* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Immune System Powerpoint
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmunity wikipedia , lookup
Social immunity wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
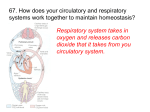
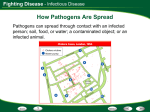
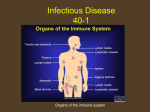
Immune System SC.912.L.14.52 Explain the basic functions of the human immune system, including specific and nonspecific immune response, vaccines, and antibiotics -Students will identify and/or explain the basic functions of the human immune system, including specific and nonspecific immune responses. -Students will describe how the human immune system responds to vaccines and/or antibiotics. -Students will explain the significance of genetic factors, environmental factors, and pathogenic agents to health from the perspective of both individual and public health. Pathogens and Human Illness Germ theory states that microscopic particles cause certain diseases. – proposed by Louis Pasteur – led to rapid advances in understanding disease – Koch’s postulates support the theory. – Disease-causing agents are called pathogens There are different types of pathogens. Bacteria are single-celled organisms. – cause illness by destroying cells – release toxic chemicals Viruses are genetic material surrounded by a protein coat. – force host cells to make more viruses – very small Fungi can be multicellular or single-celled. – take nutrients from host cells – occur in warm and damp places Protozoa are single-celled organisms. – use host cells to complete their life cycles – take nutrients from host cell Parasites are multicellular organisms – grow and feed on a host – possibly kill the host Pathogens can enter the body in different ways. Pathogens can be transferred by direct or indirect contact. Indirect contact does not require touching an infected individual. – touching an infected surface – breathing in infected air Vectors carry a pathogen and transmit it into healthy cells. Direct contact requires touching an infected individual. Includes: – kissing – sexual intercourse – hand shaking The immune systems consists of organs, cells, and molecules that fight infections. Many body systems protect you from pathogens. The immune system is the body system that fights off infection and pathogens. Many other tissues and systems help the immune system. – Skin is a physical barrier to infection. – Mucous membranes trap pathogens entering the body. – The circulatory system transports immune cells. Cells and proteins fight the body’s infections. White blood cells attack infections inside the body. – Phagocytes engulf and destroy pathogens. – T cells destroy infected cells. – B cells produce antibodies. Three types of proteins fight off invading pathogens. – Complement proteins weaken pathogen membranes. – Antibodies make pathogens ineffective. – Interferons prevent viruses from infecting healthy cells. Immunity prevents or limits a person from getting sick from a pathogen. In all immunity, pathogens are destroyed before you get sick. Passive immunity occurs without an immune response. – mother’s milk – genetics Active immunity occurs after a specific immune response Immune Response The immune system has many responses to pathogens and foreign cells. Many body systems work to produce nonspecific responses. Nonspecific responses are the same for every pathogen. In inflammation, blood vessels become leaky. – white blood cells move toward infection and damaged tissue – characterized by swelling, redness, and pain In fever, body temperature increases. – Low fevers stimulate white blood cells to mature. – High fevers can cause seizure, brain damage, and even death. Cells of the immune system produce specific responses. Specific immune responses begin with the detection of antigens. – Antigens are surface proteins on pathogens. – Each pathogen has a different antigen. There are two specific immune responses. – Cellular immunity uses T cells to destroy infected body cells. – Humoral immunity uses B cells to produce antibodies. Both responses produce memory cells. – specialized T and B cells – provide acquired (active) immunity The immune system rejects foreign tissues. Tissue rejection occurs in organ or tissue transplants. Tissue rejection is the result of an immune response. – immune system detects protein markers on the donor tissue – makes antibodies against the donor’s tissue Immunity and Technology Living in a clean environment and building immunity help keep a person healthy. Many methods are used to control pathogens. Antibiotics and antiseptics cause pathogens to burst. Antiseptics kill pathogens outside of the body. – do not target specific pathogens – examples include vinegar and soap Antibiotics kill pathogens inside the body. – target one specific bacterium or fungus – not effective against viruses Antibiotic resistance can cause medicines to become ineffective. – Some bacteria in a population have genes that make them immune to antibiotics. – These bacteria spread the gene, making the antibiotics useless. Vaccines artificially produce acquired immunity. Vaccines also control pathogens and disease. – given to prevent illness – contain the antigen of a weakened pathogen l Vaccination provides immunity. – stimulates a specific immune response – causes memory cells to be produced – allows immune system to respond quickly to infection Overreaction of the Immune System An overactive immune system can make the body very unhealthy. Allergies occur when the immune system responds to harmless antigens. An allergy is an response to a harmless antigen. Allergies are caused by allergens. – Allergens are antigens that cause an allergic reaction. – Allergens cause inflammation responses. There are many different allergens. – food, e.g. peanuts, milk, wheat, etc. – airborne, e.g. pollen, dust mite feces, mold, etc. – chemical, e.g. nickel, medicine, bee stings, etc. Allergens can cause anaphylaxis. – Anaphylaxis is an extreme inflammation response. – Blood vessels and airways become too porous. – If not treated immediately, anaphylaxis can cause death. In autoimmune diseases, white blood cells attack the body’s healthy cells. Autoimmune diseases are failures of the immune system. – White blood cells cannot recognize healthy cells. – White blood cells attack healthy body cells. – Tissues fail because of attack. – There are over 60 autoimmune diseases.