* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Kuby Immunology 6/e - Dr. Jennifer Capers, PhD
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
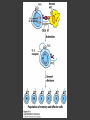
Chapter 11 T-cell Activation and Differentiation Dr. Capers Kindt • Goldsby • Osborne Kuby IMMUNOLOGY Sixth Edition Chapter 10 T-Cell Maturation, Activation, and Differentiation Copyright © 2007 by W. H. Freeman and Company Initiating event of adaptive immune response ○ Interaction between niave T cell and an antigen-presenting cell ○ Signal 1 – provided by antigen-specific TCR engagement ○ Signal 2 – provided by contact with costimulatory ligand expressed by APC - Example - CD28 ○ Signal 3 - cytokines T cell Activation Initiated by TCR-CD3 complex with processed antigen on MHC molecule ○ CD8+ cells with Class I ○ CD4+ cells with Class II Initiates cascade of biochemical events ○ Inducing resting T cell to enter cell cycle, proliferate, differentiate into memory and effector T cells T cell Activation Cascade of biochemical events leading to gene expression: Interaction of signal and molecule (example: TCR + MHC and antigen) Generation of “second messenger” that diffuses to other areas of cell Protein kinases and protein phosphatases are activated or inhibitied Signals are amplified by enzyme cascades Click on link to see example http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tMMrTRnFdI4&f eature=player_detailpage T cell Activation Gene products after activation ○ Immediate genes (1/2 hour of recognition) Transcription factors (c-Myc, NFAT, NF-κB) ○ Early genes (1-2 hours from recognition) IL-2, IL2R, IL-6, IFN-γ ○ Late genes (more than 2 days later) Encode adhesion molecules Go onto Next slide Superantigens Bind to BOTH the TCR and MHC Can cause over-activation Overproduction of TH-cell cytokines, leading to systemic toxicity Exogeneous Variety of exotoxins secreted by some Gram+ bacteria Endogeneous Cell membrane proteins encoded by viruses T-Cell Differentiation CD4+ and CD8+ cells leave thymus and enter circulation in G0 phase ○ Naïve cells (condensed chromatin, little cytoplasm) ○ About twice as many CD4+ Naïve cell recognized MHC-antigen complex ○ Initiated primary response ○ After 48 hours, enlarges into blast cell and undergoes repeated rounds of cell division ○ Differentiate into: - Effector cells – cytokine secretion, B-cell help - Memory cells – long lived, respond with heightened activity (secondary response) Treg Cells Shown to inhibit proliferation of other T cells in vitro CD4+CD25+ Shown to inhibit development of autoimmune diseases Cell Death and T Cell Populations Apoptosis plays critical role Deletion of potentially autoreactive thymocytes Deletion of T cell populations after activation ○ Fas and FasL pathway to induce self death