7th Ancient Rome
... • As the number of slaves increased, many poor farmers were put out of work – Efforts to help the poor were blocked by wealthy Senators who owned most of the slaves – In 73BCE a gladiator named Spartacus led a rebellion of 100,000 slaves that nearly destroyed the city – Eventually, Spartacus and his ...
... • As the number of slaves increased, many poor farmers were put out of work – Efforts to help the poor were blocked by wealthy Senators who owned most of the slaves – In 73BCE a gladiator named Spartacus led a rebellion of 100,000 slaves that nearly destroyed the city – Eventually, Spartacus and his ...
The Roman Empire
... buildings) help spread their influence to the world • Many cities around the world were founded at this time that still exist (all because of Rome) • Latin is the basis for many current languages – Ex: Italian, French, Spanish, Portuguese, & Romanian ...
... buildings) help spread their influence to the world • Many cities around the world were founded at this time that still exist (all because of Rome) • Latin is the basis for many current languages – Ex: Italian, French, Spanish, Portuguese, & Romanian ...
Roman Art.pptx - Wando High School
... She-Wolf, and later established the city of Rome on its fabled seven hills. ¤ At first the state was ruled by kings, who were later overthrown and replaced by a Senate and two elected consul. ¤ The Romans then established a democracy of a sort, with magistrates ruling the country in conjunction ...
... She-Wolf, and later established the city of Rome on its fabled seven hills. ¤ At first the state was ruled by kings, who were later overthrown and replaced by a Senate and two elected consul. ¤ The Romans then established a democracy of a sort, with magistrates ruling the country in conjunction ...
The Roman Republic
... tried to improve conditions in Rome. Tiberius Gracchus became a tribune in 133 B.C. and was the first reformer. He wanted to limit the amount of land a person could own. He was killed in a riot staged by the Senate when he ran for a second term as tribune. In 123 B.C., Tiberius Gracchus’s younger br ...
... tried to improve conditions in Rome. Tiberius Gracchus became a tribune in 133 B.C. and was the first reformer. He wanted to limit the amount of land a person could own. He was killed in a riot staged by the Senate when he ran for a second term as tribune. In 123 B.C., Tiberius Gracchus’s younger br ...
Western Civilization
... Italy s Geography help its development? How did Italy’s Geography hurt its development? ...
... Italy s Geography help its development? How did Italy’s Geography hurt its development? ...
Mediterranean Sea Italian Peninsula Rome
... Directions: Label the following items on the map below!!! Bodies of Water: Mediterranean Sea Adriatic Sea Tiber River ...
... Directions: Label the following items on the map below!!! Bodies of Water: Mediterranean Sea Adriatic Sea Tiber River ...
Name: Block:______ The Founding of Rome The founding of Rome
... Like many other ancient civilizations, the agricultural system of ancient Rome was supported by the presence of a major river. The Tiber provided a reliable source of fresh water which the Romans used for irrigating their farms, as well as drinking water for humans and animals. However, unlike many ...
... Like many other ancient civilizations, the agricultural system of ancient Rome was supported by the presence of a major river. The Tiber provided a reliable source of fresh water which the Romans used for irrigating their farms, as well as drinking water for humans and animals. However, unlike many ...
The Roman Empire
... – Agriculture is the most important industry in the empire; 90% of Romans farm. – Common coin, denarius, makes trade within ...
... – Agriculture is the most important industry in the empire; 90% of Romans farm. – Common coin, denarius, makes trade within ...
The Roman Empire - Harrison High School
... – Agriculture is the most important industry in the empire; 90% of Romans farm. – Common coin, denarius, makes trade within ...
... – Agriculture is the most important industry in the empire; 90% of Romans farm. – Common coin, denarius, makes trade within ...
Rome - Mater Academy Lakes High School
... A republic is a form of government in which citizens elect their leaders, like a representative democracy By 267 BC, Rome controlled all of Italy The Roman republic stressed the need to treat all conquered people fairly Every citizen of Rome had to swear loyalty to Rome, had to serve in the army and ...
... A republic is a form of government in which citizens elect their leaders, like a representative democracy By 267 BC, Rome controlled all of Italy The Roman republic stressed the need to treat all conquered people fairly Every citizen of Rome had to swear loyalty to Rome, had to serve in the army and ...
Chapter 11-1: From Republic to Empire
... Why did Octavian turn against Marc Antony? What happened to Marc Antony and his 2nd wife? What does the name “Augustus” signify? Under Emperor Claudius, how did the Roman empire grow? What kind of goods did traders bring to Rome from other places? What goods did the Romans send in Return? The first ...
... Why did Octavian turn against Marc Antony? What happened to Marc Antony and his 2nd wife? What does the name “Augustus” signify? Under Emperor Claudius, how did the Roman empire grow? What kind of goods did traders bring to Rome from other places? What goods did the Romans send in Return? The first ...
The Roman Empire
... If they couldn’t talk a neighbor into joining them, they would send in their armies. ...
... If they couldn’t talk a neighbor into joining them, they would send in their armies. ...
Chapter 7 – The Roman World (1000 BC – AD 476)
... Greeks also settled in southern Italy and Sicily ...
... Greeks also settled in southern Italy and Sicily ...
Roman Republic 509 – 270 BC
... The Punic Wars The fiercest of the wars Rome fought were the Punic (PYOO-nik) Wars, a series of wars against Carthage, a city in northern Africa. The word Punic means “Phoenician” in Latin. As you learned earlier in this book, the Phoenicians were an ancient civilization that had built the city of ...
... The Punic Wars The fiercest of the wars Rome fought were the Punic (PYOO-nik) Wars, a series of wars against Carthage, a city in northern Africa. The word Punic means “Phoenician” in Latin. As you learned earlier in this book, the Phoenicians were an ancient civilization that had built the city of ...
paedogogus
... At nightfall, the Achaeans, who had taken refuge in Corinth after the battle, escaped from the city; most of the Corinthians escaped with them as well. Mummius at first held back from entering Corinth, though the gates were open, suspecting that an ambush had been set inside the walls; however, on t ...
... At nightfall, the Achaeans, who had taken refuge in Corinth after the battle, escaped from the city; most of the Corinthians escaped with them as well. Mummius at first held back from entering Corinth, though the gates were open, suspecting that an ambush had been set inside the walls; however, on t ...
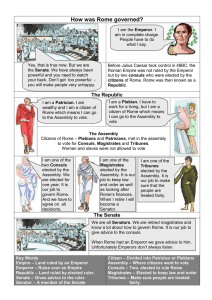
How was Rome governed?
... Citizens of Rome – Plebians and Patricians, met in the assembly to vote for Consuls, Magistrates and Tribunes. Women and slaves were not allowed to vote I am one of the two Consuls elected by the Assembly. We are elected for one year. It is our job to govern Rome. And we have to ...
... Citizens of Rome – Plebians and Patricians, met in the assembly to vote for Consuls, Magistrates and Tribunes. Women and slaves were not allowed to vote I am one of the two Consuls elected by the Assembly. We are elected for one year. It is our job to govern Rome. And we have to ...
Chp.34.Review
... 34.5 Expansion During the Final Years of the Republic: From ____________ to ___________ B.C.E. Civil War Pompey vs. Caesar ...
... 34.5 Expansion During the Final Years of the Republic: From ____________ to ___________ B.C.E. Civil War Pompey vs. Caesar ...
Reasons for Rome`s Downfall
... Christianity produced dramatic changes in Roman society at the very time were pressure from the barbarians was increasing. They argue that Christianity made its followers into pacifists (those who oppose war), thus making it more difficult to defend the Empire from attacks. Furthermore, the Church a ...
... Christianity produced dramatic changes in Roman society at the very time were pressure from the barbarians was increasing. They argue that Christianity made its followers into pacifists (those who oppose war), thus making it more difficult to defend the Empire from attacks. Furthermore, the Church a ...
In 300 A.D. the Roman Empire began to D.E.C.L.I.N.E.
... Christianity spreads rapidly through Mediterranean area because of missionaries. Romans become uneasy with Christianity gaining so much popularity. Roman leaders like Nero and Diocletian begin to blame Christians for any problems. Many Christians become martyrs. Martyr= person who suffers/dies ...
... Christianity spreads rapidly through Mediterranean area because of missionaries. Romans become uneasy with Christianity gaining so much popularity. Roman leaders like Nero and Diocletian begin to blame Christians for any problems. Many Christians become martyrs. Martyr= person who suffers/dies ...