* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WORLD HISTORY Origins and Expansion of Islam 600 CE
Regensburg lecture wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Islam in South Africa wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Romania wikipedia , lookup
Islam in the Netherlands wikipedia , lookup
Islamic–Jewish relations wikipedia , lookup
Reception of Islam in Early Modern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Spread of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Islam in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
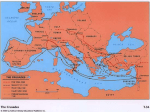
WORLD HISTORY Greer ORIGINS AND EXPANSION OF ISLAM APPLICABLE GEORGIA STANDARD(S): SSWH5 The student will trace the origins and expansion of the Islamic World between 600 CE and 1300 CE. a. Explain the origins of Islam and the growth of the Islamic Empire. b. Identify the Muslim trade routes to India, China, Europe, and Africa and assess the economic impact of this trade. c. Explain the reasons for the split between Sunni and Shia Muslims. d. Identify the contributions of Islamic scholars in medicine (Ibn Sina) and geography (Ibn Battuta). f. Analyze the relationship between Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. What is Islam? Religion developed on the Arabian Peninsula (modern-day Saudi Arabia) o Like Christianity, offshoot faith of Judaism Name comes from Arabic word salaam o Same meaning as Hebrew word shalom (peace - used as greeting and parting) o Both are Semitic languages and very similar o Literal meaning: “True peace can only be attained by total submission to God’s will.” Key element here is concept of “surrender” Religion named for a “concept,” rather than a person (i.e. Christianity) People who practice Islam are called “Muslims” o One who surrenders his/her whole being to the will of the Creator o All other creatures natural “Muslims,” who cannot help but do God’s will o Man alone has freedom of choice and can make act of “Islam” Total surrender to God’s will Islam is a Monotheistic Religion Not a “heathen” religion o “Heathen” refers to those who do not worship Judeo-Christian God Traditional thoughts by Jews and Muslims: o Descendants of Abraham’s son Isaac (Yitzak) became history’s Jews o Descendants of Abraham’s son Ishmael became history’s Muslims “Allah” is Simply Arabic Word for “God” Allah had been seen earlier as the “high god” of the pagan/heathen Arabs Later seen by Arabs as god of Abraham and Jesus Page 1 of 5 Five Pillars of Islam Shahada (confession) Basic profession of faith required of all Muslims o “There is no god by Allah and Mohammad is His prophet.” Salaah (prayer) - Five times daily, facing holy city of Mecca Siyaam (fasting) - Sunrise to sunset during holy month of Ramadan Zakaah (charity) - Muslims must give 2.5% of income to charity Hajj (pilgrimage) - Muslims required to travel once in lifetime to Mecca o Only if they can afford to do so Purpose is to visit Ka’aba Holdover from pagan Arab tradition Ka’aba believed to be site of Abraham’s first shrine to God MUHAMMAD (570 CE-632 CE) Founder of Islam Born in city of Mecca (on the Arabian Peninsula) o Area where many trade routes crossed Became a religious reformer who condemned his people’s worship of idol Not considered divine, as Christ is to Christians Tends to be treated as such Considered “Seal of the Prophets” o Last of God’s prophets o Life should be guide to living for all Muslims “Night of Power” Occurred at age 40 Visited by and fought with an angel Angel Gabriel began dictating verses that would become Koran (Quran) - Islam’s holy book o Process supposedly continued for next 25 years 613 CE - Mohammed begins preaching new religion in and around Mecca 622 CE. - Mohammad and Followers Driven From Mecca New religion seen as upsetting to existing order in Mecca Flight known to Muslims as “Hegira”(Hijrah) o Mohammad and followers welcomed in Medina (Mahdinah) o Attracted many new followers and gained political influence Page 2 of 5 The Arab Muslims Spread Islam 750 CE - Islam Had Spread Across Arabian Peninsula Conquered non-Muslims offered a choice: o Convert to Islam o Pay a reasonable tax o Die Jews and Christians usually just paid the tax Mohammed stopped early massacres of Jews and Christians (“People of the Book”) Restrictions sometimes placed on property rights and movements of Jews and Christians The Muslim Empire Extent in 8th Century o Extended from India to Spain o Unified by Islam and military might o Empire ruled by Caliphs o Empire’s first capital was at Baghdad (capital of modern-day Iraq) Large cities of the empire surpassed those of Europe for splendor and cleanliness Break-up of the Empire (by the 10th century) o Empire gradually disintegrated over a 200-year period o Rival chieftains gained control over their own domains Empire eventually divided into a number of independent Muslim kingdoms Muslims’ Loss of Spain o Spain remained under Muslim rule (and prosperity) for 700+ years Continuous guerrilla warfare by Christians Reunited under Christian rule in 1492 by King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella The Turks Create a Muslim Empire By 10th century, Turkish tribes of central Asia had adopted Islam 11th century – Seljuk Turks seized Baghdad and dominated Muslim Middle East As power of Seljuk Turks waned, Ottoman Turks achieved Muslim leadership 14th century – Ottoman Turks conquered part of southwest Europe 15th century – Muhammad II captured Constantinople and ended Byzantine Empire 16th & 17th centuries – Muslim armies advanced deep into Europe, but were held back 17th century – Turkish power began to decline and Turks were driven almost entirely out of Europe Muslim Contributions to “Civilization” While European culture declined during the “Dark Ages,” Muslims developed a flourishing civilization o Education, mathematics, physical science, medicine, agriculture, industry, navigation technology, literature, language, architecture, numerous outstanding Arab-Muslim scholars Page 3 of 5 Miscellaneous Terms and Concepts Jihad - Muslim concept of “holy” war o Refers to literal and figurative struggle to win converts and battle within human soul to submit to God’s will o Some misuse(?) term to justify terrorism Polygamy - having more than one wife (Muslim men can have as many as four) o Practice frowned upon (most Muslim men have only one wife) o Each wife must enjoy equal attention and existing living arrangements must not be disrupted Hajib and Chador - Veil and dress worn by Arab and Persian women Not Muslim requirements, but cultural (although enforced by Muslim governments in some countries) o This type of dress pre-dates Islam by centuries Sunni Muslims - Majority of world’s Muslims o Consider themselves to be orthodox Muslims o Based on early quarrels of who would rightly succeed Mohammed Shi’a (Shiite) Muslims - Minority Muslims who sought a different line of succession from Mohammed’s heirs o Mostly Iranian Muslims today o Minority in Iraq (persecuted by Saddam Hussein) CHRISTIAN ZEAL AND THE CRUSADES 1096 CE - Pope Urban II Called for Military Mission to “Holy Land” 50,000-60,000 volunteers from Europe Mission was to take Jerusalem from Muslims Impetus had come when Byzantine emperor asked pope for help against Seljuk Turks Pope’s goals: Reunite Christendom (Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox Churches) Display papal power o Pope and monarchs saw it as way to rid Europe of contentious nobles who disturbed peace and fought constantly Knights’ goals: Forgiveness for sins Glory in battle Plunder and riches Merchants’ goals: Make money selling arms and supplies to Christian armies Establish control of profitable Middle East trade routes Page 4 of 5 First Crusade Won Jerusalem (temporarily) Approx. 15,000 Muslims slaughtered in the streets Crusader states established at Edessa, Antioch, Tripoli, and Jerusalem o 1120s – Muslims striking back Later Crusades accomplished little o 1202 - Constaninople sacked by Crusaders o By 1200’s, Crusading spirit dwindled Consequences of Crusades: Decline of papal prestige Decline in power of European nobles Decrease in power of Byzantine Empire Increase in religious intolerance o Christians had behaved very badly o Muslim distrust and resentment of Christians grew o Still a problem today (Osama bin Laden/terrorism) Increase in trade European demand for eastern goods led to exploration TERMS TO KNOW: Judaism Allah Siyaam Seal of the Prophets Caliphs Seljuk Turks Hijab/chador Crusade shalom/salaam Five Pillars Zakaah Hegira Baghdad Ottoman Turks Sunni Muslim Shahada Hajj Medina King Ferdinand jihad Shi’a/Shi’ite Isaac/Ishmael Salaah Mecca People of the Book Queen Isabella polygamy Pope Urban II Page 5 of 5