* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 10mb ppt - UCLA.edu
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Major histocompatibility complex wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
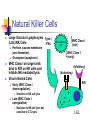
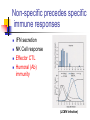
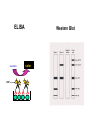
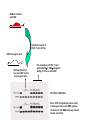
Immune Responses to Viral Infection Non-Specific Responses (Innate Immunity) Interferon Natural Killer Cells Complement and “Natural” Antibodies Specific Responses (Adaptive Immunity) Humoral (antibodies) Cell-mediated (e.g. CTLs) Interferons Interferon effects are mostly indirect Type I IFNs Induction of antiviral proteins (e.g Mx) Augmentation of cellular immune response (upregulation of MHC Class I) a, b, , t Induced by dsRNA, virus infection, IL1/IL-2/TNFa Produced by all cells Type II IFNs (IFN-g) Mediator of Ag-specific response Induced by IL-12 Produced by T cells, NK cells Significance of IFN response “Knock-out” mice IFN a/b knock-outs (Type I) IFN g knock-outs (Type II) Increased susceptibility to most viral infections Slight increase in susceptibility to some viruses Interpretation: Type I is more crucial than Type II IFN response Type I (secreted by all cells) is essential first line defense, Type II IFN is only one part of multicomponent effector immune response Natural Killer Cells Large Granular Lymphocytes Type I (LGL)/NK Cells IFNs Perforin (causes membrane pore formation) Granzymes (apoptosis) MHC Class I on target cells bind to KIR on NK cells and inhibits NK mediated lysis Virus Infected Cells MHC Class I (late) MHC Class I (early) (Inhibitory) (Activating) KIR Early (MHC Class I downregulation) Virus-infected cell Sensitive to NK cell lysis Late (MHC Class I upregulation) Resistant to NK cell lysis but sensitive to CTL lysis LGL Non-specific precedes specific immune responses IFN secretion NK Cell response Effector CTL Humoral (Ab) immunity (LCMV Infection) Complement and “NaturalAbs Complement cascade results in MAC--->cytolysis Initiated usually by Ag-Ab complex Usually, acts as effector mechanism for adaptive immune response May also act as “natural” antiviral p15e protein on some retroviruses binds C1q and activates complement cascade without effector antibodies p15e Complement and “Natural” Abs Gal (a1-->3) Gal Digalactose moiety not found in humans and Old World primates due to lack of a1--->3 galactosyl-transferase (a1--->3 GCT) Viruses grown in other mammalian cells can be neutralized by human or old-world primate sera (that have never seen the virus) due to high titer anti- Gal (a1-->3) Gal antibodies anti- Gal (a1-->3) Gal antibodies are pre-existing “natural” antibodies anti- Gal (a1-->3) Gal antibodies responsible for hyperacute rejection during xenotransplantation (e.g. using pig organs) Adaptive Immune Response B cell response T cell response Humoral “Cellul ar” B lymphocyte CD8 CTLp CD4 cytokine p Plasma cell CD8 CTL CD4 (cytokine) Immu nog lobuli ns (Igs) Perforins, gra nzymes, cytokines Persistence of effectors YES NO Ana mnestic (memory) response YES YES Type of immuni ty Precursor (memory) cell Effector cell Mediator molecules B Cell Responses IL-4 T Cell Responses IL-2, IFN-g Seeks out virally infected cells with viral peptides presented in context of MHC Class I Antibody Response Measurement Effector Functions Functional (Neutralization titers) Quantitative (ELISA) Qualitative (Western Blot) Viral Coating (inhibition of attachment, infection) Complement activation Opsonization (Virus-Ab complex removed by phagocytosis via Fc rceeptors on macrophages) Kinetics Neutralization Ab Titers 12 10 Ctrl Ab Neut. Ab PFU/ml 8 6 4 2 0 1/10,000 1/1,000 1/100 50% Neutralization titer 1/10 ELISA substrate color Y Y Y YYY HRP Western Blot Antibody Response Measurement Effector Functions Functional (Neutralization titers) Quantitative (ELISA) Qualitative (Western Blot) Viral Coating (inhibition of attachment, infection) Complement activation (Fc portion binds C1q and initiates complement cascade) Opsonization (Virus-Ab complex removed by phagocytosis via Fc receptors on macrophages) Kinetics Poliovirus Ab Titer (Reciprocal) Kinetics of Ab Response IgA --mucosal antibodies --IgA secreting plasma cells home into gut via CCR10; gut epithelium secretes MEC, which is the ligand for CCR10 --other chemokines can skew Ig response Time course and localization of Plasma Cells (Antibody Secreting Cells) Serum Ab Marrow ASC Ab titer is maintained for A long while (as opposed to Ag-specific CD8 effector cells) Measurement of Cellular Immune Response ssay Fresh or cultured cells Target cell or marker Readout DA miti ng dilution LDA say) Cultured Cell presentin g epitope bound to syngeneic Class I MHC 51 TL CTL ytolytic T cells) Fresh Cell presentin g epitope bound to syngeneic Class I MHC 51 etra mer Fresh Fluorescent complex with epitope bound to syngeneic Class I MHC FACS (fluore scent activated ce ll sorter) Intracellular ytokine Cytokine trace llul ar Fresh Fluorescent complex bound to intra cellular cytokine FACS (fluore scent activated ce ll sorter) LISPOT ELISPOT Fresh Secreted cytokine Monocellul ar focus of released cytokine Tetramer Cr release from targe t cells Cr release from targe t cells Tetramer Staining Y Y Y YY Staining using E (Effector Cell) CTL a-perforin Abs SAV TCR HIV-specific CTL Viral Antigen MHC Class I 51Cr T (Target Cell) Effector Functions of CD8 Lymphocytes Perforin and granzyme secretion upon recognition of Peptide/MHC I complex by TCR Perforin:pore formation, cytolysis Granzyme: tiggers apoptosis Cytokine secretion(IFN-g, TNF-a,IL-2) Activation induced apoptosis, viral purging(?) Relative contribution of CTL effector functions to viral clearance is virus specific E.g. clearance of LCMV is CTL dependent, while clearance of HBV is more cytokine dependent Wt Mice infected with HBV Adoptive Transfer of CD8+ T cells (CTLs) HBV Transgenic mice HBV-speciifc CTLs can clear HBV in liver of transgenic mice Pre-incubation of CD8+ T cells with anti-IFNg or TNFa abrogates ability of CTLs to clear HBV RT-PCR for HBV RNA Since 100% of hepatocytes (liver cells) in trasngenic mice carry HBV genome, clearance of viral RNA obviously cannot Involve cell death Kinetics of Cellular Immune Response: Effector vs Memory T Cells Effector CTLs appear rapidly but wane by 3-6 weeks post-infection Memory T cells persist for life time; maintained by homeostatic proliferation Neut. Ab Titer % Paralyzed Ab response: Protection against Re-infection Anamnestic Ab response Immmunity as host defense CTL response most important in controlling primary infection Ab response most important in protecting against re-infection