* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Induction and Patterning of the Nervous System
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Recurrent neural network wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
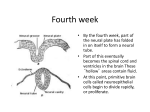
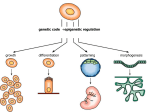
The Induction and Patterning of the Nervous System 서울대학교 어린이병원 신경외과 왕규창 Factors Determining Gene Expression inducing factor receptor transcription factor competence: ability of the cell to respond to inductive signals – determined by the repertory of receptors, transduction molecules and transcription factors Organizer Region Spemann and Mangold amphibian embryos dorsal lip of blastopore, future dorsal mesoderm transplantation: generated notochord, induced second nervous system Neural Induction default state of the ectoderm dissociated single cell without intercellular signaling: neural cell suppressor of neural differentiation: BMP abnormal BMP receptor: neural differentiation BMP Blockade Xenopus ectoderm organizer region endogenous neural inducers – follistatin, noggin, chordin Neural differentiation by inhibition of BMP signaling involves transcription factors of the Sox gene family. Sonic Hedgehog (SHH) as an inducer: both necessary and sufficient for the induction of most cell types in the ventral half of the neural tube as a morphogen: directs different cell fates at different concentration thresholds Sonic Hedgehog (SHH) synthesized as an inactive precursor: cleaved to be active addition of cholesterol molecule: – tether most of SHH to the surface of notochord and floor plate cells – permits diffusion of small amount Holoprosencephaly fused cerebral hemispheres, especially at the ventral area mutations in the human SHH gene SHH Signaling Pathway and Disease mutations in the human patched, smoothened, and gli proteins spina bifida, limb deformities, cancer Dorsal Induction BMP decapentaplegic in Drosophila BMP receptor – transmembrane serine-threonine kinases SMADs (transcription factors) phosphorylation Common Principles in Ventral and Dorsal Halves SHH vs BMP homeogenetic induction – like begets like – floor plate and roof plate Signals for Brain Patterning SHH: dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area forebrain: BMP signals were translocated from dorsal to ventral: distinctive cell types in the forebrain Rostrocaudal Axis forebrain: follistatin, noggin, chordin more posterior: FGF family protein hindbrain and spinal cord: retinoic acid patterning of the hindbrain Hox Gene Cluster Homeobox genes – 180bp, encodes homeodomain four separate chromosomal complexes or clusters derive from a common ancestral Hox complex mutations: homeotic transformation HOM-C in Drosophila Hox Gene Cluster homeodomain – encoded by homeobox genes – highly conserved 60 a.a. DNA binding domain – transcription factors control of rhombomere(segmentation) identity in hindbrain Retinoic Acid vs. Hox retinoic acid treatment: Hox gene expression at more anterior level of the hindbrain more posterior identity teratogenic and craniofacial abnormalities Patterning of the Midbrain Hox gene expression (-) long-range action of signals from the isthmus region (junction of mesencephalon-metencephalon) Wnt-1 and FGF8: regulates homeodomain protein expression: engrailed 1 and 2 Forebrain Patterning 6 prosomeres SHH: prosomeres 2 and 3 Not all subdivisions of the telencephalon develop independently. Forebrain Patterning Some neurons in neocortex are from striatal subdivisions. striatal progenitors – homeodomain proteins Dlx-1 and 2 – mutations: failure of striatal progenitors to migrate into the neocortex, marked depletion of GABA neurons Cortical Differentiation afferent input – somatosensory cortex experiment – barrels in the rodents – organization of whisker field intrinsic programs of cell differentiation – lac-Z transgenic mouse experiment Economy in Development small number of inducing factors conserved signaling molecules, receptors, developmental programs throughout animal evolution combination of genes for segmentation same processes at different developmental stages