regulate body activities. (6) Circulatory system-consists of the heart and blood vessels. (7)Lymphatic system-consists of lymph nodes, lymphatic vessels ,lymph and lymphoid organs. (8)Respiratory system-consists of the lungs and other structures that conduct air to and from the lungs. (9) Digestive system-consists of organs designed to eat food, break it down into substances that can be absorbed by the body and eliminate the waste. (10) Urinary system-consists of the kidneys and other structures that help execrete waste products from the body through the urine. (11) Reproductive system-consists of organs and structures that enable humans to reproduce. Homeostasis-the body’s ability to maintain a stable internal environment in response to a changing external environment. Ex. Body temp. remains the same even when the external temperature reaches highs or lows. Anatomical position-the body is standing erect, with face forward, the arms at the sides, and the toes and palms of the hands directed forward. Specific terms describe the position of one body part in relation to another body part. Terms are in pairs. Two terms in each pair are generally opposite. Superior-the part is above another part or closer to the head. Ex. The head is superior to the chest. Inferior-the part is located below another part or is closer to the feet. Ex. The chest is inferior to the head. Anterior-toward the front surface. (the belly surface) Another word for anterior is ventral. Ex. The heart is anterior to the spine. Posterior-toward the back surface. Another word for posterior is dorsal. Ex. The heart is posterior to the breastbone. Medial-toward the midline. Ex. The nose is medial to the ears. Lateral-away from the midline of the body. Ex. The ears are lateral to the nose. Proximal-structure is nearer the point of attachment, usually the trunk of the body. Ex. Elbow is proximal to the wrist. Distal-part is farther away from the point of attachment than is another part. Ex. Wrist is distal to the elbow. Superficial-part is located on or near the surface of the body. Ex. Skin is superficial to the muscles. Deep-the body part is away from the surface of the body. Ex. The bones are deep to the skin. Central-part located in the center. Ex. The heart is located centrally. Peripheral-away from the center. Ex. Blood vessels are located peripherally. Planes divide the body with an imaginary line, three important planes: 1. Sagittal planedivides the body lengthwise into equal right and left portions. 2. Frontal planedivides the body into anterior (ventral) and posterior (dorsal) portions. Also called the coronal plane because an imaginary line is made where a crown sits on the head. 3. Transverse planedivides the body horizontally, creating an upper (superior) and a lower (inferior) body. Abdominal-anterior trunk just below the ribs. Antecubital-area in front of the elbow. Axillary-armpit. Brachial-arm. Buccal-cheek area, specifically between the gum and cheek. Cephalic-head. Cervical-neck region. Cranial-nearer to the head. Digital-fingers, toes. Femoral-thigh area. Flank-fleshy area along each side between the lower ribs and the top of the hip bones. Inguinal-area where the hips meet the trunk Oral-mouth. Orbital-area around the eye. Patellar-front of the knee. Pedal-foot of the body. Pubic-genital area. Umbilical-navel. Caudal-nearer to the lower region of the spinal Deltoid-rounded area of the shoulder closest to Gluteal-buttocks. column (near your tailbone). the upper arm. Lumbar-area of back between the hips and Occipital-back of the head. Popliteal-behind, or back of, the knee area. Scapular-shoulder blade area. the ribs. Cavity-large ,internal space. Viscera-the organs located within the cavities of the body. Two major cavities: dorsal and ventral. Dorsal cavity-located toward the back of the body. Dorsal cavity has two divisions: cranial cavity and the spinal cavity. Has two divisions: 1. Cranial cavity-located within the skull and contains the brain. 2. Spinal cavity-extends downward from the cranial cavity and is surrounded by bony vertebrae, contains the spinal cord, these two areas form one continuous space. Ventral Cavitylocated toward the front of the body, has two divisions: 1. Thoracic cavity 2. Abdominopelvic cavity Thoracic cavity-located above the diaphragm and is surrounded by the rib cage. Divided into two compartments: 1. Mediastinum-space that contains the heart, esophagus, trachea, thymus gland, and large blood vessels attached to the heart. 2. Pleural cavity-contains the right and left lungs. Abdominopelvic cavity-located below the diaphragm. Upper portion is the abdominal cavity. Contains the stomach, most of the intestine, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen and kidneys. Pelvic cavity-lower portion of the abdominopelvic cavity. Extends downward from the level of the hips and includes the remainder of the intestines, rectum, urinary bladder, and internal parts of the reproductive system. Abdominopelvic cavity can be divided into four quadrants: (RUQ)-right upper quadrant. (RLQ)-right lower quadrant. (LUQ)-left upper quadrant. (LLQ)-left lower quadrant. Abdominopelvic cavity can be separated into nine regions: 1. Right hypochondriac region 2. Right lumbar region 3. Right iliac region 4. Epigastric region 5. Umbilical region 6. Hypogastric region 7. Left hypochondriac region 8. Left lumbar region 9. Left iliac region There are four smaller cavities ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Oral- mouth Nasal - nose Orbital - eyes Middle ear – area between the ear drum and the Eustachian tube