* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lymphatic System and Immunity
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
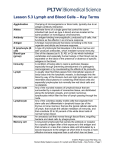
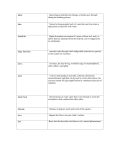
Lymphatic System and Immunity 22B Organ Systems • • • • • • • Integumentary Skeletal Muscular Respiratory Circulatory Digestive Excretory • • • • Nervous Reproductive Lymphatic Endocrine Lymphatic System • Water and some dissolved substances diffuse out of capillaries into the space between cells • Picked up by vessels of the lymphatic system • Once the watery solution is picked up by the lymphatic system it is called lymph • Pressure on the outside is greater than on the inside of the lymph capillaries so lymph diffuses in • Lymph capillary walls are a single cell layer. Cells overlap and only open in Lymph Pathway • Lymph capillaries- where lymph is picked up • Lymph vessels- lymph capillaries combine to form these, structurally similar to veins • Smooth muscle fibers in the walls move lymph along • One-way valves keep lymph moving in 1 direction • Lymph flows through numerous lymph nodes • Drains into two main ducts that join the blood stream where the jugular and subclavian veins meet in the shoulder region Lymphatic System • Lymphatic system doesn’t just pick up and return lymph to the bloodstream • It also is a part of immunity Pathogen • Infectious agent • Biological agent that causes disease or illness to its host • Virus, bacteria, fungus… (a) Streptococcus pneumonia, (b) Pseudomonas aeruginosa, (c) Candida, (d) Staphylococcus aureus, and (e) Escherichia coli. Infections with any of these pathogens can lead to sepsis. If a patient does not receive medical intervention within hours, death is imminent. st 1 Line of Defense • Skin- keeps things out • Mucous membranes- line internal surfaces exposed to outside. Nose, mouth, lungs, eyelids, sex organs Inflammatory Response • Inflammatory Response – Mast Cells- specialized cells in connective tissue that search for antigens (unknown proteins) and release signaling molecules like histamine – Histamine makes blood vessels more permeable allowing fluid and white blood cells to flow to infected area causing inflammation – Allergic reactions are an inflammatory response so you may take an antihistamine Leukocytes (White Blood Cells) • Leukocytes – Phagocytes – phagocytosis is the process where a cell ingests solid material • Neutrophils – eat and die, these dead cells are what form pus, mobile traveling through blood and lymph • Macrophages – big eaters, more stationary, embedded in various tissues • Natural Killer Cells – Lymphocytes • T Cells – – – – Helper Cytotoxic or Killer Suppressor Memory • B Cells http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BDr44vLNnPY Types of Immunity • Innate Immunity – – – – – Quick Nonspecific Every animal has it, even sponges Have it from birth Macrophages play primary role • Acquired or Adaptive Immunity – Develops only in vertebrates – Specific – Lymphocytes play primary role Innate or Nonspecific Immunity • • • • All living things have this You are born with it Responds the same to different pathogens Involves humoral and cell mediated components, but it is just a basic immune response Acquired or Adaptive Immunity • Only in vertebrates • Develops during your life • Memory cells allow your body to respond specifically and quickly to secondary infections which are infections from pathogens your body has previously identified • Vaccines- weakened pathogens that don’t cause disease but allow your body to learn how to defend against that disease • Booster shots- additional vaccine that builds up your immune system • Serum- antibodies extracted from the blood of an immune person or animal. Provides short term immunity, but could allow a person’s body to learn how to fight an infection Leukocytes Lymph Nodes • Numerous masses of tissue along the lymph vessels • Filters and destroys bacteria, viruses, and other foreign matter from lymph Lymph Node Anatomy • Layer of connective tissue surrounding small groups of cells • Pinhead to dime size • All over the body, but usually more numerous in the floor of the mouth, neck region, armpit, and groin Fixed Macrophages • Engulf pathogens and digest them in vacuoles • Lymph nodes around infected area may become swollen as the fixed macrophages fight the infection • Severe Bacterial Infection – Bacteria could overwhelm lymph node and grow there – Could enter blood stream and be carried to other parts of the body • Some things cannot be digested – Tobacco smoke particles – Asbestos Lymphatic Disorders and Diseases • Edema – Body tissues swell with excess fluid – Lymph vessels could be blocked causing elephantiasis – Backup of blood in systemic circulation due to congestive heart failure • Hodgkin’s disease- cancer that causes lymph nodes, spleen, and liver to become abnormally large • Mononucleosis – Lots of monocytes (another type of leukocyte) in blood – Virus that usually infects people who are fatigued, stressed, and lacking proper rest and nourishment • Tonsillitis – Inflammation of the tonsils – May be caused by a variety of organisms and viruses Lymphatic Organs • Tonsils – In the pharynx region – Several small lymph nodes covered by connective tissue • Thymus gland – Between aorta and sternum – Produces T lymphocytes • Spleen – Immediately inferior to the diaphragm on the left side – Similar to a large lymph node, but it filters blood instead of lymph Immunity • Immune- body reacts to the presence of a pathogen by destroying it or rendering it harmless • Antigen (antibody generator)- any foreign substance (usually a protein) to which the body responds by making chemicals or specialized cells that eliminate that antigen, could be produced by a pathogen or on the surface of a pathogen • Antibodies- proteins that circulate through the body dissolved in blood or lymph, involved in destroying antigens, most of the time they tag foreign molecules or cells and send out a chemical signal so macrophages or lymphocytes can come and destroy the antigen Lymphocytes • A kind of white blood cell (leukocyte) responsible for the bodies immune response • Produced in red bone marrow • All are initially alike but they mature into different kinds • Recognize specific antigens 2 Types of Lymphocytes • T cells – Develop in the thymus – 70-80% of circulating lymphocytes – Cell mediated immunity • B cells – Develop in the bone marrow – 20-30% of circulating lymphocytes – Humoral immunity Cell Mediated Immunity • Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)- set of cell surface molecules that all cells in your body have. Mediate the interaction of leukocytes with cells • The cell‐mediated response involves mostly T cells and responds to any cell that displays abnormal MHC markers, including cells invaded by pathogens, tumor cells, or transplanted cells. Cell Mediated Immunity Activation • Antigen presentation occurs – Macrophage ingests an antigen forming an antigenmacrophage complex – Helper T cells with a matching receptor bind to the complex • Macrophage secretes a polypeptide called interleukin-1 • Helper T cell secretes another polypeptide called interleukin 2 • Helper T cells rapidly divide and activate the other types of T cells Types of T Cells • • • • Helper Cytotoxic or Killer Suppressor Memory Helper T Cells • May cause plasma cells to produce antibodies and other chemicals • Some of those chemicals attract macrophages Cytotoxic T Cells • Attack body cells affected by antigen • Attaches to affected cell and releases protein that perforates the cell’s membrane and kills it Suppressor T Cells • Produced and released towards the end of the fight • Stop cytotoxic T cells, helper T cells, and plasma cells Memory T Cells • Made during an infection • Recognize antigen-macrophage complex if it appears again and divides rapidly forming cytotoxic and helper T cells Humoral Immunity • The humoral response (or antibody‐mediated response) involves B cells that recognize antigens or pathogens that are circulating in the lymph or blood (“humor” is a medieval term for body fluid). Humoral Immunity • Presence of an antigen and/or the presence of interleukins released by an activated helper T cell activate the B cells • B cells divide and produce plasma cells that have antibodies that bind to antigens • B cells produce memory cells Autoimmune Diseases • Immune system cannot distinguish the body from foreign invaders • Body produces antibodies and cytotoxic T cells that attack and damage cells of the body 60 Minutes – Killing Cancer – Part 1 http://www.cbsnews.com/videos/killing-cancer-part-one/ 60 Minutes – Killing Cancer – Part 2 http://www.cbsnews.com/videos/killing-cancer-part-two/ Review Videos Lymphatic System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_GinTV94hUk What is Lymph? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2Bq2xopLew8 Lymphatic System and Immunity https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kjLwVqxwaIM