* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Roman Art.pptx - Wando High School
Alpine regiments of the Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Roman architecture wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Roman temple wikipedia , lookup
Elections in the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Slovakia in the Roman era wikipedia , lookup
History of the Roman Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Romanization of Hispania wikipedia , lookup
Switzerland in the Roman era wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Roman funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
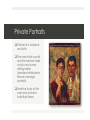
Roman Art 753 BCE – 5th Century CE “The Roman Empire existed by virtue of the grandest application of technology that the world had hitherto seen.” - Alfred North Whitehead, Philosopher Time Periods ¤ Founding of Rome by Romulus and Remus ¤ 753 BCE ¤ Roman Republic ¤ 509 BCE – 27 BCE ¤ Early and High Roman Empire ¤ 27 BCE – 192 CE ¤ Late Roman Empire ¤ 192 BCE – 410 CE Key Concepts ¤ Roman art reflects the ambitions of a powerful empire – monumental buildings and sculptures reflect the glory of the gods and the state. ¤ Roman architecture is revolutionary in its understanding of the powers of the arch, the vault, the dome, and concrete. ¤ A history of Roman painting survives on the walls of Pompeiian villas. ¤ Romans show an interest in the basic elements of perspective and foreshortening. ¤ Roman sculpture is greatly indebted to Greek sculpture. Background ¤ According to legend, Romulus and Remus, abandoned twins, were suckled by a She-Wolf, and later established the city of Rome on its fabled seven hills. ¤ At first the state was ruled by kings, who were later overthrown and replaced by a Senate and two elected consul. ¤ The Romans then established a democracy of a sort, with magistrates ruling the country in conjunction with the Senate, an elected body of privileged Roman men. ¤ Various well-executed wars increased Rome’s fortunes and boundaries. ¤ Greek colony of Syracuse in Sicily (211 BCE) and then Greece (146 BCE) were absorbed into Roman life. ¤ Civil war in the late Republic caused power to shift to rule by emperors (Augustus Caesar in 27 BCE, etc.) until it was sacked in 410 CE. Patronage ¤ Roman state and wealthiest individuals were the major patrons of the arts: spending lavishly for themselves and for the general good with public projects. ¤ Workshops were established to meet the demands for Greek works. ¤ Homes of wealthy Romans demonstrated power and privilege. ¤ Artists were considered low members of the social scale and were treated poorly. Innovations in Roman Architecture Barrel Vault: _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ Groin Vault: _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ Dome: _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ Republic Rome 509 BCE – 27 BCE Temple of Portunus ¤ Republican temple on the east bank of the Tiber River ¤ Combination of cultures: Etruscan and Greek. Veristic Sculpture ¤ Standard Republican superrealistic fashion. ¤ Stern frontal portraits of prominent Roman Republican figures. ¤ Subjects were almost exclusively men of advanced age. ¤ Features may have been exaggerated to suggest the Republican virtues. Pompeii and the Cities of Vesuvius Domestic/Residential Architecture q Atrium – q Compluvium – q Impluvium – q Cubicula - Restored view and plan of a typical Roman house (domus) of the Late Republic and Early Empire. (1) fauces, (2) atrium, (3) impluvium, (4) cubiculum, (5) ala, (6) tablinum, (7) triclinium, (8) peristyle. First Pompeian Style ¤ First Style (masonry style) was intended to imitate costly marble panels using painted/ modeled stucco relief. Villa of Mysteries Second Pompeian Style Boscoreale Frescoes Second Pompeian Style Third Pompeian Style ¤ Characterized by small scenes set in a field of color. ¤ Framed by delicately traced columns. Ixion Room (Fourth Style) q Fourth Style combines elements from the previous three: q Painted marble from First Style, q Large scenes of the Second Style, q Delicate small scenes of the Third Style. q Fragmentary architectural vistas (central and upper zones) are unmistakably Fourth Style. Private Portraits q Portrait of a husband and wife. q The man holds a scroll and the woman holds a stylus and a wax writing tablet (standard attributes in Roman marriage portraits). q Sensitive study of the man and woman’s individual faces. Still Life with Peaches q Frequent inclusion of still-life paintings in the mural schemes of the Second, Third, and Fourth Styles. q Attention to shadows and highlights. q Art historians have not found evidence of anything like these Roman studies of food and other inanimate objects until the Dutch still lifes from the 17th and 18th centuries.