* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nerve Fibers
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
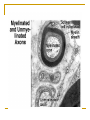
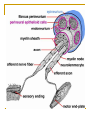
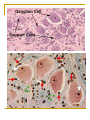
NERVOUS SYSTEM-2 Sixth lecture By Dr. Wahda A. M. Kharofa Objectives: To give information about: Peripheral nervous system (PNS). Peripheral nerve. Neuroglia. Types of neuroglia. Spinal ganglia. Autonomic ganglia. The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) The main components of peripheral nervous system are the nerves, ganglia, and nerve ending Nerves: are bundles of nerve fiber surrounded by a series of connective tissue sheaths Nerve Fibers: consist of axons enveloped by a special sheath derived from cells of ectodermal..In peripheral nerve fibers the sheath cell is the schwann cell, and in central nerve fibers it’s the oligodendrocyte. Myelinated nerve fibers: myelin sheath which surrounds the axon and shows gaps along the length of the axon, they are called "Nodes of Raniver", represent the spaces between schwann cells. The distance between two nodes is called an "Internode" and consists of one schwann cell. Unmyelinated nerve fibers: absence of myelinated sheath and the axon is covered with schwans sheath, and they do not have nodes of ranvier because are united to form a continuous sheath. Peripheral Nerve : It is a cord like structure firmer than the other parts of the nervous tissue due to presence of large amount of collagen fibers . the peripheral nerve is formed either of one bundle or more than one bundle depending upon the size of the nerve . Each peripheral nerve is surrounded by a c.t. called epineurium from which a septa arise to surround each bundle of nerve fibers this c.t. called perineurium . each bundle consist of a number of nerve fibers ( axon with surrounding sheath ) which are either myelinated or non- myelinated . the nerve fiber is surrounded by a c.t. called endoneurium. Neuroglia : Cells whose function is the metabolic and mechanical support and protection of neurons form the nuuroglia . There are many types of neuroglial cells as shown: 2- Oligodendrocytes: These cells are small and contain fewer processes, with sparse branching, and they are located in both gray and white matter of CNS. The cytoplasm contains small nucleus. These cells producing a myelin sheath. 4- Microglia: These cells are small elongated, with short irregular processes. These cells function as phagocytes in clearing debris and damaged structures in the CNS. Ganglia : The ganglia are nodules that contain an aggregation of the cell bodies of neurons. There are two kinds of ganglia: 1- Spinal ganglia: They are present in the dorsal root of the spinal nerves & it also present in cranial sensory nerves, it is rounded or oval in shape surrounded from outside by a c.t. capsule which is the continuous of epineurium of the nerve which connected to it , this c.t. extends inside the ganglion & divided it into groups of cells .Each cell is enveloped by a double layers, the outer one is a c.t. ( fibers with fibroblast ) which is a continuous of the endoneurium. The inner layer is called satellite cells applied closely to the ganglion cells. The cells are of pseudounipolar, most of them are large spherical in shape . the fibers which are present inside the ganglion are of myelinated type. Each cell contains a centrally located nucleus. Nissle granules are scattered in the cytoplasm. 2- Autonomic ganglia: it's structure similar to spinal ganglia but there are some differences between them which are: a- the nerve cell is of multipolar type & smaller than that of spinal ganglia . b- the nucleus of the nerve cell is eccentric in position which is oval or rounded with one or two nucleolus . c- the nerve fibers are of non – myelinated type . d- the ganglion cells surrounded by less satellite cells . e- the cells are not arranged in groups but they scattered irregularly .