* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Elements Compounds Mixtures
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Colloidal crystal wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear binding energy wikipedia , lookup
Photopolymer wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Liquid–liquid extraction wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Crystallization wikipedia , lookup
Particle-size distribution wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear transmutation wikipedia , lookup
Periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Solvent models wikipedia , lookup
Molecular dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
Implicit solvation wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
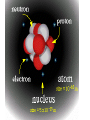
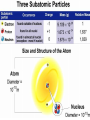
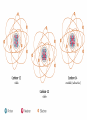
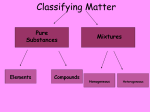
MATTER: matter can be classified into mixtures, solutions, elements and compounds. Matter that consists of 2 or more substances that are NOT chemically combined. They are Physically Combined They keep their own properties. They can change physically. Any amount of each substance is ok. Most mixtures can be separated physically by: magnets, evaporation, filtration, or centrifuge, and distillation. TYPES OF MIXTURES HETEROGENEOUS: • Not well mixed; Does not appear the same throughout. • Will separate upon standing. • Particles are large, and can be seen. • Ex: concrete, oil and vinegar; cereal and bananas; salad, BLT; PB&J HOMOGENEOUS • Two or more substances evenly mixed. • You can NOT see the different substances, even with a microscope! • Examples: gatorade, salt water, brass, air Heterogeneous mixtures A type of mixture where two or more substances are not evenly mixed. You can see with your eyes the different parts that make up the mixture. •The particles are insoluble. This means the particles do NOT dissolve. •Only scatter throughout when shaken. •*Often cloudy • Scatter light(Tyndall Effect) Mixture that is EVENLY mixed. • Appears the same throughout • Particles are very small , and sometimes dissolved. Also known as Solutions — have 2 parts to them: solute and solvent Solute—substance that dissolves (ex. Salt, sugar) Solvent—substance that does the dissolving (Water is called the Universal solvent!) o Particles are dissolved in a solution. o Solutions do Not scatter light o They often appear clear o 1 substance dissolves in another. ( ex: water) Solute and solvent Key terms about solutions: • Soluble: a substance can dissolve in another substance (salt) • • Insoluble: Substance can NOT dissolve in another substance (pepper, oil) Solubility: Amt. of solute that can completely dissolve in a specific amt. of solvent at a given temperature. (Salt water) • Saturated: all the solute that can be dissolved in a specific amt of solvent at a given temp. – can’t absorb any more. Alloy: Metal solutions that are Solids dissolved in solids— Brass: copper and Zinc Gold: gold and copper The tyndall effect EXAMPLES OF COLLOIDS: Fog= liquid in gas Butter= liquid in solid Smoke=liquid in gas Mayo= liquid in liquid HOW ARE ELEMENTS DIFFERENT FROM MIXTURES? When all particles are alike, it is a pure substance. Elements- simplest pure substance; there are MORE THAN 113 elements; they Began to be discovered in the 1940’s. Atom- smallest particle of an element that has all the properties of that element. SO WHAT ARE COMPOUNDS AND MOLECULES, THEN? Compound- 2 or more different elements chemically combined ex. H2O, NaCl Molecules- 2 or more atoms chemically combined. ex. H2, H2O, N2 Elements Compounds Mixtures Made up of only 1 Made up of more Made up of more kind of atom. than 1 kind of than 1 kind of atom. molecule. Can’t be broken Can be broken Can be separated down by chemical down by by physical means. chemical means. means. Have same properties as atoms making it up. Have different properties from elements making it up. Have same properties as substances making them up. Have same properties throughout. Have same properties throughout. Have different properties throughout. Chemical Symbols- shorthand way to represent elements. ex. C, H, Na (sodium) Ca, Cl Chemical Formula- combinations of chemical symbols ex. H2O Subscript- tells the number of atoms in a compound ex. H2O CO2 Coefficient- tells the number of molecules ex. 2H2O Chemical Equation- describes the chemical reaction using symbols and formulas WHAT IS INSIDE AN ATOM???? STRUCTURE OF AN ATOM !!!!! THE PLAYERS: • 3 major subatomic particles: • Proton- positively charged, 1 AMU, inside the nucleus, determines the element • Neutron- no charge, 1 AMU, inside the nucleus. • Electron-negatively charged, 1/1836 AMU , outside the nucleus on energy shells and energy levels. • AMU= ATOMIC MASS UNIT– (THEIR MASS!!) HOW DO WE WORK WITH ATOMS AND ELEMENTS????? • Atomic #--# of protons of an element. It identifies the element. • A#= #P • Mass # - This is the # that is = to the # of protons and the neutrons in the nucleus. • m# = P + N • NEUTRAL ATOM: # E = # P • Atomic Mass (weight) -- the average mass # of all of the isotopes of an element BUT WHAT IS THE NUMBER UNDERNEATH THEM ON THE PERIODIC TABLE??? Isotopes—These are when an element has its regular # of protons, but a different # of neutrons. Isotopes of an element are that element, with a different # of neutrons. • ex: H-3, U-238.