* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Faculty of Science Department of science Chemistry of
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Synthetic biology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Self-assembling peptide wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
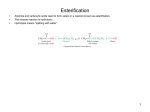
Faculty of Science Department of science Time of lectures: Instructor: Office hours: 2015/2016 Semester: Chemistry of Biomolecules كيمياء الجزيئات الحيوية 111111 Prerequisite (s):111212 Lecture room (s) : 1st Text books & References: Text Book 1. Organic Chemistry, Solomons Other 2. Organic Chemistry, Morrison and Boyd References 3. Biochemistry, Streyer Course Description: Course outline: Week Topic detailes 1. Stereochemistry (3) Stereoselective and stereospecific reactions, pro-chiral centers and faces, enantioselectivity and diastereoselectivity. 2. ■ Carbohydrates (1) Definition and chemical composition. Importance and occurance. 3. Monosaccharides (4) Monosaccharide structures and stereochemistry. Aldoses and ketoses. Nomenclature. Fischer projection formula. Cyclic hemiacetal formation. Hawarth formula. Furanoses and pyranoses. The anomeric effect. Reactions and methods of synthesis. 4. ■Di- and Polysaccharides (4) The Glycosidic linkage. Reducing and nonreducing sugars. Synthesis of glycosides. Identification and structure determination (sequencing) of polysaccharides by enzymetic and by chemical methods. Examples of some common disaccharides and polysaccharides. Chemically modified cellulose. 5. ■Amino acids (4) physical Properties. Isoelectric point and effect of pH. Chemical properties and reactions. Synthesis of α-amino acids. 6. ■Proteins (6) The peptide bond. Examples of biologically important oligopeptides. Types, structure, and biological function of proteins. Synthetic methods for peptides and polypeptides. Methods of Sequencing of polypeptides and proteins. ■Lipids- Fats and Oils (4) Classification of fats. Types of fatty acids. Saturated and unsaturated fats. Effect of unsaturation on physical and chemical properties and the biological consequences. Industrial uses of fatty acids. Phospholipids, sphingolipids, waxes. ■Lipids- Steroids, Prostaglandins, and Terpenes (4) Types and structural differences of prostaglandins. Biological function. Types of steroids. Biological functions. Structure and stereochemical aspects related to the steroid ring system. Examples of some chemical transformations with emphasis on Regio- and stereoselectivity. ■Nucleic acids (6) Structure of nucleic acids DNA and RNA. Biological function in relation to structure. Nucleosides and nucleotides. Transcription and protein synthesis. Synthesis of nucleosides and nucleotides. Sequencing with chemical and enzymetic methods. Genetic engineering. Attendance Policies: Be Punctual. Attendance is mandatory. Students are not allowed to miss more than 15% of the lectures, without acceptable real cause. If a student misses more that 15 % of the course lectures, she/he will forfeit the course credits. After this, medical reports may be submitted for evaluation, for a total absence of no more than 20%. If student misses more than 20% of lectures, regardless of the cause, the course will be failed. Grading system: Assessment First Exam Second Exam Activities and Evaluation Final Examination Total Grade 25% 25% 10% 40% 100%