* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Electromyography wikipedia , lookup
Neural modeling fields wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
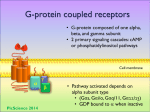
Overview of links between sections 9 to 13 From signal perception (by a GPCR) to response (28/11 -13) Starting point: GPCR & a/b/g complex P.M. GDP b ga Ligand: e.g. fMet, adrenalin, “smell”, light, etc. P.M. GDP b ga b + GTP a GDP GTP The trimeric G-protein complex is recruited to the receptor GDP/GTP exchange (the receptor acts as a GEF) 1 Examples of down-stream GPCR effectors Organ specific Most cells GTP aq PLC-b GTP as GTP ai Adenylyl cyclase GTP aolf GTP at cGMP-phosphodiesterase ADRENALIN: cAMP synthesis in liver and muscle cells Protein kinase A SMELL: cAMP synthesis in olfactory cells Ion channels LIGTH: cGMP hydrolysis in cells of the retina Ion channels 2 Transmission of signals through CNS & PNS De-polarization or hyper-polarization (electrical signals) Synaptic signaling (electrical signals & neurotransmitters) : Electrical signal Control of smooth muscle relaxation Default state = contraction : Electrical signal Ca2+ 1. Acetylcholine (synaptic signaling) 2. Endothelial cells produce NO 3. Diffusion of NO to smooth muscle cells (paracrine signal) 4. Activation of guanylyl cyclase cGMP 5. Activation of an “in ward” Ca2+ pump 6. Decreased cytosolic [Ca2+] 7. Actin-myosin filaments slides apart smooth muscle relaxation 8. Increased blood flow Ca2+ Response = relaxation 4 Neuromuscular junction Somatic motor neurons project their axons to skeletal muscles. The interface between motor neurons and skeletal muscles is a specialized synapse termed neuromuscular junction. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction Depolarization of muscle cells (-70 mV ~0 mV) Opening of Ca2+ channels Increased cytosolic Ca2+ Troponin mediated translocation of tropomyosin Response = contraction Tropomyosin Tropomyosin Tropomyosin Tropomyosin Ca2+ The Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal system Physical work/stress Two distinct signals to AG SNS signal ACTH secretion GPCR (AG medulla): Adrenalin secretion into the blood GPCR (AG cortex): Cortisol secretion into the blood (lipolysis etc etc) Neuroendocrine integration GPCR (liver and muscles) adenylyl cyclase cAMP Protein kinase A Glycogen phosphorylase AG: Adrenal Gland Glycogen breakdown ACTH: AdrenoCorticoTropic Hormone, SNS: Sympathetic Nervous System 6