* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter28ReadingQuiz..
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Uncertainty principle wikipedia , lookup
Quantum tunnelling wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
ATLAS experiment wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Relational approach to quantum physics wikipedia , lookup
Identical particles wikipedia , lookup
Wave function wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Compact Muon Solenoid wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Wave packet wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
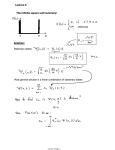
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Chapter 28 Reading Quiz Dr. Harold Williams Reading Quiz 1. The photoelectric effect tells us that A. B. C. D. electrons have a wave nature. light has a particle nature. a photon can be converted into an electron. electrons are the conductors in metals. Slide 28-6 Answer 1. The photoelectric effect tells us that A. B. C. D. electrons have a wave nature. light has a particle nature. a photon can be converted into an electron. electrons are the conductors in metals. Slide 28-7 Reading Quiz 2. Which of the following wave properties are exhibited by particles? A. B. C. D. Diffraction Interference Superposition All of the above Slide 28-8 Answer 2. Which of the following wave properties are exhibited by particles? A. B. C. D. Diffraction Interference Superposition All of the above Slide 28-9 Reading Quiz 3. If you precisely measure the position of a particle, you A. B. C. D. destroy its wave nature. cause it to diffract. destroy all information about its speed or momentum. cause the particle to be annihilated. Slide 28-10 Answer 3. If you precisely measure the position of a particle, you A. B. C. D. destroy its wave nature. cause it to diffract. destroy all information about its speed or momentum. cause the particle to be annihilated. Slide 28-11