* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Roman Republic and Philosophy
Legislative assemblies of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Conflict of the Orders wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Executive magistrates of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Demography of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
First secessio plebis wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Elections in the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Roman technology wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Treaties between Rome and Carthage wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Constitution of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
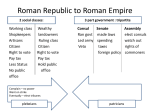
Roman Philosophy Stoicism Epicureanism Stoicism Zeno – Greek Source of happiness is wisdom Only man has morals Apathy – Emotion and passion destroy reason Epicureanism Epicurus – Greek No afterlife Maximize pleasure & minimize pain Materialists Roman Republic Roman Republic Internally – Republic a political system in which the supreme power lies in a body of citizens who can elect people to represent them Externally – Empire Empire Building: Italian Peninsula By 268 BC, Rome controlled most of Italy Empire Building: Punic Wars Carthage versus Rome Generals Both wanted the western Mediterranean & Sicily Hannibal for Carthage Scipio for Rome Rome Won Kept Spain & North Africa Literally destroyed Carthage Empire Building: Macedonian & Seleucid Wars During & after Punic Wars Gained control of Greece and Syria Total control of the Mediterranean Empire Building: Asia Anatolian king willed his empire to Rome What allowed them to conquer so much territory? Military Disciplined & well trained Each province contributed soldiers Roads Slavery People from conquered provinces Free labor source helped expansion Why didn’t conquered peoples rebel? Effective governance Romanization Roman culture Latin language Roman laws Trade benefits Protection/Peace Citizenship Standardized money Safe trade Cities Roads Aqueducts Roman Government The Republic Senate In charge of: Treasury Foreign relations Enforced laws Declared war Patricians and Plebeians Patricians Aristocrats Held political and religious power Large landowners Government officials Priests Forbidden to marry outside their class Plebian Lower social class Land owning men Had to be a citizen of Rome Tribune Elected from the Plebeians Had the power to veto any law Defended assembly against Patricians Consuls From the Patricians Made all legislation Shared rule by electing two Consuls at a time Civil decisions Military power One consul could veto the other Dictator Appointed in times of crisis A single leader who had absolute power to make laws and command the army Temporary – 6 months