* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download T cell
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
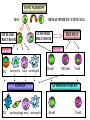
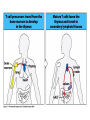
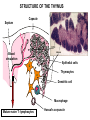
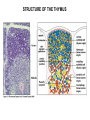
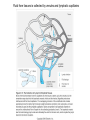
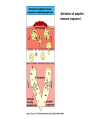
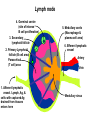
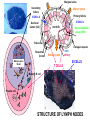
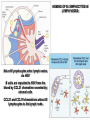
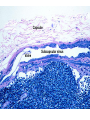
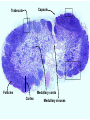
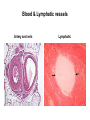
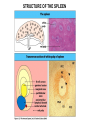
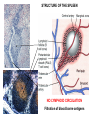
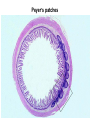
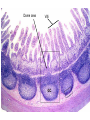
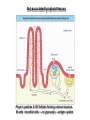
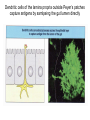
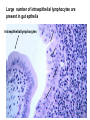
Organization of the lymphoid organs and tissues BONE MARROW HSC MYELOID PRECURSOR HEMATOPOIETIC STEM CELL LYMPHOID PRECURSOR BLOOD BLOOD DC monocyte mast neutrophil TISSUES DC THYMUS mackrophage mast neutrophil B-cell NK-cell T-cell LYMPHOID TISSUES B-cell T-cell STRUCTURE OF THE THYMUS Capsule Septum Blood circulation Epithelial cells Thymocytes Dendritic cell Macrophage Mature naive T- lymphocytes Hassal’s corpuscle STRUCTURE OF THE THYMUS THYMUS INVOLUTION PERIPHERAL LYMPHOID ORGANS Sites of lymphocyte activation and differentiation Spleen Lymph nodes Epithelial cell – associated lymphoid tissues Skin-associated lymphoid tissue (SALT) Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) Gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) Bronchial tract-associated lymphoid tissue (BALT) Organization (levels) of immunocytes Diffuse cells Follicle Patch organ Lymph nodes are communication centers within the immune system They form a unified, interconnected system via circulation of blood and lymph Fluid from tissues is collected by venules and lymphatic capillaries Activation of adaptive immune response I. Activation of adaptive immune response II. Lymph node 4. Germinal centre (site of intense B cell proliferation) 3. Secondary lymphoid follicle 2. Primary Lymphoid follicle (B cell area) Paracortical (T cell) area 1. Afferent lymphatic vessel. Lymph, Ag, & cells with captured Ag drained from tissues enters here 5. Medullary cords (Macrophage & plasma cell area) 6. Efferent lymphatic vessel Artery Vein Medullary sinus Marginal sinus Secondory follicle Afferent lymph Primary follicle B CELLS Germinal Center (GC) B CELLS medulla High endothelial venule (HEV) Trabecula Collagen capsule Paracortex Cortex mature,naive Mature,naive BB-sejt cell FDC Efferent lymph vein arthery B CELLS T CELLS Memory B cell Plasma cell STRUCTURE OF LYMPH NODES HOMING OF B LYMPHOCYTES IN LYMPH NODES Naive B lymphocytes enter lymph nodes via HEV B cells are reqruited to HEV from the blood by CCL21 chemokine secreted by stromal cells CCL21 and CCL19 chemokines attract B lymphocytes to the lymph node Capsule Subcapsular sinus Valve Capsule Trabecula Medullary cords Follicles Cortex Medullary sinuses Blood & Lymphatic vessels Artery and vein Lymphatic STRUCTURE OF THE SPLEEN STRUCTURE OF THE SPLEEN NO LYMPHOID CIRCULATION Filtration of blood borne antigens Spleen white pulp Transverse section Marginal sinus B cell corona Red pulp Germinal centre Marginal zone Periarteriolar lymphocytic sheath (PALS) – T cell area Central arteriole MALT Most pathogens attack mucosal epithelia Covered by mucus containing glycoproteins, proteoglycans, enzymes Antimicrobial peptides protect against physical damage and infection Thin dynamic layers covering large areas Well protected by the immune system More lymphocytes are assigned to the mucosal surfaces than to the rest of the body Peyer’s patches Dome area Villi GC Gut-associated lymphoid tissues Peyer’s patches 5-100 follicles forming a dome structure M-cells: microfold cells --- no glycocalyx – antigen uptake Transport of antigens via M cells Dendritic cells of the lamina propria outside Peyer’s patches capture antigens by samlpeing the gut lumen directly Large number of intraepithelial lymphocytes are present in gut epthelia Intraepithelial lymphocytes