* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 10. Cody Mills - Hemophilia A
Tay–Sachs disease wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
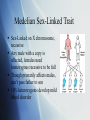
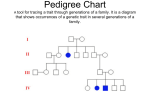
Hemophilia A Cody Mills Biochemistry 118Q Fall 2010 Disease Overview Hemophilia A is a blood disorder that affects clotting Type A mutation results in abnormal version of Coagulation Factor VIII Superficial and subtle dangers- spontaneity Biggest danger is in complications from internal bleeding (joints, muscles, brain organs) Medelian Sex-Linked Trait Sex-Linked on X chromosome, recessive Any male with a copy is affected, females need homozygous recessive to be full Though primarily affects males, can’t pass father to son 10% heterozygotes develop mild blood disorder History of Hemophilia “The Royal Disease” Russia, Germany, Spain via Victoria Today, affects about 1 in 5,000 live male births (equal geographically because of spontaneous mutation) Also Hemophilia B which is on the F9 gene, affects other factor Traditional Treatment Gene counseling Assessment of situation Management of symptoms Lifestyle Changes Vigilance for symptoms Genetic Basis for Disease A mutation of the F8 gene, located on the X chromosome at Xq28 Mutation between bases 154,064,062 to 154,250,997 Causes the protein to be deactivated because of improper coding Inversion of 1kb introns 1 and 5’ leads to severe phenotype. Point mutation stop codons Penetrance and Expression Penetrance is nearly universal in affected males and homozygous females Varying levels of expressivity Most severe usually diagnosed in first year Medium severity can be at 5-6 years Mild can be late in life Families generally have consistent expressivity New Diagnosis Options Factor VIII level vs. von Willebrand Prenatal sequence tests are possible but carry risk Only done when there is reason Gene sequencing tests can confirm the disease in 98% of individuals Contemporary Genetic Treatment Understanding the location and coding of the genes allows for infusions of blood with F8 concentrate No way to change or replace the gene sequence is in clinical trial, but the disease can be managed effectively Pre-clinical experiments in progress Developing viral infections from human clotting factors Works Cited http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi? book=gene&part=hemo-a http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Penetrance http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov:80/bookshelf/br.fcgi? book=gnd&part=hemophiliaa http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/hemophilia http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/dci/Diseases/hemophilia/he mophilia_treatments.html http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/gene/F8 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim/306700