* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 08 Human immune system
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
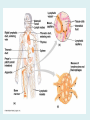
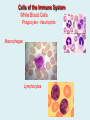
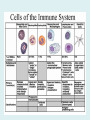
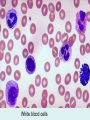
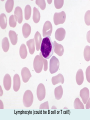
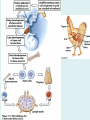
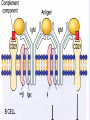
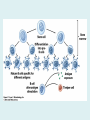
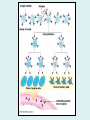
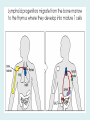
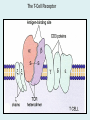
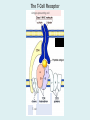
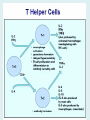
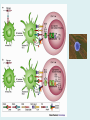
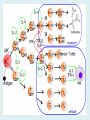
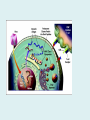
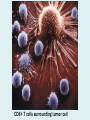
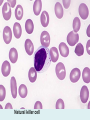
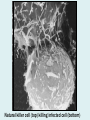
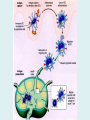
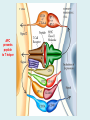
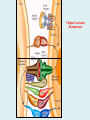
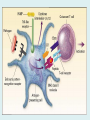
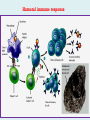
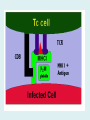
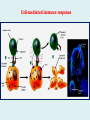
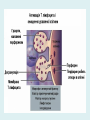
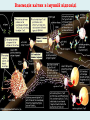
Human immune system CELLS COOPERATION IN IMMUNE RESPONSE PRIMARY OR CENTRAL LYMPHOID ORGANS are responsible for synthesis and maturation of immunocompetant cells. These include the bone marrow and the thymus. PERIPHERAL OR SECONDARY LYMPHOID ORGANS are sites where the lymphocytes localise, recognise foreign antigen and mount response against it. These include the lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils, adenoids, appendix, and clumps of lymphoid tissue in the small intestine known as Peyer's patches. They trap and concentrate foreign substances, and they are the main sites of production of antibodies. Cells of the Immune System White Blood Cells Phagocytes - Neutrophils Macrophages Lymphocytes White blood cells Lymphocyte (could be B cell or T cell!) Lymphocytes • Present in lymphoid organs and in blood • Groups • T-lymphocytes (grow up in thymus) • B-lymphocytes (grow up in bone marrow) • Each one has receptors for a specific antigen • Recognize millions of different antigens! • Diversity generated by: • rearrangement of antigen receptor genes • different joining of the gene segments • Gene rearrangement studies Lymphocytes B lymphocytes • Live in blood, bone marrow, lymphoid tissues • Basic function: make antibodies (immunoglobulins) • B-cell receptor complex recognizes antigens • binds antigen • sends signals to T cells • Antigens can be free and circulating (don’t have to be bound to MHCs or displayed by other cells to be recognized!) The B-Cell Receptor Lymphocytes T lymphocytes • Live in blood, bone marrow, lymphoid tissues • Two basic functions: • kill stuff • help other cells do their jobs • T-cell receptor (TCR) complex recognizes antigens • binds antigen • sends signals to the T cell • Antigens must be: • displayed by other cells… • …AND bound to an MHC receptor T Cell Selection in the Thymus Chapter 21, Immune System 1821.7 Figure The T-Cell Receptor The T-Cell Receptor Antigen-presenting cell T cell Lymphocytes T lymphocytes • Helper T cells • CD4+ (and CD8-) • help B cells make antibodies • help macrophages eat bugs • decreased in patients with AIDS • Cytotoxic T cells • CD8+ (and CD4-) • kill virus-infected cells and tumor cells CD8+ T cells surrounding tumor cell Lymphocytes Natural Killer Cells • Belong to innate immunity arm • No highly variable receptors like T and B cells • Main job: recognize and kill damaged or infected cells • Antigens don’t have to be bound to MHCs or displayed by other cells! Natural killer cell Natural killer cell (top) killing infected cell (bottom) Antigen-presenting cells • Main job: catch antigens and display them to lymphocytes • Dendritic cells • Have fine cytoplasmic projections • Present all over body: skin, lymph nodes, organs • Capture bug antigens, display to B and T cells • Other APCs • Macrophages eat bugs and present antigens to T cells, which tell macrophages to kill bugs • B cells present antigens to helper T cells, which tell B cells to make antibodies dendritic cells Antigen-presenting cells (APC) activate T helper cells APC presents peptide to Т helper T helper 2 activates B lymphocyte Humoral immune response Cell-mediated immune response Взаємодія клітин в імунній відповіді