* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ipSecMicrosof
Cryptanalysis wikipedia , lookup
Quantum key distribution wikipedia , lookup
Airport security wikipedia , lookup
Unix security wikipedia , lookup
Cyber-security regulation wikipedia , lookup
Information security wikipedia , lookup
Secure multi-party computation wikipedia , lookup
Next-Generation Secure Computing Base wikipedia , lookup
Computer and network surveillance wikipedia , lookup
Post-quantum cryptography wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Security and safety features new to Windows Vista wikipedia , lookup
Mobile security wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Security-focused operating system wikipedia , lookup
Authentication wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Cybercrime countermeasures wikipedia , lookup
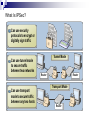
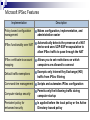
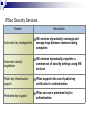
Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) Reviewing IPSec Understanding Vulnerabilities Threat Analysis What Is IPSec? Microsoft IPSec Features Advantages and Disadvantages of IPSec IPSec Security Services Authentication Methods How IPSec Is Deployed Threat Analysis 1. Identify threats 2. Prioritize threats based on: Probability of occurrence Severity of potential damage 3. Divide the number representing damage by the number representing probability to determine the threat level 4. Address threats with the highest threat levels first Example Assume that you have identified two potential threats to your enterprise: 1. Threat A has been identified as having a high amount of damage (Damage = 10) and a low probability of occurring (Probability = 10), so the threat level is 1 (10/10 = 1). 2. Threat B has been identified as having a high amount of damage (Damage = 8) and a fairly high probability of occurring (Probability = 3), so the threat level is 2.67 (8/3 = 2.67). Therefore, you would address Threat B first, because it has a higher threat level. What Is IPSec? Can use security protocols to encrypt or digitally sign traffic Can use tunnel mode to secure traffic between two networks Can use transport mode to secure traffic between any two hosts Tunnel Mode Router Router Transport Mode Router Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) is a set of extensions to the Internet Protocol (IP) family. It provides cryptographic security services that allow for authentication, integrity, access control, and confidentiality. IPSec services are similar to Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), but at the network layer, in a way that is completely transparent to your applications and much more powerful. This is because your applications do not need to have any knowledge of IPSec to be able to use it. You can create encrypted tunnels, (virtual private networks [VPNs]), or simply perform encryption between computers. The many options offered by IPSec make it much more complex than SSL. Microsoft IPSec Features Implementation Policy-based configuration management IPSec functionality over NAT Description Makes configuration, implementation, and administration easier Automatically detects the presence of a NAT device and uses UDP-ESP encapsulation to allow IPSec traffic to pass through the NAT IPSec certificate-to-account mapping Allows you to set restrictions on which computers are allowed to connect Default traffic exemptions Exempts only Internet Key Exchange (IKE) traffic from IPSec filtering Command-line management Scripts and automates IPSec configuration Computer startup security Permits only the following traffic during computer startup Persistent policy for enhanced security Is applied before the local policy or the Active Directory–based policy IPSec is based on an end-to-end security model that establishes trust and security from a source IP to a destination IP address. Any computers that only route data from source to destination are not required to support IPSec, unless firewall-type packet filtering or network address translation (NAT) is in place. This model allows for the successful deployment of IPSec in the following enterprise scenarios: Local area network (LAN): client/server and peer-to-peer Wide area network (WAN): router-to-router and gateway-to-gateway using IPSec tunnels Remote access: dial-up clients and Internet access from private networks IPSec tunnel mode When you use IPSec tunnel mode, IPSec encrypts the IP header and the payload. Tunnel mode provides the protection of an entire IP packet. IPSec transport mode Transport mode is the default mode IPSec encrypts only the IP payload. Advantages and Disadvantages of IPSec Advantages Flexible security protocols Transparent to users and applications Authentication Confidentiality Open industry (IETF) standards Data integrity Dynamic rekeying Secure end-to-end links Easy implementation and centralized management by using policies Disadvantages Administrative overhead Increased performance requirement Supportability Policy management Local policy configuration IPSec Security Services Feature Description Automatic key management IKE services dynamically exchange and manage keys between communicating computers Automatic security negotiation IKE services dynamically negotiate a common set of security settings using IKE services Public key infrastructure support IPSec supports the use of public key certificates for authentication Preshared key support IPSec can use a preshared key for authentication Authentication Methods Kerberos V5 The default authentication method for IPSec Public key certificates Using this authentication method, security credentials can be presented without being compromised in the process Preshared key authentication Both parties agree on a shared, secret key that is used for authentication in an IPSec policy How IPSec Is Deployed Using policy-based management Easy management Easy implementation Eliminates administrative overhead Using local policies One local policy Group Policy settings can be stored on individual computers Policy-based configuration management You can assign IPSec policies through Group Policy configuration of Active Directory domains and organizational units. This allows the IPSec policy to be assigned at the site, domain, or organizational unit level, eliminating the administrative overhead of configuring each computer separately. IPSec Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) packets can now pass through a NAT device that allows UDP traffic. The Internet Key Exchange (IKE) protocol automatically detects the presence of a NAT device and uses UDP. ESP encapsulation to allow IPSec traffic to pass through the NAT device. Refs: www.microsoft.com www.wikipedia.com