* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 16: DEVELOPMENTAL PSYCHOPATHOLOGY
Bipolar II disorder wikipedia , lookup
Anorexia nervosa wikipedia , lookup
Impulsivity wikipedia , lookup
Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Fragile X syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Bipolar disorder wikipedia , lookup
Autism and working memory wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Rumination syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Social anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Empathizing–systemizing theory wikipedia , lookup
Munchausen by Internet wikipedia , lookup
Depersonalization disorder wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Schizoaffective disorder wikipedia , lookup
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology of autism wikipedia , lookup
Global perceptions of autism wikipedia , lookup
Eating disorders and memory wikipedia , lookup
Eating disorder wikipedia , lookup
Antisocial personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Major depressive disorder wikipedia , lookup
Conduct disorder wikipedia , lookup
Combat stress reaction wikipedia , lookup
Memory disorder wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Discrete trial training wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
Conversion disorder wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary approaches to depression wikipedia , lookup
Autism therapies wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
History of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Treatment of bipolar disorder wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral theories of depression wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Autism spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Externalizing disorders wikipedia , lookup
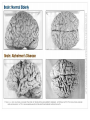
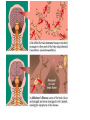
Chapter 16 Developmental Psychopathology • Chapter 16: DEVELOPMENTAL PSYCHOPATHOLOGY Abnormality – Statistical deviance – Maladaptiveness • Interferes with personal and social life • Poses danger to self or others – Personal distress – DSM-5 diagnostic criteria (APA) • Developmental Aspects Developmental psychopathology – study of origins and course of maladaptive behavior • Disorders and not disease (you have it or you don’t) – A pattern of maladaption, not defects • Social and Age Norms • Developmental issues – Nature/Nurture (origin of maladaptive behaviors) – Risk factors – Prediction The Diathesis-Stress Model • Diathesis – predisposition or vulnerability • • • • • (genetic, cognitive, personality) Stress – environmental pressure Interaction of genes and environment Example: Depression – Genetic vulnerability – Environmental trigger(s) Not specific stressors for specific disorders “Bad things have bad effects for some people some of the time” • Extreme stress and high vulnerability (severe • • • disorder) Extreme stress and high resiliency (mild disorder) Low stress and high vulnerability (mild disorder) Low stress and high resiliency (no disorder) Autism Spectrum Disorder This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: • any public performance or display, including transmission of any image over a network; • preparation of any derivative work, including the extraction, in whole or in part, of any images; • any rental, lease, or lending of the program. Copyright © Allyn & Bacon 2008 Autism • Begins in infancy: more boys • Several autistic spectrum disorders • Impaired social interaction, communication • Repetitive, stereotyped behaviors • 75% have intellectual disabilities: 10% have • • • savant syndrome Severe cognitive impairment Biologically based Concordance: MZ=60%, DZ= 0% Autism Spectrum Disorder • Asperger syndrome – – – – Normal or above-average intelligence Good verbal skills Clear desire to establish social relationships Deficient social cognitive and social-communication skills Autism Spectrum Disorder • Is there an epidemic? – 1987: autism affected 4 or 5 of every 10,000 children – 2006: 1 in 110 – Two years later: 1 in 88 Autism Spectrum Disorder • Why are rates rising? – Increased awareness – Broader definition that includes the entire autistic spectrum (including more mild cases) – Increased diagnosis – Variations in diagnostic practices Mirror Neurons Depression • Infancy – Somatic symptoms – Depressive-like states – Related to poor attachment – “At risk” if mother depressed – “Failure to thrive” syndrome may occur Childhood • Externalizing problems • – “Undercontrolled” disorders – Acting out – Aggressive, out of control Internalizing problems – “Overcontrolled” disorders – Inner distress, shyness – More girls Figure 16.3 Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder • DSM-5 Criteria: some combination of • • – Inattention subtype – Hyperactivity/Impulsivity subtype – Combined subtype – More boys; 3-5% of US kids – Comorbidity common Overactive behavior wanes with age Attentional, adjustment problems remain ADHD-Causes and Treatment • Neurological: low Dopamine, Serotonin • • • – Underactivity in frontal lobes Genetic predisposition; Environmental stress 70% helped by stimulants – Overprescription a problem Most successful if combined with behavioral treatment Psychostimulants • Ritalin • Concerta • Focalin • Adderall • Strattera • Cylert Depression • Childhood • – Somatic symptoms – Psychotherapy, medication effective – Nature/Nurture question Adolescence – Often related to childhood symptoms Adolescence • Storm and stress • • – Only about 20% – Heightened vulnerability to psych disorders Alcohol and drugs are problems Eating disorders – Anorexia nervosa; more girls (10/1) – Bulemia nervosa; binge-eating – Binge eating disorder – Some genetic predisposition; stress also – Psychological treatment usually successful “Copyright© Allyn & “Copyright© Allyn & Adolescent Depression and Suicide • 35% depressed; 7% diagnosable • – Cognitive symptoms – Behavioral acting out – Genetic link – Environmental triggers Suicide 3rd leading cause of death – Males commit 3:1 compared to females – Females attempt 3:1 compared to males Adulthood • Rates of disorder decrease after age 18 • Depression – Elderly less vulnerable to major depression – Concern with elderly • Depression often related to health • 15% have some symptoms • 1-3% diagnosable • Difficult to diagnose – More women (2:1) Depression and Dementia • • • • Many undiagnosed and untreated Elderly can benefit, should NOT be excluded from treatment Dementia: deterioration of neural Alzheimer’s Disease – Leading cause of dementia – Progressive and irreversible Causes of Alzheimer’s • Senile plaques – masses of dying neural material with toxic protein called beta amyloid • The plaque injures/kills neurons • Neurofibrillary tangles – twisted strands of neural material Early-onset form (prior to age 60)-genetic links Late-onset form (after age 70)-family history not predictive Figure 16.6 Aging and Dementia