* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cognitive Learning Theories
Behavioral economics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Clark L. Hull wikipedia , lookup
Perceptual learning wikipedia , lookup
Instructional simulation wikipedia , lookup
Machine learning wikipedia , lookup
Deeper learning wikipedia , lookup
Transformative learning wikipedia , lookup
Gamification of learning wikipedia , lookup
Differentiated instruction wikipedia , lookup
Situated learning wikipedia , lookup
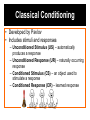
Overview of Learning Theory Scholar Training Project for Southwest Jiaotong University Presented by Dr. J. Shane Robinson Associate Director, ITLE Behavioral Learning Theories • Behaviorism • Social Cognitive Behaviorism Theory • Learning is a change in behavior. • Explains learning in terms of environmental and external events. • Interested in how people respond to stimuli. Behaviorism cont. • Stimuli – perceivable units of the environment or events that may affect behavior • Responses – observable reactions to stimuli • Contiguity – whenever two sensations occur together over and over again, they become associated • School bell (stimulus) • Scurrying student – zipping backpacks, slamming lockers, crowded hallways, etc. (responses) Types of Behaviorism 1. Classical Conditioning 2. Operant Conditioning Classical Conditioning • Developed by Pavlov • Includes stimuli and responses – Unconditioned Stimulus (US) – automatically produces a response – Unconditioned Response (UR) – naturally occurring response – Conditioned Stimulus (CS) – an object used to stimulate a response – Conditioned Response (CR) – learned response Operant Conditioning • Developed by B. F. Skinner • People learn by doing. • Learn through reinforcement & punishment. – Reinforcer – A stimulus that increases the frequency of behaviors. Social Cognitive Theory • Developed by Albert Bandura • Learning occurs in a social environment. • Assesses one’s self-esteem and self-efficacy. Social Cognitive cont. • Social Cognition – learning occurs through modeling and observing. – Observational learning – when a person observes or imitates someone else’s behavior. – Self-efficacy – the belief that one can master a situation and produce positive outcomes. 4 Factors of Observational Learning 1. Attention – Learners must attend to the model. 2. Retention – Learners must retain the behavior. 3. Production – Learners attempt to produce the behavior. 4. Motivation – Desire to reproduce the behavior. Cognitive Learning Theories AGED 3103 Dr. Robinson What do you see? Kitchel & Torres (2005) Comparing the two sets of Theories • Behavioral Learning Theories – focuses on observable changes in outward behavior & on the impact of external stimuli to effect change. • Cognitive Learning Theories – focuses on the internal mental processes, how they change, and how they affect external behavior changes. Behavioral vs. Cognitive Learning Behavioral • New behaviors are learned. • Reinforcement strengthens responses. • Teacher-centered instruction Cognitive • Knowledge is learned. • Reinforcement is feedback or information. • Student-centered instruction Cognitive View of Learning • Look at how people process and organize information and construct knowledge. • Assess how people make sense of the knowledge they gain. • Assume that humans are active participants in their own acts of cognition. Cognitive Learning Theories • Constructivism • Information Processing • Brain-Based Learning (BBL) Constructivism • Individuals must experience learning. • Meaning must occur. • Prior knowledge must exist. Elements of Constructivism • Embed learning in complex, realistic, and relevant learning environments. • Learning is a shared responsibility. • Learning supports multiple perspectives. • Encourages ownership in learning. Information Processing Theory • Encoding – process of gathering and representing information • Storage – process of putting new information in memory • Retrieval – remembering previously stored information Types of memory • Sensory • Working • Long-term Sensory memory • Holds information in original form • Has large capacity • Short duration (1-3 seconds) Working memory • Where info. is held while it is processed • 5-9 bits of info. for 20-30 seconds • Maintenance rehearsal – repeating info. over and over again • Elaborative rehearsal – associating info. with something you already know Long-term memory • Holds info. for long periods of time • Declarative knowledge – “knowing that” something is the case; facts – Semantic – general knowledge about the world – Episodic – info. tied to a particular time & place • Procedural memory – how to do things • Large capacity Quiz • • • • • • • • Utah Banana Shoe Alabama Corn Shirt Washington Hat • • • • • • • • California Watermelon Dress Louisiana Cantaloupe Coat Florida Boxers Quiz Brain-Based Learning • An extension of info. processing theory. • Identifies the brain and its functions in the learning process. • Determines ways in which the brain operates. • Focuses on emotions and experiences. • Focuses on the learning environment. – Safety and security of students are a must! How the brain functions • New dendrites are formed. • Connections increase in complexity. • Neurons fire to create a stronger, more intense, connection. Factors associated with BBL • • • • Emotion Relevance Patterns and Context Meaning What do you see? Kitchel & Torres (2005) What about now? Kitchel & Torres (2005)