* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Modern Physics Guide
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum teleportation wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Coherent states wikipedia , lookup
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Hamiltonian wikipedia , lookup
Ensemble interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Delayed choice quantum eraser wikipedia , lookup
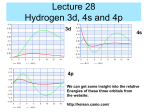
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Identical particles wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
Wheeler's delayed choice experiment wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Copenhagen interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Probability amplitude wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Wave function wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Modern Physics Guide Relativity: What will all observers agree on? Speed of light What events take place (collisions, emission and absorption, and so forth) What events cause others. The mass of an object. What measurements change from one observer to another? Simultaneity of events separated in space. Elapsed time Length in direction of motion Early Quantum: Discovery of electrons, nuclei, neutrons. Black body radiation led to light quantization, constant h. Radioactivity, alpha and beta particles, gamma rays. Xray diffraction and atomic spacing. Atomic line spectra, led to Bohr’s orbit model of the atom. Photoelectric effect Einstein brings the photon to light. QM E=hf, p = h/λ De Broglie, confirmed by photoelectric effect and e- diffraction. Subatomic quanta are particle and wave simultaneously. Square of wave function is a probability amplitude. (standard) Square of wave function is a distribution of energy density of particle. (Ol’ Doc Grey) Double slit interference: quantum must pass through both slits to produce interference. Interference pattern is a probability distribution for finding the quantum at the screen. Making a measurement collapses the wave function to that for the result. Uncertainty principle: ΔpΔx≥ħ ; ΔEΔt≥ħ due to the wave nature of the quantum. Pattern of wave functions (like standing waves), shape and order of functions. Exponential decay of wave function when E<potential energy. Tunneling and how it works. Particle in a well solution, energy and confinement of particle. Spin and angular momentum. Nuclear Fission and fusion Calculation of energy from mass difference. Identifying single missing particles. High Energy Physics Leptons, mesons, baryons Fundamental forces, exchange bosons. Feynman diagram of an interaction. Conservation laws: charge, angular momentum, lepton number, baryon number, momentum Antiparticles