* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Artifacts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
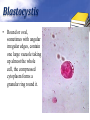
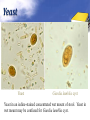
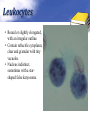
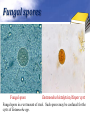
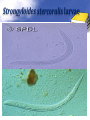
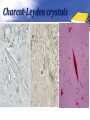
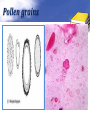
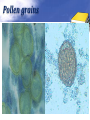
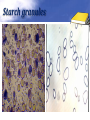
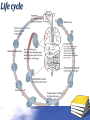
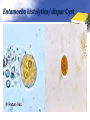
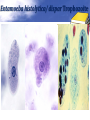
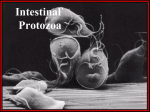
Definition Artifacts: other things, living or artificial, present in the stool that are not parasites and could mislead the laboratory worker. Note: “Artifacts not to be mistaken for cysts”. Blastocystis • Round or oval, sometimes with angular irregular edges, contain one large vacuole taking up almost the whole cell, the compressed cytoplasm forms a granular ring round it. Blastocystis Yeast • Oval, often with buds, often contain eccentric cluster of 3-6 small granules. • Some related forms of yeast are rectangular, with a very clear oval cytoplasm inside: arthrospores. Yeast Yeast Giardia lamblia cyst Yeast in an iodine-stained concentrated wet mount of stool. Yeast in wet mount may be confused for Giardia lamblia cyst. Leukocytes • Round or slightly elongated, with an irregular outline. • Contain refractile cytoplasm, clear and granular with tiny vacuoles. • Nucleus indistinct, sometimes with a starshaped false karyosome. Pus • Pus can be seen by the naked eye as opaque, greyish streaks( not transparent like mucus). • Under the microscope it appears as a mass of more or less degenerate leukocytes Bacteria Coccidia • These are protozoa that may be parasite of men without causing any significant pathogenic effects, or may be found in transit in stool following the consumption of infected foods. • They appear in stool in a form resembling cyst called oocysts or sporocysts. • An elongated oval, sometimes tapered at one pole. • There three types: a. 4 sporozoites (small banana shaped rods), each containing a small round nucleus, sometimes a few large granules massed at one pole. b. One large round granular cell. c. Refractile granules completely fill the interior. Coccidia (cont.) Coccidia (cont.) Air bubbles Oil droplet Fungal spores Fungal spore Entamoeba histolytica/dispar cyst Fungal spore in a wet mount of stool. Such spores may be confused for the cysts of Entamoeba spp. Plant fiber Strongyloides stercoralis larvae Misdiagnosis can lead to improper treatment Hair fiber Plant cell May confused with helminthes eggs Plant cell • Plant material in an iodine-stained concentrated wet mount of stool. This material can be confused for a hookworm egg Charcot-Leyden crystals Epithelial cells Macrophages RBCs Raed Z. Ahmed, Medical Parasitology Lab.,2012 Pollen grains Pollen grains Starch granules Crystals Non- parasitic structure found in stool Non parasitic objects may be misidentified as parasites. The differentiation of the most common pseudoparasites is as follow: 1. Protozoan cyst: may be confused with air bubbles, fat globules or yeasts. – Iodine should be added to the wet preparation so that the internal structure of the cyst is stained and identifiable. 2. Amoebic trophozoites: must be differentiated from non- pathogenic protozoan trophozoites and macrophages. – Trophozoites of Entamoeba histolytica/dispar must be motile and hematophagus. – Macrophages found in cases of intestinal amoebiasis are distinguishable from amoebic trophozoites by possessing a larger nucleus and, although they can haematophagus, they are only motile for a very short time. Their pseudopodia are small, blunt and granular. Cont. 3. Ova, their general shape, except for Entrobius, is perfectly symmetrical, distinguishing them from various objects found in stools. 4. Trichuris and Taenia ova may be confused with pollen grains. 5. Ascaris ova may be confused with vegetable cells, the latter having smooth, thick walls but irregular shape. 6. Strongyloides or hookworm larvae can be confused with hair or vegetable fibers. The latter are usually tapered at one end and the other being blunt and with no internal structure. – Free living nematode larvae may be found in concentrates if contaminated water is used Cont. 7. Fasciola ova resemble vegetable cells. 8. Insect and may be found in stools as spurious infection. Mite eggs may be confused with hookworm eggs. 9. Dipylidium caninum eggs sacs can look similar to vegetable cells. 10. Other structure found in stool are crystals, CharcotLeyden are the breakdown products of eosinophil cells and may be present in stools or sputum. 11. Starch granules are sometimes seen in stool. When undigested, they appear as concentric rings and stain blue with iodine, when partially digested, they stain red. Entamoeba histolytica/ dispar • E. histolytica inhabit large intestine and cause amoebic dysentery. • There is two diagnostic stages for E. histolytica/ dispar: 1. Cyst is regular round measuring measure 10 – 20u in diameter with 4 nuclei, and it’s the infective stage. 2. Trophozoite is the motile form, measure 15-20u in diameter with large nucleus. (motility by pseudopodia). • Diagnosis: – Stool examination to see cyst stage, or trophozoite stage if the sample is fresh. Life cycle Entamoeba histolytica/ dispar Cyst Entamoeba histolytica/ dispar Trophozoite