Unit 5
... emperor of Rome in 27 BCE. 2. For the first 200 years of the Roman Empire, Rome went through a golden age. This period was known as the Pax Romana. 3. During the Pax Romana… a. Trade increased b. Laws were standardized c. All children were allowed to attend school until at least 12 years old d. Free ...
... emperor of Rome in 27 BCE. 2. For the first 200 years of the Roman Empire, Rome went through a golden age. This period was known as the Pax Romana. 3. During the Pax Romana… a. Trade increased b. Laws were standardized c. All children were allowed to attend school until at least 12 years old d. Free ...
8:1 The Roman Republic
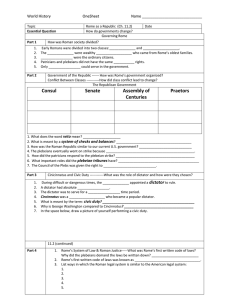
... What is the difference between a democracy and a republic? Democracy— Republic— Difference-Compare and Contrast (p.239) Patricians ...
... What is the difference between a democracy and a republic? Democracy— Republic— Difference-Compare and Contrast (p.239) Patricians ...
Ancient Rome Study Guide
... _____ 27. Famous leader of the Huns _____ 28. This Carthaginian general who fought Rome in the Punic Wars; his goal was to destroy Rome _____ 29. Emperor who was a philosopher and orator; wanted to give more power to the Senate _____ 30. The first emperor of Rome; the Senate gave him a title that me ...
... _____ 27. Famous leader of the Huns _____ 28. This Carthaginian general who fought Rome in the Punic Wars; his goal was to destroy Rome _____ 29. Emperor who was a philosopher and orator; wanted to give more power to the Senate _____ 30. The first emperor of Rome; the Senate gave him a title that me ...
The Roman Republic and Empire
... Fearing his increasing power, the Senate orders him to return to Rome and disband his army. Instead, he destroys roman forces and marches towards the capitol. He then forced senate to declare him as dictator. He kept senate and other features of the republic but held ultimate power. Between 48- 44 B ...
... Fearing his increasing power, the Senate orders him to return to Rome and disband his army. Instead, he destroys roman forces and marches towards the capitol. He then forced senate to declare him as dictator. He kept senate and other features of the republic but held ultimate power. Between 48- 44 B ...
Class Notes Chapter 7, Lesson 2 The Roman Republic
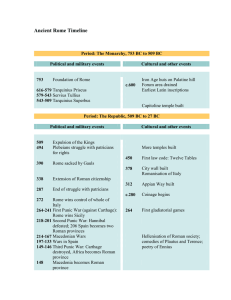
... survive to build the city of Rome (named after Romulus, its first king. This legend provides Rome with a noble, strong beginning. (2) The Birth of a Republic Between 600 and 509 B.C., Rome was ruled by seven different kings. In 509 B.C., however, the people established a republic (government where t ...
... survive to build the city of Rome (named after Romulus, its first king. This legend provides Rome with a noble, strong beginning. (2) The Birth of a Republic Between 600 and 509 B.C., Rome was ruled by seven different kings. In 509 B.C., however, the people established a republic (government where t ...
6.13.2 page 514 Vocabulary Pictures - buaron
... Caligula: Roman emperor who demanded that his statue be placed in the Jewish Temple in Jerusalem Augustus: Julius Caesar’s grandnephew and adopted son Octavian, later known as Augustus; by defeating Mark Antony, he gained rule of all Roman lands; he was Rome’s first true emperor Antonius Pius: Emper ...
... Caligula: Roman emperor who demanded that his statue be placed in the Jewish Temple in Jerusalem Augustus: Julius Caesar’s grandnephew and adopted son Octavian, later known as Augustus; by defeating Mark Antony, he gained rule of all Roman lands; he was Rome’s first true emperor Antonius Pius: Emper ...
The Geography of Rome - Warren County Schools
... islands [green]: Corsica, Sardinia, Sicily cities [red]: Rome, Ostia, Syracuse, Carthage, Pompeii, Brindisium, Tarentum peoples [purple]: Latins, Gauls, Etruscans, Greeks other [black]: Magna Graecia 2. What natural/geographic advantages did the city of Rome have? ...
... islands [green]: Corsica, Sardinia, Sicily cities [red]: Rome, Ostia, Syracuse, Carthage, Pompeii, Brindisium, Tarentum peoples [purple]: Latins, Gauls, Etruscans, Greeks other [black]: Magna Graecia 2. What natural/geographic advantages did the city of Rome have? ...
Topic
... Cinicinnatus and Civic Duty ------------What was the role of dictator and how were they chosen? During difficult or dangerous times, the ______________ appointed a dictator to rule. A dictator had absolute _________________. The dictator was to serve for a _________________ time period. Cincinnatus ...
... Cinicinnatus and Civic Duty ------------What was the role of dictator and how were they chosen? During difficult or dangerous times, the ______________ appointed a dictator to rule. A dictator had absolute _________________. The dictator was to serve for a _________________ time period. Cincinnatus ...
The Early Empire
... He is best remembered for having “fiddled while Rome burned.” He was playing music miles from home when a fire destroyed much of the city. ...
... He is best remembered for having “fiddled while Rome burned.” He was playing music miles from home when a fire destroyed much of the city. ...
Romans - Humanities 191
... Legislative and judicial powers – to an assembly. Senate – Plebians – none until 287 BC Julius Caesar – emperor – 60-44 BC. Acted in the name of the equestrian social class (who gained wealth during the Punic wars but lacked the political powers of the patricians.) Founded Rome’s 1st public library ...
... Legislative and judicial powers – to an assembly. Senate – Plebians – none until 287 BC Julius Caesar – emperor – 60-44 BC. Acted in the name of the equestrian social class (who gained wealth during the Punic wars but lacked the political powers of the patricians.) Founded Rome’s 1st public library ...