* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diffusion, Osmosis, Active Transport
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
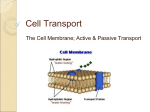
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Diffusion, Osmosis, Active Transport Biology Notes GCE Study Buddy Diffusion Diffusion is the net movement of ions or molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration, down a concentration gradient In liquids and gases, molecules possess kinetic energy and constantly move about As this movement is random, an equilibrium is reached when the molecules are evenly spread out, where there is no more net change – dynamic equilibrium reached The steeper the gradient for a substance, the faster the rate of diffusion No energy input is required for diffusion because the particles already are in motion. Hence, it is know as passive transport Diffusion permeable membrane water 20 potassium iodide ions 20 copper sulphate ions Key potassium iodide ions copper sulphate ions 10 potassium iodide ions, 10 copper sulphate ions 10 copper sulphate ions, 10 potassium iodide ions Factors affecting diffusion What are some factors affecting the rate of diffusion? Concentration gradient Temperature Pressure size of particles surface area to volume ratio Osmosis Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from a solution of higher water potential to a solution of lower water potential through a partially permeable membrane Water potential is a measure of the tendency of water to move from one place to another A water potential gradient is established when a partially-permeable membrane separates two solutions of different water potentials. A dilute solution contains more water molecules per unit volume than a concentrated solution so it has a higher water potential than a concentrated solution Osmosis Osmotic pressure is the pressure that must be applied to a solution to prevent the inward flow of water across a partially permeable membrane . Osmotic pressure is the opposite of water potential. A partially permeable membrane is a membrane that will allow certain molecules or ions to pass through it by diffusion. The cell membrane is partially permeable. What other structures or organs are partially permeable? Osmosis rise in level A B A 5% sucrose solution (more water, less sucrose) B A B drop in level water molecules diffuse from B to A. partially permeable membrane 8 sucrose molecules, 9 water molecules 4 sucrose molecules, 18 water molecules Key sucrose molecule water molecule Net movement of water molecules 8 sucrose molecules, 18 water molecules 4 sucrose molecules, 9 water molecules Hypotonic, Isotonic, Hypertonic (animal cells only) Lower water potential Equal water potential Higher water potential Plant cell in high water potential solution As water enters the cell, the vacuole increases in size and pushes the cell contents against the cellulose cell wall. The cell wall prevents over expansion of the cell by exerting an opposing pressure preventing the entry of more water A plant in this state becomes turgid The turgidity of the cell with water is called turgor pressure The plant cell does not burst because the cell wall is strong and relatively inelastic Animal cell in high water potential solution Animal cell will swell and may bust in a hypotonic solution because it does not have a cell wall in a solution with high water potential Plant cell in low water potential solution The water potential of the cell sap is higher than that of the solution outside the cell. Osmosis takes place and water moves out of the cell As water is lost from the cell, the vacuole decreases in size and the cytoplasm shrinks away from the cellulose cell wall. This shrinkage of the cytoplasm away from the cell wall when plant cells are immersed in a solution of low water potential is known as plasmolysis The cells are said to be plasmolysed. The cells can be restored by placing them in water or solution of high water potential Plant cell in low water potential solution water leaves by osmosis Cytoplasm shrinks away from cell wall in a solution with low water potential As the cell loses water, the vacuole decreases in size. The cell becomes plasmolysed Animal cell in low water potential solution Animal cells in hypertonic solution: it will lose water and the cell membrane will form little spikes as water is lost and the cell shrinks, a process called crenation. The cell dies eventually Spikes form in a solution with low water potential Turgor in plants Turgor is very important in maintaining the shape of soft tissues in plants Young stems and most leaves, esp. those of herbaceous or non-woody plants, can remain firm and erect because of the turgor pressure within their cells. When there is a high rate of evaporation of water from the cells, they lose their turgidity and the plant wilts The movement of certain plants are due to changes in turgor Eg opening and closing of the stomata, folding of leaflets of the Mimosa plant Active Transport Active transport is the process in which energy is used to move the particles of a substance against a concentration gradient from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration Occurs in living cells because only living cells respire Active transport The energy used in cells is called “ATP”. Active transport requires: Protein transporters ATP (or energy) Active transport occurs in: Absorption of mineral salts by root hair cells. Absorption of glucose and amino acids by cells in the small intestine. Na-K pump Example of Active Transport Absorption of mineral salts by root hair cells The soil solution has to have a higher water potential than the root hair cell in order for water to move into the root hair cell by osmosis. This means that the soil solution has a lower concentration of ions (ie. mineral salts) than the root hair cell. Therefore, active transport is used to transport ions into the root hair cell. Specific transporter proteins Energy expended. Transport of large molecules Some substances are too large to cross the plasma membrane by diffusion, facilitated diffusion and osmosis Other means of transport are necessary: Endocytosis Exocytosis Surface area: Volume ratio The greater the area of cell surface membrane, the faster will be the rate of diffusion of a substance for a given concentration gradient Surface area: Volume ratio The greater the surface area to volume ratio, the faster the rate of diffusion. This explains why cells are so small: nutrients, oxygen and waste substances have to diffuse into and out of cells quickly. Eg. Question Four clear agar blocks were placed into solutions of methylene blue as shown. Which agar block would be first to become completely stained? A D C B 6mm 4mm 4mm 2mm 2mm 2mm 2mm 2mmRanee Mohan 2mm 2mm 4mm 4mm Question An experiment to investigate osmosis is set up as shown. What happens? A B C D Volume of the liquid in tube X Decreases Decreases Increases Increases Concentration of the sugar solution Decreases Increases Decreases Increases Ranee Mohan Tube X Partially permeable membrane Question A plasmolysed cell is shown. Which numbered structures are partially-permeable? A. 1 only B. 2 only C. 1 and 2 only 1 2 D. 1 and 3 only 3 Question Four identical pieces of potato are treated in two stages, as shown. Which piece of potato will be the largest after two hours? Stage 1 A Stage 2 Placed in 10% salt solution C Boiled in water for 10 min Boiled in water for 10 min Unboiled D Unboiled Placed in distilled water B Ranee Mohan Placed in distilled water Placed in 10% salt solution Question Which one of the following enters plant cells by active transport? A. Carbon dioxide B. Nitrate ions C. Water D. Oxygen