* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download (spinal) Cavity
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
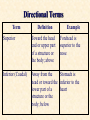
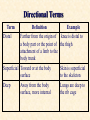
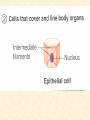
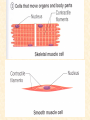
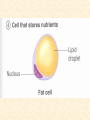
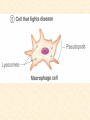
Body Cavities • 2 major cavities –Ventral cavities –Dorsal cavities • Other cavities: oral, nasal, orbital, middle ear, & synovial Dorsal Cavity • Posterior region of body • 2 regions –Cranial cavity (skull): supports and protects brain –Vertebral (spinal) Cavity: supports and protects spinal cord Ventral Cavities • Anterior region of trunk • Serosa: thin membrane that covers the wall of cavity and outer surface of its organs –Parietal serosa: lines cavity wall –Visceral serosa: covers organ Ventral Cavities cont. • 2 regions – 1)Thoracic cavity: subdivided • contains lungs, heart, trachea, esophagus, thymus, lymph nodes • Region between lungs = mediastinum Ventral Cavities cont. • 2 regions – 2)Abdominopelvic cavity: subdivided • A) Abdominal cavity: superior portion of abdominopelvic cavity • Stomach, intestine, spleen, liver • B) Pelvic cavity:inferior to abdominal cavity; bladder, reproductive organs, & rectum – Serosa is called peritoneum Other Cavities (Smaller Cavities) • Oral= teeth & tongue • Nasal = within nose; left and right side divided by nasal septum • Orbital = contains eyes & associated muscles and nerves • Middle ear = contains ossicles (ear bones) Planes of Section Transverse Section Coronal Section Sagittal Section Transverse Section (Plane) (Cross-Section) • Runs horizontally at right angle to the vertical axis • It divides the structure into superior and inferior regions Sagittal Section (Plane) • Runs longitudinally (lengthwise) and divides the body into left and right regions • Midsagittal (median section) = cut is made down the median plane of body and left and right parts are equal in size Coronal (Frontal) Section (Plane) • Runs longitudinally but at a right angle to sagittal plane • It divides the body into anterior and posterior regions Directional Terms Term Definition Example Superior Toward the head end or upper part of a structure or the body; above Forehead is superior to the nose Inferior (Caudal) Away from the Stomach is head or toward the inferior to the lower part of a heart structure or the body; below Directional Terms Term Definition Example Anterior (Ventral) Toward or at the front of the body; in front of Sternum is anterior to spine Posterior (dorsal) Heart is posterior to the sternum Toward or at the backside of the body; behind Directional Terms Term Definition Example Medial Toward or at the Heart is medial to midline of the the arm body; on the inner side Lateral Away from the Arms are lateral to midline of the the chest body; on the outer side Directional Terms Term Intermediate Proximal Definition Between a more medial and more lateral structure Example The armpit is intermediate between the sternum & shoulder Close to the origin Elbow is proximal of the body part or to the wrist the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk Directional Terms Term Distal Definition Farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk Superficial Toward or at the body surface Example knee is distal to the thigh Deep Lungs are deep to the rib cage Away from the body surface, more internal Skin is superficial to the skeleton Anatomy • Study of structure of the body & relationship of its parts – Subdivisions • Gross Anatomy: study of anatomic structures visible to unaided eye • Descriptive Anatomy: study of individual body parts in an ordered fashion. i.e. nervous system • Regional Anatomy: study of limited portions or region of the body. i.e. head & neck region Anatomy Subdivisions cont. • Applied Anatomy: application of anatomic findings to diagnosis & treatment of medical disorders • Comparative Anatomy: comparison of the structure of different animals and plants • Pathologic Anatomy: study of abnormal, diseased or injured tissue Anatomy Subdivisions cont. • Microanatomy: study of anatomic structures using a microscope – Cytology: study of cellular structure • Molecular biology: study of structures at subcellular level – Histology: microscopic study of tissues Anatomy subdivisions cont. • Developmental Anatomy: Study of structural changes from conception – 2 subdivisions: • Embryology: study of developmental changes before birth • Gerontology: study of structural changes that accompany aging Cell Diversity