* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 投影片 1
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Monte Carlo methods for electron transport wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum logic wikipedia , lookup
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Identical particles wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Quantum vacuum thruster wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Compact Muon Solenoid wikipedia , lookup
Uncertainty principle wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Future Circular Collider wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Wave packet wikipedia , lookup
Relational approach to quantum physics wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Probability amplitude wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum tunnelling wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
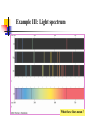
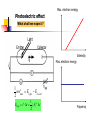
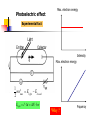
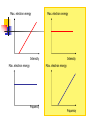
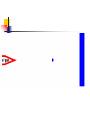
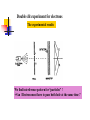
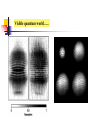
波動還是粒子? ─量子世界的奧秘 清華大學物理系 王道維教授 Wave or particle ? Brief History: Let’s go back to 100 years ago ….. 1684 Isaac Newton, Principa 1768 Stream engine was invented.. 1781 I. Kant, Critique of Pure Reason 1783 American independence revolution 1789 French revolution 1831 Electric engine was invented Science is almost ended in the Newton physics and Maxwell equations. All others are just details. From human side, they believe that human beings are good enough to protect this world and themselves. However, the first was broken by the discovery of quantum physics in 1905, while the second hope was broken by World War I in 1914…. Example I: Periodic table Order ? Example II: Atom structure How can atom be stable ? Example III: Light spectrum What these lines mean ? Max. electron energy Photoelectric effect What shall we expect ? Intensity Max. electron energy 1 2 mvmax Elight Ebound 2 Elight I t 1 | A |2 t 2 Frquency Photoelectric effect Max. electron energy Experimental fact Intensity Max. electron energy 1 2 mvmax Elight Ebound 2 Elight I t N h Why ? Frquency Max. electron energy Max. electron energy Intensity Intensity Max. electron energy Max. electron energy Frquency Frquency Conceptual questions…. What is the meaning of “frequency”, “waveelngth” for a single photon ? What is the meaning of “quantized energy” for a light wave ? How could we understand the interference effects between two light sources by photons ? Is light a wave or a particle ? Double slit experiment for electrons What shall we expect ? A particle cannot pass two holes at the same time It must pass through one of them Probability=P1+P2 What is this wavelength about ? Double slit experiment for electrons The experimental results We find interference pattern for “particles” ! An Electron must have to pass both hole at the same time ? If we want to measure it….. We find a very surprising result…. Both light and massive particles are not like what we expect in the ordinary situation…. Their properties cannot be simply understood by our common sense in the ordinary world…. We need to do the experiment to measure their properties before we could say about them. But measurement can changes the results dramatically …. Is there something wrong ? Basic concept of Quantum mechanics 1. For an EM wave, we have E h 2. For a massive particle, we have h p 3. For a single particle, it is described by a wavefunction, (r , t ) which describe the probability to find a particle at position r at time t is P(r , t ) | (r , t ) |2 4. The wavefunction follows the Schrodinger equation: ( x, t ) 2 2 ( x, t ) i V ( x) ( x, t ) 2 t 2m x 5. One could not know anything (but probability) about a single event But not only we do not like it…. A. Einstein: God does not play dice with the universe. Gradually we used to it…. R.P. Feynman: I think it is fair to say that no on really understand quantum mechanics…. We just know how to calculate it…. Quantum tunneling: STM STM image: STM Matter wave to understand this world….. Standing wave gives discrete energy level ! Pauli exclusion principle then explains the preriodic table ! E=hv makes the discrete energy level to be observed by discrete light spectroum. Visible quantum world….. Quantum world is much more dramatic than what people could image in ordinary life ! What is more surprising is : we human beings can “understand” this strange world ?!