* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Risk & Rates of Return
Internal rate of return wikipedia , lookup
Stock trader wikipedia , lookup
Interbank lending market wikipedia , lookup
Rate of return wikipedia , lookup
Investment banking wikipedia , lookup
Investment fund wikipedia , lookup
Securitization wikipedia , lookup
Value at risk wikipedia , lookup
Fixed-income attribution wikipedia , lookup
Hedge (finance) wikipedia , lookup
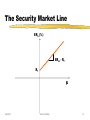
Risk and Return 5/25/2017 Richard MacMinn 1 Objectives: Define Expected Return Define Risk Systematic versus Unsystematic Examine the relationship between Asset Risk and Return Understand the effect of diversification on the Risk and Return of a portfolio Determine an investor’s required rate of return on a security as a function of its risk 5/25/2017 Richard MacMinn 2 Expected Returns The expected benefits or returns that an investment generates come in the form of cash flows. Cash flows, not accounting profits, are the relevant variable used to measure returns. Conventionally, we measure the expected cash flow as n follows: EX pi X i p1 X1 p2 X 2 pn X n EX = X1 P1i +1 X2 P2 + . . . + X n Pn where Xi is the cash flow in the ith state of the economy and Pi is the probability of the ith state of the economy 5/25/2017 Richard MacMinn 3 Expected Returns Similarly, the Expected Rate of Return is given by: n ER = R i Pi n ER pi Ri i=1 p1 R1 p2 R2 pn Rn i 1 where Ri is the rate of return in the ith state of the economy and pi is the probability of ith state of the economy. 5/25/2017 Richard MacMinn 4 Risk Risk can be defined as the possible variation in cash flow about an expected cash flow. Statistically, risk may be measured by the standard deviation of the random cash flow. The standard deviation of an asset a is denoted by a and is calculated as follows: n n 2 2 p R ER = R – ERa P i ai a i =1 i i i 1 a f where n is the number of states of the economy, Rai is the return in the ith state and pi is the probability of the ith state of the economy 5/25/2017 Richard MacMinn 5 Risk 5/25/2017 Richard MacMinn 6 Summary Statistics Example State Probability Recession 20% Moderate Growth 30% Strong Growth 50% Cash Flow $ 1,000 $ 1,200 $ 1,400 EX ER Var X Var R 5/25/2017 $ 1,260 13% Richard MacMinn Return 10% 12% 14% 24400 0.000244 7 Risk The attractiveness of a security cannot be determined by standard deviation alone. The risk and return of a security has to be compared with the alternatives available for investment. If two securities have the same risk, the one with the higher return is preferable. Alternatively, if two securities have the same return, then the one with lower risk is preferable. 5/25/2017 Richard MacMinn 8 Risk & Diversification Total Risk or variability of returns can be divided into: The variability of returns unique to the security Commonly referred to as Firm Specific Risk or Unique Risk or Diversifiable Risk or Unsystematic Risk The risk related to market movements Also referred to as Market Risk or Non-diversifiable Risk or Systematic Risk By diversifying, the investor can eliminate the “unique” security risk. The systematic risk, however, cannot be diversified. 5/25/2017 Richard MacMinn 9 Effects of Diversification Standard Deviation Total Risk = Unique Risk + Systematic Risk Unique Risk Systematic Risk Number of Stocks in Portfolio 5/25/2017 Richard MacMinn 10 Benefits of Diversification State Rainy Season Sunny Season ERU ERR Var RU Cov(RR, RU) Correlation Portfolio ERP Var RP 5/25/2017 Probability Umbrella Manufacturer 50% 50.0% 50% -25.0% Resort Portfolio Owner -25.0% 12.5% 50.0% 12.5% 12.5% Cov(RU, RR) Var RR 14.06% -14.06% -1 50% 12.5% -14.06% 14.06% -1 50% 12.5% 0.0% Richard MacMinn 0.0% 11 How do investors diversify? The Portfolio Problem Markowitz (Portfolio Selection) Tobin (Portfolio Separation) Sharpe (CAPM) 5/25/2017 Richard MacMinn 12 What risk is priced? Risk averse investors demand higher returns, or equivalently, a risk premium for undertaking risk. Investors cannot expect the market to compensate them for risk that they can eliminate through diversification. Because stocks can be combined in portfolios to eliminate specific risk, only diversifiable or systematic risk matters, i.e. commands a risk premium. Only systematic risk contributes to the riskiness of a portfolio and cannot be eliminated through diversification. 5/25/2017 Richard MacMinn 13 Measuring Systematic Risk Systematic Risk affects all securities. To measure systematic risk, we measure the tendency of a stock to move relative to the market. The plot of firm excess returns versus market excess returns is called the characteristic line, i.e., ERa - Rf = (ERm - Rf) The measure of a stock’s systematic risk or market risk is commonly called beta Beta is also the slope of the characteristic line. 5/25/2017 Richard MacMinn 14 Characteristic Line Stock/Portfolio Returns (%) Characteristic line Market Returns (%) 5/25/2017 Richard MacMinn 15 Measuring Beta The beta of stock A is calculated as follows: Cov(R , R ) a m ,R Cov R a = aVar Rm a m Var Ra a f where Ra is the return on stock A and Rm is the return on the market portfolio and where a f n a fa Cov Ra ,Rm pi Rai ERa Rmi ERm i 1 f The beta of a portfolio is the weighted average of the individual securities’ betas The beta of the market is 1. 5/25/2017 Richard MacMinn 16 Required Rate of Return The required rate of return equals the risk free rate plus a return to compensate for the additional risk. The required rate of return can be expressed as R = Rf + RP, where R is the investor’s required rate of return, Rf is the risk-free rate, and RP is the risk premium 5/25/2017 Richard MacMinn 17 The Required Rate of Return Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) According to the CAPM ERa = Rf + a [ERm - Rf ] where ERa is the expected rate of return on stock “a” and ERm is the expected rate of return on the market portfolio. 5/25/2017 Richard MacMinn 18 The Security Market Line ERa (%) ERm - Rf Rf a 5/25/2017 Richard MacMinn 19 Criticisms of CAPM Can Beta capture all dimensions of risk? Is beta the appropriate measure of risk? Some empirical research has shown that the CAPM does not hold. Various anomalies such as the size effect and the friday the 13th effect have been known and investigated for some time. How do we determine the market portfolio? 5/25/2017 Richard MacMinn 20