* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download hello
Vasopressin wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis wikipedia , lookup
Hormonal breast enhancement wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hypothyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Pituitary apoplexy wikipedia , lookup
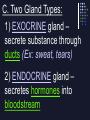
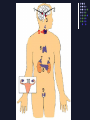
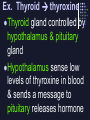
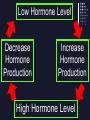
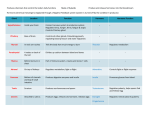
Ch. 39-1 & 39-2: I. Endocrine System FUNCTION: Transmit chemical messages to control growth, development & metabolism A. Hormones & Glands Hormone = secreted chemical in blood stream or ducts that affects cells Ex: Human growth hormone (HGH), insulin Gland = organ that releases hormones into body B. Compared to nervous system Message delivered throughout the body Body’s response is slower than nerve impulse C. Two Gland Types: 1) EXOCRINE gland – secrete substance through ducts (Ex: sweat, tears) 2) ENDOCRINE gland – secretes hormones into bloodstream D. Endocrine Glands: 1. Pituitary gland (in brain) • most important •regulates other glands 2. Thyroid (in neck) • makes thyroxine; regulates metabolism 3. Adrenal glands (above each kidney) • makes epinephrine (adrenaline) ; response to stress 4. Pancreas • makes insulin; regulates glucose levels E. Feedback Mechanism • adjusts to regulate hormone levels • maintains HOMEOSTASIS Ex. Thyroid thyroxine Thyroid gland controlled by hypothalamus & pituitary gland Hypothalamus sense low levels of thyroxine in blood & sends a message to pituitary releases hormone Signals the thyroid to produce & release thyroxine Thyroxine sent to cells to speed metabolism Low Hormone Level Decrease Hormone Production Increase Hormone Production High Hormone Level