nutrition - Volusia Academies
... Saturated vs. Unsaturated fats (next slide) Foods: meats, butter, margarine, oils, nuts, ...
... Saturated vs. Unsaturated fats (next slide) Foods: meats, butter, margarine, oils, nuts, ...
Organic Compounds Test ~Please DO NOT write on the test!~ 1
... A. a single unit of a macromolecule B. multiple units of a macromolecules that are bonded together C. same as a molecule D. the entire structure of a macromolecule 10. A major characteristic that all lipids have in common is A. They all contain phosphorus B. They all contain nitrogen C. None of them ...
... A. a single unit of a macromolecule B. multiple units of a macromolecules that are bonded together C. same as a molecule D. the entire structure of a macromolecule 10. A major characteristic that all lipids have in common is A. They all contain phosphorus B. They all contain nitrogen C. None of them ...
Fatty acid composition of some common oils and fats from plant
... Fatty acids: Common long-chain carboxylic acids are shown in table 3.1 Some key points about fatty acid structure & properties: 1) The number of C in the chain is always even Biosynthesis by the acetate pathway involves condensation of decarboxylated malonyl esters contributing 2C each 2) Saturated ...
... Fatty acids: Common long-chain carboxylic acids are shown in table 3.1 Some key points about fatty acid structure & properties: 1) The number of C in the chain is always even Biosynthesis by the acetate pathway involves condensation of decarboxylated malonyl esters contributing 2C each 2) Saturated ...
Cellular Respiration
... •Electrons captured when food is broken down •Held by electron carriers •NADH, FADH2 ...
... •Electrons captured when food is broken down •Held by electron carriers •NADH, FADH2 ...
UNIT 2 BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY ORGANIC MOLECULES
... -The Carboxyl end of a fatty acid is polar and therefore Hydrophilic. -The hydrocarbon chain end however is hydrophobic because it is non-polar. These characteristics make fatty acids an integral part of cell membranes. ...
... -The Carboxyl end of a fatty acid is polar and therefore Hydrophilic. -The hydrocarbon chain end however is hydrophobic because it is non-polar. These characteristics make fatty acids an integral part of cell membranes. ...
2007
... T / F hydrolysis of glycerolipids releases glycerol 3-phosphate and fatty acids T / F The rate limiting step in fatty acid oxidation is the activation of free fatty acids with ATP T / F fatty acids are transported into mitochondria as acyl carnitine T / F β-oxidation of odd numbered fatty acids yiel ...
... T / F hydrolysis of glycerolipids releases glycerol 3-phosphate and fatty acids T / F The rate limiting step in fatty acid oxidation is the activation of free fatty acids with ATP T / F fatty acids are transported into mitochondria as acyl carnitine T / F β-oxidation of odd numbered fatty acids yiel ...
Which macromolecule stores genetic information? A. proteins B
... Which macromolecule makes up the cell wall of plant cells? A. carbohydrates B. proteins C. lipids D. nucleic acids ...
... Which macromolecule makes up the cell wall of plant cells? A. carbohydrates B. proteins C. lipids D. nucleic acids ...
O Describe how tissues, organs, and organ systems are related. O
... The three kinds of muscle tissue are smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and skeletal muscle. Skeletal muscles work in pairs. Skeletal muscles contract to ...
... The three kinds of muscle tissue are smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and skeletal muscle. Skeletal muscles work in pairs. Skeletal muscles contract to ...
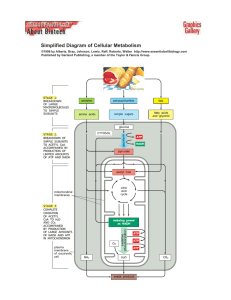
Simplified Diagram of Cellular Metabolism
... . http://www.essentialcellbiology.com Published by Garland Publishing, a member of the Taylor & Francis Group. ...
... . http://www.essentialcellbiology.com Published by Garland Publishing, a member of the Taylor & Francis Group. ...
Chapter 1 - Nutrition Gardener
... can dissipate stress hormones. This can be so helpful for the obese individual that learned to eat in response to stress. If an individual’s self-esteem has been lowered because of their overweight, exercise can generally help to improve self esteem and reduce stress. Many chronic diseases such as c ...
... can dissipate stress hormones. This can be so helpful for the obese individual that learned to eat in response to stress. If an individual’s self-esteem has been lowered because of their overweight, exercise can generally help to improve self esteem and reduce stress. Many chronic diseases such as c ...
Lecture 27
... intermediates or precursors to be metabolized to CO2, H2O, or for use in gluconeogenesis. Aminoacids are glucogenic, ketogenic or both. Glucogenic amino acids-carbon skeletons are broken down to pyruvate, -ketoglutarate, succinyl-CoA, fumarate, or oxaloacetate (glucose precursors). Ketogenic amino ...
... intermediates or precursors to be metabolized to CO2, H2O, or for use in gluconeogenesis. Aminoacids are glucogenic, ketogenic or both. Glucogenic amino acids-carbon skeletons are broken down to pyruvate, -ketoglutarate, succinyl-CoA, fumarate, or oxaloacetate (glucose precursors). Ketogenic amino ...
Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
... H2O can be added to cis-aconitate in two different ways. Isocitrate is normally formed due to the low concentration of isocitrate, rapidly converted to a-ketoglutarate. ...
... H2O can be added to cis-aconitate in two different ways. Isocitrate is normally formed due to the low concentration of isocitrate, rapidly converted to a-ketoglutarate. ...
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE DEPARTMENT OF BIOCHEMISTRY ADVANCED PLACEMENT TEST (SAMPLE)
... 1. Which of the following statements about the biophysical property of water is INCORRECT? A. Water molecule forms H-bonds B. Water retains heat well C. Water is dielectrict D. Water at freezing point has the highest density E. Water is polar 2. Which of the following is NOT a strong electrolyte and ...
... 1. Which of the following statements about the biophysical property of water is INCORRECT? A. Water molecule forms H-bonds B. Water retains heat well C. Water is dielectrict D. Water at freezing point has the highest density E. Water is polar 2. Which of the following is NOT a strong electrolyte and ...
CH 2 - Faperta UGM
... from which fatty acids are synthesis 2. It must be first converted to acetylCoA 3. Acetyl-CoA is produced in large quantities from pyruvate in mitochondria of photosynthetic tissue or from glucose via the glycolitic pathway in non-photosynthetic tissue 4. In addition to acetyl CoA, malonyl CoA is an ...
... from which fatty acids are synthesis 2. It must be first converted to acetylCoA 3. Acetyl-CoA is produced in large quantities from pyruvate in mitochondria of photosynthetic tissue or from glucose via the glycolitic pathway in non-photosynthetic tissue 4. In addition to acetyl CoA, malonyl CoA is an ...
The b-oxidation pathway as an energy source
... • Usually precipitated by infection • lipolysis is the major energy source increases acetyl CoA levels which increases ketone body formation.Acetone excreted by the lungs/kidney. e.g. by starvation or diabetes mellitus (insulin-stimulated glucose entry into cells is impaired fatty acids are oxidise ...
... • Usually precipitated by infection • lipolysis is the major energy source increases acetyl CoA levels which increases ketone body formation.Acetone excreted by the lungs/kidney. e.g. by starvation or diabetes mellitus (insulin-stimulated glucose entry into cells is impaired fatty acids are oxidise ...
Cellular_Respiration_overviewap
... Remember that for every glucose molecule, the Krebs happens twice, because two acetylCoA’s are produced from one glucose molecule and that ATP generation is via substrate level phosphorylation. Below is the general reaction per one glucose molecule: 2 acetylCoA + 2 oxaloacetate 2 oxaloacetate + 2A ...
... Remember that for every glucose molecule, the Krebs happens twice, because two acetylCoA’s are produced from one glucose molecule and that ATP generation is via substrate level phosphorylation. Below is the general reaction per one glucose molecule: 2 acetylCoA + 2 oxaloacetate 2 oxaloacetate + 2A ...
Muscle Tissue C1
... ATP is generated by breakdown of several nutrient energy fuels by aerobic pathway. This pathway uses oxygen released from myoglobin or delivered in the blood by hemoglobin. When it ...
... ATP is generated by breakdown of several nutrient energy fuels by aerobic pathway. This pathway uses oxygen released from myoglobin or delivered in the blood by hemoglobin. When it ...
division - IRIS - Lake Land College
... Write chemical equations for the reactions of hydrocarbons and their halogen derivatives. Name and write structural formulas for alcohols, ethers, thiols, and phenols. Write chemical equations for the reactions of alcohols, ethers, thiols and phenols. Name and write structural formulas for aldehydes ...
... Write chemical equations for the reactions of hydrocarbons and their halogen derivatives. Name and write structural formulas for alcohols, ethers, thiols, and phenols. Write chemical equations for the reactions of alcohols, ethers, thiols and phenols. Name and write structural formulas for aldehydes ...
H - Liberty Public Schools
... as potential chemical energy. • May also be used as monomers to build more complex polymers for energy storage or structural molecules. ...
... as potential chemical energy. • May also be used as monomers to build more complex polymers for energy storage or structural molecules. ...
Cellular Respiration (Chapter 8) Outline The Killers Are Coming
... 2. Examples of such bacteria include those that reduce sulfate to hydrogen sulfide ( a foul-smelling gas indeed) and those that convert nitrate to nitrite. ...
... 2. Examples of such bacteria include those that reduce sulfate to hydrogen sulfide ( a foul-smelling gas indeed) and those that convert nitrate to nitrite. ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.