Metabolic Pathways a..
... 2 ATP molecules and 2 NADH + 2 H+ Two ATP used in adding phosphate groups to glucose and fructose-6-phosphate (- 2 ATP) Four ATP generated in direct transfer to ADP by two 3C molecules (+ 4 ATP) Glucose + 2 ADP + 2 Pi + 2 NAD+ 2pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2 H+ ...
... 2 ATP molecules and 2 NADH + 2 H+ Two ATP used in adding phosphate groups to glucose and fructose-6-phosphate (- 2 ATP) Four ATP generated in direct transfer to ADP by two 3C molecules (+ 4 ATP) Glucose + 2 ADP + 2 Pi + 2 NAD+ 2pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2 H+ ...
Cellular Respiration (Chapter 8) Outline The Killers Are Coming
... 2. Examples of such bacteria include those that reduce sulfate to hydrogen sulfide ( a foul-smelling gas indeed) and those that convert nitrate to nitrite. ...
... 2. Examples of such bacteria include those that reduce sulfate to hydrogen sulfide ( a foul-smelling gas indeed) and those that convert nitrate to nitrite. ...
Chapter 5 – Macromolecules
... 2. A nucleic acid strand is a polymer of nucleotides •Nucleic acids are polymers of monomers called nucleotides. •Each nucleotide consists of three parts: a nitrogen base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. •The nitrogen bases, rings of C and nitrogen, come in two types: purines and pyrimidines ...
... 2. A nucleic acid strand is a polymer of nucleotides •Nucleic acids are polymers of monomers called nucleotides. •Each nucleotide consists of three parts: a nitrogen base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. •The nitrogen bases, rings of C and nitrogen, come in two types: purines and pyrimidines ...
Neonatal Glucose Homeostasis
... Fetus can use alternate substrates if necessary, but depends entirely on maternal supply and placental transfer of glucose, amino acids, free fatty acids, ketones, and glycerol for energy needs. Normal lower limit of fetal glucose concentration remains around 3 mmol/L (54 mg/dL) over most of gestati ...
... Fetus can use alternate substrates if necessary, but depends entirely on maternal supply and placental transfer of glucose, amino acids, free fatty acids, ketones, and glycerol for energy needs. Normal lower limit of fetal glucose concentration remains around 3 mmol/L (54 mg/dL) over most of gestati ...
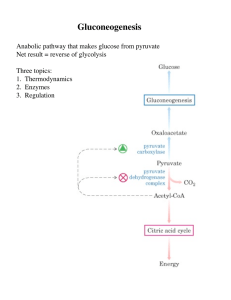
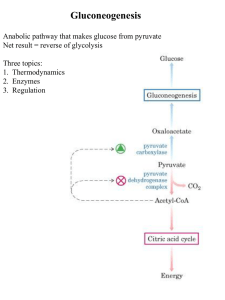
Gluconeogenesis - Creighton Chemistry Webserver
... When does gluconeogenesis occur? When dietary sources of glc are not available When liver has exhausted its glycogen stores (stored glc) What precursors does gluconeogenesis use? Lactate & pyruvate (glycolysis) TCA intermediates Carbon skeletons of AAs ...
... When does gluconeogenesis occur? When dietary sources of glc are not available When liver has exhausted its glycogen stores (stored glc) What precursors does gluconeogenesis use? Lactate & pyruvate (glycolysis) TCA intermediates Carbon skeletons of AAs ...
Recovery Nutrition
... glycogen synthesis, protein rebuilding proceeds much faster in the first 2 hours following intense exercise. It has been suggested that the optimal formula for post-exercise nutritional recovery be 4 grams of carbohydrate for every 1 gram of protein1. I agree with this formula, and have utilized it ...
... glycogen synthesis, protein rebuilding proceeds much faster in the first 2 hours following intense exercise. It has been suggested that the optimal formula for post-exercise nutritional recovery be 4 grams of carbohydrate for every 1 gram of protein1. I agree with this formula, and have utilized it ...
ATP - Mhanafi123`s Blog
... NAD+ is the target product. Lactate is the by product. Lactate is one of the substrate of gluconeogenesis, will be taken up by the liver and changed into glucose. ...
... NAD+ is the target product. Lactate is the by product. Lactate is one of the substrate of gluconeogenesis, will be taken up by the liver and changed into glucose. ...
No Slide Title
... PFK-2 and FBPase-2 are two distinct enzyme activities on 1 protein Balance of the 2 activities in the liver, which determines cellular level of F2,6BP, is regulated by glucagon Glucagon - released by pancreas to signal low blood sugar ...
... PFK-2 and FBPase-2 are two distinct enzyme activities on 1 protein Balance of the 2 activities in the liver, which determines cellular level of F2,6BP, is regulated by glucagon Glucagon - released by pancreas to signal low blood sugar ...
GLUCONEOGENESIS
... erythrocytes is a source of energy for other organs. • The only purpose of the reduction of pyruvate to lactate is to regenerate NAD+ so that glycolysis can proceed in active skeletal muscle and erythrocytes. • lactate is a dead end in metabolism. – It must be converted back into pyruvate before it ...
... erythrocytes is a source of energy for other organs. • The only purpose of the reduction of pyruvate to lactate is to regenerate NAD+ so that glycolysis can proceed in active skeletal muscle and erythrocytes. • lactate is a dead end in metabolism. – It must be converted back into pyruvate before it ...
Metabolism II
... How much ATP can be formed by oxidation of fatty acid? It is now possible to calculate the amount of ATP formed during complete oxidation of a fatty acid, e.g. palmitic acid 8 Acetyl-CoA in the tricarboxylic acid cycle: 8 x 3 = 24 NADH 8 x 1 = 8 FADH2 8 x 1 = 8 GTP -Oxidation yields: 7 NADH 7 FADH ...
... How much ATP can be formed by oxidation of fatty acid? It is now possible to calculate the amount of ATP formed during complete oxidation of a fatty acid, e.g. palmitic acid 8 Acetyl-CoA in the tricarboxylic acid cycle: 8 x 3 = 24 NADH 8 x 1 = 8 FADH2 8 x 1 = 8 GTP -Oxidation yields: 7 NADH 7 FADH ...
Cellular Respiration
... present After glycolysis, pyruvate is converted into ______________________ ...
... present After glycolysis, pyruvate is converted into ______________________ ...
Document
... carbon dioxide +6 water 36 or 38 ATPs are produced (total after all cycles: glycolysis, krebs and ETC) ...
... carbon dioxide +6 water 36 or 38 ATPs are produced (total after all cycles: glycolysis, krebs and ETC) ...
Metabolism of RBC
... • Role of NADPH in RBC’s is to reduce gluthathione to sulfhydryl form • Essential for maintaining structure of Hb (keeps Hb in ferrous state) ...
... • Role of NADPH in RBC’s is to reduce gluthathione to sulfhydryl form • Essential for maintaining structure of Hb (keeps Hb in ferrous state) ...
ncibi-rcmi-2010-workshop
... Obese individuals have elevated plasma levels of amino acids (and other nutrients) Hypothesis 1.The brain requires a certain amount of nutrients to feel ‘sated’. 2. Amino acids and/or lipids may provide part of the signal. 3. People eat until the nutrient level in the brain is adequate. 4. Overweig ...
... Obese individuals have elevated plasma levels of amino acids (and other nutrients) Hypothesis 1.The brain requires a certain amount of nutrients to feel ‘sated’. 2. Amino acids and/or lipids may provide part of the signal. 3. People eat until the nutrient level in the brain is adequate. 4. Overweig ...
Lecture notes Chapter 27-28
... Every time we contract muscles, move substances across cellular membranes, send nerve signals, or synthesize an enzyme, we use energy from ATP hydrolysis. In a cell that is doing work (anabolic processes), 1-2 million ATP molecules may be hydrolysized in one second. The amount of ATP hydrolyzed in o ...
... Every time we contract muscles, move substances across cellular membranes, send nerve signals, or synthesize an enzyme, we use energy from ATP hydrolysis. In a cell that is doing work (anabolic processes), 1-2 million ATP molecules may be hydrolysized in one second. The amount of ATP hydrolyzed in o ...
Biology 20 Lecture Quiz #3 – Take Home Cellular Respiration
... 6. What is the name of the process in which pyruvate is converted to lactate? a) chemiostic theory; b) fermentation; c) glycolysis; d) citric acid cycle 7. Enzymes such as succinic acid dehydrogenase (SDH) are important in the citric acid cycle. They can be found? a) cytosol; b) mitochondrial matrix ...
... 6. What is the name of the process in which pyruvate is converted to lactate? a) chemiostic theory; b) fermentation; c) glycolysis; d) citric acid cycle 7. Enzymes such as succinic acid dehydrogenase (SDH) are important in the citric acid cycle. They can be found? a) cytosol; b) mitochondrial matrix ...
Focus on Metabolism
... known as anabolism. Each of the essential nutrients plays a unique role in metabolism. ...
... known as anabolism. Each of the essential nutrients plays a unique role in metabolism. ...
Lecture Power Point
... •The citric acid cycle begins with acetyl CoA transferring its two-carbon acetyl group to the four-carbon acceptor compound (Oxaloacetate) to form a sixcarbon compound (citrate). •The citrate then goes through a series of chemical transformations, losing CO2 and gives Oxaloacetate. ...
... •The citric acid cycle begins with acetyl CoA transferring its two-carbon acetyl group to the four-carbon acceptor compound (Oxaloacetate) to form a sixcarbon compound (citrate). •The citrate then goes through a series of chemical transformations, losing CO2 and gives Oxaloacetate. ...
Asian Odyssey
... A reduction in fatty acid synthesis enzymes like acetyl coA carboxylase and the fatty acid synthase (FAS) complex No increase in fatty acid (beta) oxidation, that is “fat burning”, apparently occurs ...
... A reduction in fatty acid synthesis enzymes like acetyl coA carboxylase and the fatty acid synthase (FAS) complex No increase in fatty acid (beta) oxidation, that is “fat burning”, apparently occurs ...
hanan abas
... By drawing upon the glycogen stores of the liver ,and Aslight amount may also be derived from the kidney , Both of these organs contain the specific eutyrac , Glucose_6_phosphates is necessary for the conversion Of glucose_6_phosphate to glucose As blood glucose level increase,usually by absorption ...
... By drawing upon the glycogen stores of the liver ,and Aslight amount may also be derived from the kidney , Both of these organs contain the specific eutyrac , Glucose_6_phosphates is necessary for the conversion Of glucose_6_phosphate to glucose As blood glucose level increase,usually by absorption ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.