* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Motivation and Emotion
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Cross-cultural psychology wikipedia , lookup
Bullying and emotional intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Positive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Expressive suppression wikipedia , lookup
Psychological stress wikipedia , lookup
Emotional labor wikipedia , lookup
Vladimir J. Konečni wikipedia , lookup
Emotion in animals wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Emotional self-regulation wikipedia , lookup
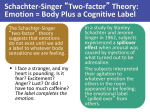
Physiological Differences – Polygraph – supports CannonBard Theory • Used to detect lies • measures physiological responses such as perspiration, heart rate, breathing • Problems – Anxiety, irritation, guilt have similar physiological activity • Guilty Knowledge Test – assesses physiological responses to crime scene details only known by investigators Cognition and Emotion • Sometimes emotions precede cognition (Zajonc) – Develop emotional preference for stimuli to which have been unknowingly exposed . • Some emotions occur without cognition, by-passing the cortex (LeDoux).Go directly from thalamus to amygdala = fast/ automatic emotional response – Ex. Jump at rustling bushes in the forest (fear most likely precedes conscious thinking) • Emotions arise when appraise event to be beneficial or harmful whether we know it or not(Lazarus) Detecting Emotion • Nonverbal cues – Facial muscles – Eyes (fear/anger) and mouth (happiness) – Duchenne smile – Difficult to detect lying • Introverts better than extroverts Gender, Emotion, and Nonverbal Behavior •Women better than men •Detecting emotions •Empathy •Emotional responsiveness •Facial expressions of emotion •Exception: anger Gender, Emotion, and Nonverbal Behavior Culture and Emotional Expression •Similarities: •display and interpret facial expressions – universal (Eckman) •Differences •Individualistic countries – convey visible facial expressions of inner feelings •Gestures vary Levels of Analysis for the Study of Emotion The Effects of Facial Expressions • Facial feedback – effect of facial expressions on emotion – Example: • Behavior Feedback Theory – effect of your behavior on emotions – Example: Basic Emotions • 10 Basic Emotions at birth(Izard) • Other’s are combo of the 10 basic Fear • Adaptive value of fear • Learned – Conditioning - fear things associated with naturally painful or traumatic experiences – Observational Learning • The biology of fear – Amygdala • Phobias – fear disrupts ability to cope Anger • Anger – Evoked by events – Catharsis – emotional release • Catharsis hypothesis – relieves aggressive urges/calms temporarily if – Directed against provoker – Justifiable – Target not intimidating • Example: – Expressing anger can increase anger Happiness • Happiness – Feel-good, do-good phenomenon – people are more helpful when in a good mood. • Example : – Well-being – happiness/satisfaction with life • Example: Happiness The Short Life of Emotional Ups and Downs • Watson’s studies Happiness Wealth and Well-Being Happiness Wealth and Well-Being Happiness • Happiness and Prior Experience – Adaptation-level phenomenon tendency to judge various stimuli relative to those we have previously experienced • Happiness and others’ attainments – Relative deprivation – tendency for our personal happiness to be heavily influenced by others’ attainment • Example - Happiness Predictors of Happiness Stress and Health • Health psychology - subfield of psychology that contributes to the prevention and treatment of illness – Example: • Behavioral medicine - interdisciplinary field that integrates and applies behavioral and medical knowledge to health and disease Stress and Illness • Stress - process by which we perceive and respond to environmental threats and challenges. – Stress appraisal – Short-lived or perceived as challenges = positive effects • Mobilizes immune system • Motivates – Prolonged = harms • Activation of sympathetic nervous system • Fight or flight (Cannon) - Adrenal glands secrete epinephrine and norepinephrine into blood steam – Cortisol (outer part of adrenal glands) • Tend and befriend (women) – oxytocin Stress • Social readjustment rating scale (SRRS) • Life Changing Units (LCUs)- marriage, change job, etc… • The more LCUs you have the higher your score is on the SRRS. • Those who score higher are more likely to have stress related disease. Seyle’s General Adaptation Syndrome • Describes our response to a stressful event. • Three stages 1. Alarm 2. Resistance 3. Exhaustion – Sources of Stress – daily hassles, too many things to do General Adaptation Syndrome Stress and the Heart • Coronary heart disease – closing of vessels that nourish the heart • Type A versus Type B (Friedman and Rosenman) – Type A – hard-driving impatient, verbally aggressive, anger prone – Type B – easygoing, relaxed Stress and Susceptibility to Disease • Psychophysiological illnesses – stress related physical illness – Examples – hypertension, headaches • Psychoneuroimmunology (PNI) – how psych, neural and endocrine system together affect immune system – Lymphocytes – 2 types of white blood cells • B lymphocytes – In bone marrow,release antibodies • T lymphocytes – In thymus and other lymphatic tissue, attack cancer cells, viruses – Macrophage – Immune system agent that ingests worn-out red blood cells and tiny harmful bacteria – Natural Killer (NK cells) - Immune system cells that pursue and destroy diseased body cells are called Stress and Disease • Arthritis – overactive immune system causes body to attack own tissue • AIDS – stress can speed progression of HIV to AIDS by limiting production of lymphocytes • Cancer – doesn’t create cancer cells, but may affect their growth by suppressing the activity of t-lymphocytes