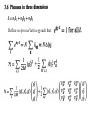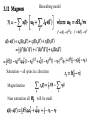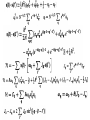* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download reciprocal lattice g
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Scalar field theory wikipedia , lookup
Nitrogen-vacancy center wikipedia , lookup
Quantum key distribution wikipedia , lookup
Coherent states wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Wave function wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Perturbation theory wikipedia , lookup
Path integral formulation wikipedia , lookup
Ising model wikipedia , lookup
Copenhagen interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Bell's theorem wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
Spin (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Dirac equation wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Physics 541 A quantum approach to condensed matter physics Define reciprocal lattice g such that Polarization directions Example - heat capacity Thermal conductivity and thermal expansion depend on phonon interactions We need a better definition for quantum mechanical magnetic moment In classical mechanics the Lorentz force is Lagrange’s equation states that This requires But remember that classically So So One spinless electron So Add magnetic field This is like a perturbation added to Spin is a relativistic effect. Expand Dirac equation in powers of 1/c Spin s is like orbital angular momentum L Heisenberg model Saturation -- all spins in z direction Magnetization Near saturation all will be small Bohr magneton At low temperatures only small excited, for which =