* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Module 49 - DID and Personality disorders
Rumination syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Reactive attachment disorder wikipedia , lookup
Emergency psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Obsessive–compulsive personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Autism spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Mental status examination wikipedia , lookup
Bipolar II disorder wikipedia , lookup
Panic disorder wikipedia , lookup
Excoriation disorder wikipedia , lookup
Bipolar disorder wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Schizoid personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Depersonalization disorder wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Schizoaffective disorder wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Pyotr Gannushkin wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Conversion disorder wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
History of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Classification of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Conduct disorder wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Antisocial personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
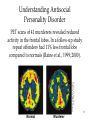
Dissociative and Personality Disorders Module 49 1 Psychological Disorders Mood Disorders Major Depressive Disorders Bipolar Disorder Explaining Mood Disorders Personality Disorders 2 Dissociative Disorder Conscious awareness becomes separated (dissociated) from previous memories, thoughts, and feelings. Symptoms 1. Sense of being unreal. 2. Being separated from the body. 3. Watching themselves as in a movie. 3 Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID) Is a disorder in which a person exhibits two or more distinct and alternating personalities formerly called multiple personality disorder. Lois Bernstein/ Gamma Liason The Three Faces of Eve Chris Sizemore (DID) 4 DID Critics Critics argue that diagnosis of DID has increased in the late 20th century. Also DID has not been found in other countries. Critics Arguments 1. Role-playing by people open to therapist’s suggestion. 2. Learned response that reinforces reductions in anxiety. 5 Personality Disorders Characterized by inflexible and enduring behavior patterns that impair social functioning. 6 Antisocial Personality Disorder Disorder in which the person (usually men) exhibits a lack of conscience for wrongdoing, even towards friends and family members. Formerly called sociopath or psychopath. 7 Understanding Antisocial Personality Disorder Like mood disorders and schizophrenia, antisocial personality disorder has biological and psychological reasons. Youngsters before committing crime respond with lower levels of stress hormones than do others their age. 8 Understanding Antisocial Personality Disorder PET scans of 41 murderers revealed reduced activity in the frontal lobes. In a follow-up study repeat offenders had 11% less frontal lobe compared to normals (Raine et al., 1999; 2000). Courtesy of Adrian Raine, University of Southern California Normal Murderer 9 Understanding Antisocial Personality Disorder Probability of crime increases twice as much when childhood poverty is compounded with peri-natal (birth) complications 10