* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Data Security - Devi Ahilya Vishwavidyalaya
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Cryptanalysis wikipedia , lookup
Airport security wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Cyberwarfare wikipedia , lookup
Information privacy law wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Operation AntiSec wikipedia , lookup
Security-focused operating system wikipedia , lookup
Mobile security wikipedia , lookup
Cyberattack wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Information security wikipedia , lookup
Computer and network surveillance wikipedia , lookup
Cyber-security regulation wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
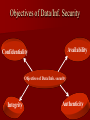
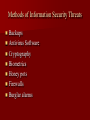
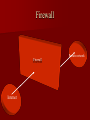
Information Security By Bhupendra Ratha, Lecturer School of Library & Information Science D.A.V.V., Indore E-mail:[email protected] Outline of Information Security Introduction Impact of information Need of Information Security. Objectives of Information Security. Areas of Information Security. Types of attackers Why attacks? Methods of Attacking on the Information Methods of Defending the Information Tips for the Information Security Introduction Information Security is a complicated area and can be addressed by well-trained and experienced Professionals. “When there is an attack on the system with the help of different threats, it means that our system is working very slowly, damaged and our information are unsecured” is called Information insecurity. This is a very big problem. The Information Security is the solution for it. Importance of Information Our work is based on records (information). We spend minimum half our day with documents 15% of Rs. spent managing documents. Can’t work without data, record or information Need of Information Security To privacy of our Data/Information To safely data saving Theft own Data/Information To avoid bad use of our data Lack of time Lack of money Lack of human resources Objectives of Data/Inf. Security Availability Confidentiality Objectives of Data/Info. security Integrity Authenticity Security Areas Basically three areas of security 1. Physical security Network security Database Security 2. 3. Physical Security Keep the servers in locked room with network and power cables snipped off. Security of other hardware and machinery Network Security Network security all entry points to a network should be guarded. Switch Unprotected Network Server Internet Printer Workstation Modem Firewall Scanner Protected LAN Database Security Database Integrity User Authentication Access Control Availability Types of Attackers Hackers Lone criminals Police Malicious insiders Press/media Terrorists Industrial espionage National intelligence organizations Info warriors Hackers – Attacks for the challenge – Own subculture with names, lingo and rules – Stereotypically young, male and socially – Can have considerable expertise and passion for attacks Lone criminals – Attack for financial gain – Cause the bulk of computer-related crimes – Usually target a single method for the attack Malicious insiders – Already inside the system – Knows weaknesses and tendencies of the organization – Very difficult to catch Press/media – Gather information for a story to sell papers/ commercial time Police –Lines are sometimes crossed when gathering information to pursue a case Terrorists –Goal is disruption and damage. –Most have few resources and skilled. National Intelligence Organizations To investigation of different cases Industrial Espionage • To discover a competitors strategic marketing Info warriors – Military based group targeting information or networking infrastructures – Lots of resources – Willing to take high risks for short term gain Why attacks? To publicity To financial gain Jealousness To fun To competition with the person of same field Specific types of attacks Engineering attacks Physical attacks Environmental attacks Engineering attacks Viruses String of computer code that attaches to other programs and replicates Worms Replicates itself to multiple systems Rarely dangerous, mostly annoying Trojan Horses Collects information and sends to known site on the network Also can allow external takeover of your system Cont… colleague Attacker Virus Our system Cont.. – Password sniffing Collect first parts of data packet and look for login attempts – IP Spoofing Fake packet to “hijack” a session and gain access -Port scanning Automated process that looks for open networking ports Logs positive hits for later exploits Physical attacks Equipment failure arising from defective components. Temperature and humidity. Physical destruction of hardware and equipment Theft or sabotage. Environmental Attacks Natural Disasters Fire, Earthquakes etc. Man-Made Disasters War, Chemical Leaks etc. Methods of Information Security Threats Backups Antivirus Software Cryptography Biometrics Honey pots Firewalls Burglar alarms Backups Backups allow us to restore damaged or destroyed data. We can set up backup servers on the network. Backup media are- Floppy disks, external hard disks, ISP online backup. Antivirus Antivirus is a program that we can install on our computer to detect and remove viruses. It is used to scan hard disks, floppy disks, CDs, for viruses and scan e-mail messages and individual files, downloads from the Net. Cryptography Cryptography is the art of converting info. Into a secret code that can be interpreted only by a person who knows how to decode it. Encrypted Cipher text Plain text Decrypted Example of Cryptography Original message Sender Encrypted Original message Receiver Decrypted Bioinformatics The bioinformetics authentication process uses a person’s unique physical characteristics to authentically the identity. Bioinformatics authentication method fingerprint recognition, voice authentication, face recognition, keystroke dynamics and retina. Fingerprint Retina Honey pots A honey pots is a tool used for detecting an intrusion attempt. A honey pots simulates a vulnerable computer on a network. It contains no critical data or application but has enough data to lure an intruder. Honey pots Intruder Honey pots Firewall A firewall is a tool for the network security that stand between trusted and entrusted networks and inspecting all traffic that flows between them. In simple language firewall is a filter machine that monitors the type of traffic that flows in and out of the network. Firewall Private network Firewall Internet Burglar alarms Traps set on specific networked objects that go off if accessed Tips for information Security Use of strong password Adopt a security policy Use of anti-virus. Information security officer Use of firewalls Use of bioinformatics Beware to malicious insiders Security training Use of other security tools