* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Lymphatic System “The Garbage Disposal System”
Atherosclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency wikipedia , lookup
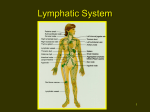
The Lymphatic System By Kristin James, Alex Christiansen, & Saundra Thomson FUN FACTS!!! The lymphatic system returns about 3.17 quarts (3 liters) of fluid each day from the tissues to the circulatory system. Production of lymphocytes (immune system) takes place in the bone marrow. The B-cells are known to fight off pathogenic bacteria. However, a special type of B-cells known as memory B-cells protect the body from attack by similar pathogens in the future. Purposes of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system aids the immune system in removing unwanted waste from the body The Lymphatic System is known as the drainage system because it removes excess fluids that cause harm to the body It also absorbs fats and fat-soluble vitamins from the digestive system The Process: Blood carries oxygen, nutrients and hormones for our cells Blood Plasma flows with the blood, then separates to reach the cells through body tissue and deliver its nutrients 90% of the plasma goes to the cells this fluid is now known as interstitial fluid the other 10% is Lymph Lymph: Lymph, (a.k.a “blood plasma”) a milkywhite to yellow, watery liquid, is the main component of the lymphatic system. The liquid originates from blood, it contains oxygen, proteins, glucose and white blood cells. It delivers nutrients to the cells, and removes undigested protein from the cells. Lymphatic Capillaries: Lypmh has to enter the lymphatic system using these specialized capillaries They begin as “blind-ended” tubes that are about as thick as a single cell Each cell is fastened to nearby tissues by an anchoring filament, where they turn into lymphatic vessels Lymphatic Vessels Lymphatic vessels are larger versions of lymphatic capillaries They’re located deeper in the body near major blood veins The vessels are also known as lymphangions There Lymph Nodes are between 600700 lymph nodes present in the average human body Their job is to filter lymph The nodes is the last stop of cancer cells, where they are trapped and destroyed- until overwhelmed Although these nodes can increase or decrease in size throughout life, any nodes that has been damaged or destroyed, does not regenerate. LAB!! Turn to a partner and play hot hands What do you think is happening beneath the skin when your hands start reddening? Lymphocytes Lymphocytes is a type of white blood cell, and they form lymph tissue. Lymphoid tissue defends the body against the infections and spread of tumors. B-lymphocytes (B-cells) and T-lymphocytes (Tcells). The T-cells are known to fight off the infection of viruses. B-cells take care of pathogenic bacteria. Major Body Parts: Thymus: Located towards the basal of the heart, made up of lymphatic tissue, and takes part in the development of the immune system Tonsils: This organ of the lymphatic system is located in the back of the throat. Adenoids: The adenoids can be described as a mass of lymphoid tissue that is situated by the tonsils. Diseases and Infections Elephantiasis Mesenteric lymphadenitis Castle-man Disease Tonsillitis Lymphodenpathy Lymphoma Vocabulary to remember: Lymphatic System: the system by which lymph is returned from the cells to the blood Lymphatics: A lymphatic Vessel Thoracic duct: the main trunk of the lymphatic system, passing along the spinal column Vocabulary: Lymphocytes: a type of white blood cell with a sphereical structure Lymphadenopathy: swollen lymph nodes Lymphadema: Cancer of the lymph nodes Elephantiasis: a chronic filarial disease resulting in lymphatic obstruction, characterized by marked enlargement of the parts affected, especially of the legs Bibliography http://www.lymphnotes.com/article.php/id/151/ http://health.howstuffworks.com/humanbody/systems/lymphatic/question138.htm http://www.medical-reference.net/2011/08/howdoes-lymphatic-system-work.html http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/lymphaticdisea ses.html http://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/bhcv2/bhcarticl es.nsf/pages/Lymphatic_system http://kidshealth.org/parent/general/body_basics/sp leen_lymphatic.html# http://www.funtrivia.com/en/SciTech/LymphaticSystem-18883.html http://www.buzzle.com/articles/lymphatic-systemfacts.html