* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neurons
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
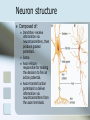
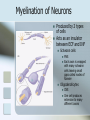
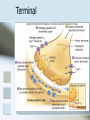
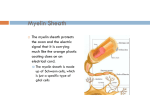
Neurons Ted Miles Neuron structure Composed of: Dendrites- receive information via neurotransmitters, then produce graded potentials. Soma Axon Hillockresponsible for making the decision to fire an action potential. Axon-transmit action potentials to deliver information via neurotransmitters from the axon terminals. Neuron conduction of Action Potential An action potential occurs when there is a reversal of the normal resting potential (goes from negative to positive). Also called depolarization. Depolarization occurs due to the opening of voltage gated Na channel allowing the influx of Na. Repolarization of the cell is due to Potassium efflux. If membrane potential is excited to the threshold level an action potential is propagated Myelination of Neurons Produced by 2 types of cells Acts as an insulator between ECF and INF Schwann cells PNS Each axon is wrapped with many schwann cells leaving small gaps called nodes of Ranvier Oligodendricytes CNS One cell produces extension to many different axons Myelination of Neurons Body has both myelinated and nonmyelinated fibers Myelination increases conduction velocity of fiber due to saltatory conduction of the action potential Action potential jumps from node of ranvier to the next without having to travel the entire length of the neuron Terminal Once the Cell reaches threshold and action potential is sent down the axon Action potential reaches axon Calcium is released into the cell Synaptic vesicles release neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft which diffuses to the receptors on the post-synaptic cell. Terminal Bibliography Widmaier, E.P., Raff, H., and Strang, K.T.; 2006. Vander’s Human Physiology, 10th edition. McGraw Hill.