* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Click - Lake County Schools
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
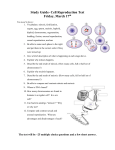
1 UNIT DATE RANGE TEACHER GRADE Cells 20 days Miller 7 UNIT LEARNING GOAL Students will compare and contrast the different parts, functions and differences in plants and animal cells, as well as discover the history of The Cell Theory. UNIT OBJECTIVES Describe the hierarchal organization from atoms to organisms. Investigate and explain the 3 components of Cell Theory. Explore how cells of all organisms undergo similar processes to maintain homeostasis. Compare and contrast the major 7 organelles of plant and animal cells. Explain why all organisms require a set of chromosomes (DNA). Explain the process of mitosis and meiosis in order to show how and why cells duplicate. UNIT ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do the organelles of plant and animal cells compare? Distinguish between the function and purpose of mitosis and meiosis. ESSENTIAL CONTENT AND UNDERSTANDING The student should be able to… Describe the hierarchal organization from atoms to organisms. Explain the 3 components of Cell Theory and describe how this theory has changed as new evidence and technology has developed. Compare and contrast the structure and function of the major 7 organelles of plant and animal cells. Compare and Contrast a plant and animal cell. Explain why all organisms require a set of chromosomes (DNA). Explain the process of mitosis and meiosis in order to show how and why cells duplicate. Use a microscope correctly. UNIT VOCABULARY cell, cell wall, nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplast, cytoplasm, cell membrane, the cell cycle, mitosis, meiosis CHUNKING THE UNIT WHAT HOW Unit Activities PowerPoint - the Cell Microscope Lab Wacky History of Cell Theory – introduction video clip Microscope – compare cells lab My fact - Your fact video activity Cell Theory PowerPoint and time line Plant and Animal Cells activity Thinking Map of difference of Plant and Animal Cells Celley’s Trip to the Cell Cell Analogy and diagram Diagram of the cell- label Find someone who activity 2 ASSESSMENT Cells Millionaire game - rags to riches Cells Game on computer Virtual lab on the Microscope Tic Tac Toe -Student choice projects Cell Cycle Student choice project Article on Meiosis and reproduction Cells: Compare cell to factory project / compare to a school Please note: Herman Advanced classes doing personalized learning for unit Various mini-assessments throughout the unit Cells poster project Unit Test LEARNING STRATEGIES UTILZED Interactive Science Notebook (ISN), inquiry labs, thinking maps/charts/graph/organization tools, multi-media, Cornell Notes, cooperative groups, Mark the Text, virtual labs, Edmodo, AVID strategies, CRISS strategies, KAGAN strategies, modeling. FLORIDA SCIENCE BENCHMARKS SC.7.N.3.1 Recognize and explain the difference between theories and laws and give several examples of scientific theories and the evidence that supports them. SC.6.L.14.2 (AA): Investigate and explain the components of the scientific theory of cells. (Cell theory: All organisms are composed of cells (single-celled or multi-cellular), all cells come from pre-existing cells and cells are the basic unit of life. SC.6.L.14.3: Recognize and explore how cells of all organisms undergo similar processes to maintain homeostasis, including extracting energy from food, getting rid of waste, and reproducing. SC.6.L.14.4: Compare and contrast the structure and function of major organelles of plant and animal cells, including cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and vacuoles. SC.7.L.16.1: Understand and explain that every organism requires a set of instructions that specifies its traits that this hereditary information (DNA) contains genes located in the chromosomes of each cell, and that heredity is the passage of these instructions from one generation to another. SC.7.N.2.1 Identify an instance from the history of science in which scientific knowledge has changed when new evidence or new interpretations are encountered. SC.7.L.16.3: Compare and contrast the general processes of sexual reproduction requiring meiosis and asexual reproduction requiring mitosis. FLORIDA SCIENCE BENCHMARKS FOR ADVANCED PLACEMENT SC.912.L.14.2: Relate structure to function for the components of plant and animal cells. Explain the role of cell membranes as a highly selective barrier (passive and active transport) SC.912.L.14.6: Compare and contrast the generate structures of plant and animal cells. Compare and contrast the general structures of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. SC.912.L.16.14: Describe the cell cycle, including the process of mitosis. Explain the role of mitosis in the formation of new cells and its importance in maintain chromosome number during asexual reproduction. 3 SC.912.L.16.16: Describe the process of meiosis, including independent assortment and crossing over. Explain how reduction division results in the formation of haploid gametes or spores. SUPPORT STANDARDS LANGUAGE ARTS MATH as required as required ESOL Extended time RTI Test Corrections ESE Making use of context clues Peer assistance Check for comprehension Organizational strategies Proximity Modeling Using multi-media Using linguistic modifications TOWER - writing strategies Language / Vocabulary Games Use of analogy Individualized instruction and assistance Peer tutoring Leave class for assistance Preferential seating Read directions aloud Students paraphrase directions Alternative test settings or small group testing Provide student choices expectation review Use of partners / collaborative groups planned movement guided practice Use of learning centers or centers / stations Organizational strategy - sorting (information) Using written and pictorial forms to teach Adjusting or shortening assignments Hands-on experiences Small group instruction Cooperative learning groups Defining content area language or terms Using alternative assessments Reducing directions to steps or parts Using role-play Adapting written text and materials to facilitate comprehension Other strategies