* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint-Präsentation
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Internal communications wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Revenue management wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Yield management wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Services marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
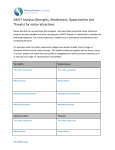
Tourism Facilities Management André Kretzschmar University of Applied Sciences Stralsund Leisure and Tourism Management WS 2008/2009 Slide Nr. 1 Basics Slide Nr. 2 Attractions • Play a vital part in encouraging visitors to a region; • Without attractions there would be a limited need for other tourism services; • Some argue that tourism would not exist if it were not for attractions. Part One \ defining attractions \ ... Slide Nr. 3 Attraction defined A designated permanent resource which is controlled and managed for the enjoyment, amusement, entertainment, and education of the visiting public. (Middleton, 1988) Part One \ defining attractions \ ... Slide Nr. 4 What is an attraction? • Natural Environment; • Man made attractions – Tourist, – Non-tourist purpose; • Special Events. Boundaries are not always clear cut ! („Reichstag“ ) Please visit: http://www.northumberland.gov.uk Part One \ defining attractions \ ... Slide Nr. 5 Terminology and Interrelations • visitor attractions and tourist attractions • attractions and destinations • attractions, support services and facilities • resort complexes • attractions and activities Part One \ defining attractions \ ... Slide Nr. 6 Classification of visitor attractions • Ownership • Primary and secondary attractions • Catchment area • Visitor numbers • Location • Size • Target markets • Benefits sought Part One \ defining attractions \ ... Slide Nr. 7 Ownership of Attractions Sector (type of ownership) Main types of attractions owned Public: - government, - local authorities, - nationalised industries. Museums, galleries Ancient monuments Archaeological sites Historic buildings Country parks Forests Private: - Commercial organisations. Theme parks Zoos Marinas Voluntary: - Trusts & charities. Part One \ defining attractions \ ... Historic buildings Heritage centres Steam railways Main motives for ownership an operation Main priority Conservation Other priorities Education, public access, increased leisure opportunities for the community, catalyst for tourism development, income, visitor management Main priority Profit Other priorities Entertainment, max. visitor numbers, market share, exploit growth markets Main priority Conservation via income from visitors Other priorities Education, visitor management Slide Nr. 8 Swarbrooke's development of destinations • Single attraction; • Embryonic destination: - Services develop around the single attraction; • Developed single market destination: - Other attractions, designed for same market; • Diversified destination: - Other attractions, designed designed for new markets. Part One \ The role ... \ Attractions and other sectors of tourism Slide Nr. 9 Development Feasibility Study Slide Nr. 10 Feasibility study contents • The market study • Who will visit the attraction? - domestic and foreign holidaymakers, day trippers, School and college groups, local residents - age, sex, class, stage in family life-cycle • How many people will visit the attraction? - population of catchment area, number of holidaymakers visiting the area, competitors targeting the same market segments • Where they will come from? - catchment area • When will the visitors come? - degree of seasonality affects staffing, attraction capacity and cash flow management Part Two \ Development process \ Feasibility study Slide Nr. 11 Feasibility study contents • Site selection criteria • Proximity to major centres of population • Transport networks and their reliability • Existence of other attractions in the area • Socio-economic profile of the catchment area • Availability of suppliers/services • Amount, type, quality and costs of land • Regulations on the use of land • The climate • Availability of qualified labour at acceptable costs • Public sector financial assistance and ‘help in kind’ • Attitude of local community towards planned project • … Part Two \ Development process \ Feasibility study Slide Nr. 12 Feasibility study contents • Financial viability • based on calculation of COSTS and REVENUES • Depending on the type of organization viability means to produce a profit or surplus on running costs • Cashflow management • Break-even analysis Profit Costs Break-even point Variable costs Fixed Costs 0 Number of visits Part Two \ Development process \ Feasibility study Slide Nr. 13 Development Business Planning Slide Nr. 14 Why Plan? • Identify what business you are in; • To determine where you are now; • Determine where you want to be in the future - 12 months / 3 years / 5 years (clear, measurable objectives); • Identify how to get there - how do you achieve those objectives? (action plan); Part Two \ Development process \ Business Planning Slide Nr. 15 What does planning encompass? • Business is primarily about one thing only, determining what it is the consumer wants and providing it at a profit. • Strategic positioning; • Market research; • Financials; • Marketing strategy; • Human resource management; ! • Operational planning. Part Two \ Development process \ Business Planning Slide Nr. 16 Management Marketing Planning Slide Nr. 17 Visitor attractions as service products 1. Staff is part of the product itself - attitudes and behaviour affect enjoyment 2. Intangible elements dominate the attraction product - encourage to buy on basis of an imagination 3. The product is perishable - ensure consumption/income before product perishes 4. Customers are part of the production process - affects on experience are largely outside control 5. Service products are never really standardized - quality control difficult; guarantees?? Part Three \ The marketing concept Slide Nr. 18 visitor attractions and tourism marketing • The product is an experience - that begins in advance of consumption and continues … - visitors rarely distinguish between responsibilities • The product offers only shared use rights - try to avoid conflicts between different groups • The product offers only temporary use rights - “the longer the stay the higher the spending” • The product is rarely being delivered to the customer - good signposting, directions and brochures are essential • The demand for the product is highly seasonal Part Three \ The marketing concept Slide Nr. 19 Scope of strategic marketing planning !!! • Where are we now? - analysing the organizations current situation and direction • Where do we want to be in the future? - establishing mission statements, setting goals and objectives • How are we going to get there? - devising strategies and tactics helping to achieve these goals and objectives, and looking at implementation issues • How will we know when we get there? - monitoring and performance evaluation strategies, and systems for modifying strategies in response to monitoring Part Three \ Strategic marketing planning Slide Nr. 20 SWOT analysis Strengths Weaknesses internal factors within control (current situation) Opportunities Threats external factors outside control (market direction) Part Three \ Strategic marketing planning \ Where are we now? Slide Nr. 21 What to do with the SWOT? • Every section holds potential to put forward strategies • For example, weaknesses and threats can be converted to strengths and opportunities. Whilst strengths can be matched to opportunities. Weakness: few visitors in off-peak season Conversion Strategy: attract school-group visits at low fares in off-peak season Strengths: - balanced cash flow - loyal visitors (return visits) - grater awareness (parents, relatives) - sanitised public image - …. Part Three \ Strategic marketing planning \ Where are we now? Slide Nr. 22 Product positioning • Where customers perceive you to be in the marketplace Expensive Inexpensive Expensive Exciting Theme Park ( ) Boring Boring Positioning disparity Competitor analysis Inexpensive Exciting • If there are disparities between the customer and the manager‘s viewpoint: - change the market or the product in order to reflect/match the views of the customers! Part Three \ Strategic marketing planning \ Where are we now? Slide Nr. 23 Management Implementing Marketing Strategies Slide Nr. 24 Basic statements Marketing strategies are generally implemented through Marketing Plans. Implementing marketing strategies is mainly about manipulating the Marketing Mix. Implementing marketing strategies requires to keep up with the latest Developments in Marketing. Part Three \ The implementation of marketing strategies \ How are we going to get there? Slide Nr. 25 Marketing Mix • Place of purchase • Distribution • Pre-booking • Pre-purchase • Intermediaries lace Booking agencies • Ticket systems P • Literature • Advertising • Signposting romotion • Sponsorship • Direct marketing • Sales promotion • Personal selling • Press and public relations P • Product levels (Kotler) • Designed characteristics • Service components • Image / Reputation • Positioning roduct • Packaging • Branding • Quality P Price • List price • Discounts • Concessions • Value for money • Cost of travelling • Methods of payment • Price / Quality trade off Part Three \ The implementation of marketing strategies \ How are we going to get there? Slide Nr. 26 The seven Ps • People – staff in terms of: training, appearance, behaviour, customer contact, … • Physical evidence – environment layout, noise, cleanliness, furnishing, … • Process – corporate policies and procedures employee empowerment, customer involvement, … • Extension of the ‘product’ category ! but emphasizes the importance of those three factors for service products Part Three \ The implementation of marketing strategies \ How are we going to get there? Slide Nr. 27 How will we know when we get there? • Evaluation requires that: - the marketing strategy contains measurable targets - there are management information systems, providing up-to-date information of the organizations performance - must provide internal data on the performance - and external information on business environment - there are control mechanisms to allow corrective actions • Corrective actions should be fed back into the strategy!!! Part Three \ The implementation of marketing strategies \ How will we know when we get there? Slide Nr. 28 Management Human Resource … Slide Nr. 29 Human Resource Management • Considered to be the most important aspect of management • Attitudes and abilities of staff have a crucial impact on the visitors experience • Labour costs are likely to be the largest single items on the attractions budget Part Three \ Human Resource Management Slide Nr. 30 Problems of HRM at visitor attractions Tourism industry suffers from bad reputation in HRM • High turnover of staff • Seasonality of demand • Poor status of jobs • Lack of career structures • Unusually demanding jobs • lack of management expertise • Lack of widely recognized qualification and training schemes Part Three \ Human Resource Management \ Problems Slide Nr. 31 Management Quality … Slide Nr. 32 Quality management and services • No standardized product - difficult to adopt standardized quality control systems - affected by a number of variables - the product is different for every customer • Intangibility and perishability - ‚faults‘ in the product cannot be easily seen - not ease to replace a ‚faulty‘ product • Services are often complex products - involving a huge number of elements which are interdependent and difficult to monitor Part Three \ Quality management Slide Nr. 33 Quality management systems at attractions • There are three main points to consider: - what definition of quality to use - what performance standards to use and what measurement system to implement - what systems to adopt to achieve quality Part Three \ Quality management Slide Nr. 34 Visitor management • visitor management incorporates aspects of both: quality management and green issues, and is the most critical part of the day-to-day management at the site • Tries to ensure an experience without disturbances by providing a trouble-free sequence of events • Aims to minimize negative environmental and socio-cultural impact caused by the use of the attr. • Although most important for non-purpose built attractions, there is a certain relevance for all types of attractions Part Three \ Visitor management Slide Nr. 35 Visitor management Financial conditions Legal conditions Human resources Experience without disturbances Maximize quality of product/service Visitor expectations Visitor satisfaction Visitor Management Management objectives Performance Conservation: - environment - and assets Marketing activities Part Three \ Visitor management HRM Operational management Minimize negative impact Slide Nr. 36 Problems to deal with • Damage on environment caused by visitors - wildlife, flora and fauna, pollution by traffic • Damage on assets caused by visitors - intentional, unintentionally caused by heavy use • Disturbances in visitor flow - bottleneck situations, waiting times • Accessibility of certain areas - restricted access caused by construction work - distances between attractions on site - handycapped visitors Part Three \ Visitor management Slide Nr. 37